
The alkali metals consist of the chemical elements lithium (Li), sodium (Na), potassium (K), rubidium (Rb), caesium (Cs), and francium (Fr). Together with hydrogen they constitute group 1, which lies in the s-block of the periodic table. All alkali metals have their outermost electron in an s-orbital: this shared electron configuration results in their having very similar characteristic properties. Indeed, the alkali metals provide the best example of group trends in properties in the periodic table, with elements exhibiting well-characterised homologous behaviour. This family of elements is also known as the lithium family after its leading element.

Caesium is a chemical element; it has symbol Cs and atomic number 55. It is a soft, silvery-golden alkali metal with a melting point of 28.5 °C, which makes it one of only five elemental metals that are liquid at or near room temperature. Caesium has physical and chemical properties similar to those of rubidium and potassium. It is pyrophoric and reacts with water even at −116 °C (−177 °F). It is the least electronegative element, with a value of 0.79 on the Pauling scale. It has only one stable isotope, caesium-133. Caesium is mined mostly from pollucite. Caesium-137, a fission product, is extracted from waste produced by nuclear reactors. It has the largest atomic radius of all elements whose radii have been measured or calculated, at about 260 picometers.

Rubidium is a chemical element; it has symbol Rb and atomic number 37. It is a very soft, whitish-grey solid in the alkali metal group, similar to potassium and caesium. Rubidium is the first alkali metal in the group to have a density higher than water. On Earth, natural rubidium comprises two isotopes: 72% is a stable isotope 85Rb, and 28% is slightly radioactive 87Rb, with a half-life of 48.8 billion years—more than three times as long as the estimated age of the universe.

Sodium cyanide is a poisonous compound with the formula NaCN. It is a white, water-soluble solid. Cyanide has a high affinity for metals, which leads to the high toxicity of this salt. Its main application, in gold mining, also exploits its high reactivity toward metals. It is a moderately strong base.

Potassium hydroxide is an inorganic compound with the formula KOH, and is commonly called caustic potash.
In chemistry, a reactivity series (or reactivity series of elements) is an empirical, calculated, and structurally analytical progression of a series of metals, arranged by their "reactivity" from highest to lowest. It is used to summarize information about the reactions of metals with acids and water, single displacement reactions and the extraction of metals from their ores.
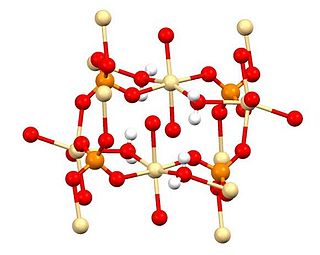
Cadmium sulfate is the name of a series of related inorganic compounds with the formula CdSO4·xH2O. The most common form is the monohydrate CdSO4·H2O, but two other forms are known CdSO4·8⁄3H2O and the anhydrous salt (CdSO4). All salts are colourless and highly soluble in water.

Caesium fluoride or cesium fluoride is an inorganic compound with the formula CsF and it is a hygroscopic white salt. Caesium fluoride can be used in organic synthesis as a source of the fluoride anion. Caesium also has the highest electropositivity of all known elements and fluorine has the highest electronegativity of all known elements.

Potassium peroxide is an inorganic compound with the molecular formula K2O2. It is formed as potassium reacts with oxygen in the air, along with potassium oxide (K2O) and potassium superoxide (KO2).

Thallium(I) hydroxide, also called thallous hydroxide, TlOH, is a hydroxide of thallium, with thallium in oxidation state +1.

Rubidium hydride is the hydride of rubidium. With the formula RbH, it is classified as an alkali metal hydride. It is a white solid and is insoluble in most solvents. It is synthesized by treating rubidium metal with hydrogen. Rubidium hydride is a powerful superbase and reacts violently with water.
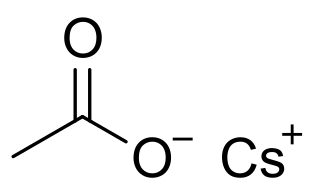
Caesium acetate or cesium acetate is an ionic caesium compound with the molecular formula CH3COOCs. It is a white solid that may be formed by the reaction of caesium hydroxide or caesium carbonate with acetic acid.

Caesium chromate or cesium chromate is an inorganic compound with the formula Cs2CrO4. It is a yellow crystalline solid that is the caesium salt of chromic acid, and it crystallises in the orthorhombic system.

Copper(II) azide is a medium density explosive with the molecular formula Cu(N3)2.

Caesium hydride or cesium hydride is an inorganic compound of caesium and hydrogen with the chemical formula CsH. It is an alkali metal hydride. It was the first substance to be created by light-induced particle formation in metal vapor, and showed promise in early studies of an ion propulsion system using caesium. It is the most reactive stable alkaline metal hydride of all. It is a powerful superbase and reacts with water extremely vigorously.

Caesium nitrate or cesium nitrate is a salt with the chemical formula Cs N O3. An alkali metal nitrate, it is used in pyrotechnic compositions, as a colorant and an oxidizer, e.g. in decoys and illumination flares. The caesium emissions are chiefly due to two powerful spectral lines at 852.113 nm and 894.347 nm.

Cadmium cyanide is an inorganic compound with the formula Cd(CN)2. It is a white crystalline compound that is used in electroplating. It is very toxic, along with other cadmium and cyanide compounds.
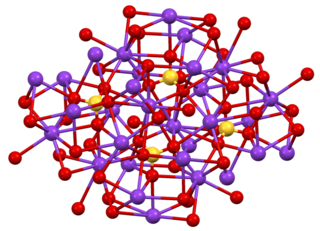
Caesium sulfate or cesium sulfate is the inorganic compound and salt with the formula Cs2SO4. It is a white water-soluble solid that is used to prepare dense aqueous solutions for use in isopycnic (or "density-gradient") centrifugation. It is isostructural with potassium salt.

4-Methyl-2-pentanol or methyl isobutyl carbinol (MIBC) is an organic chemical compound used primarily as a frother in mineral flotation and in the production of lubricant oil additives such as Zinc dithiophosphate. It is also used as a solvent, in organic synthesis, and in the manufacture of brake fluid and as a precursor to some plasticizers. It is an acetone derivative in liquid state, with limited solubility in water but generally miscible with most organic solvents.

Copper(II) tetrafluoroborate is any inorganic compound with the formula Cu(H2O)x(BF4)2. As usually encountered, it is assumed to be the hexahydrate (x = 6), but this salt can be partially dehydrated to the tetrahydrate. Regardless, these compounds are aquo complexes of copper in its +2 oxidation state, with two weakly coordinating tetrafluoroborate anions.






















