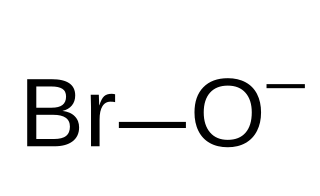Bromine is a chemical element; it has symbol Br and atomic number 35. It is a volatile red-brown liquid at room temperature that evaporates readily to form a similarly coloured vapour. Its properties are intermediate between those of chlorine and iodine. Isolated independently by two chemists, Carl Jacob Löwig and Antoine Jérôme Balard, its name was derived from the Ancient Greek βρῶμος (bromos) meaning "stench", referring to its sharp and pungent smell.
Hydrobromic acid is an aqueous solution of hydrogen bromide. It is a strong acid formed by dissolving the diatomic molecule hydrogen bromide (HBr) in water. "Constant boiling" hydrobromic acid is an aqueous solution that distills at 124.3 °C (255.7 °F) and contains 47.6% HBr by mass, which is 8.77 mol/L. Hydrobromic acid is one of the strongest mineral acids known.

Hydrogen bromide is the inorganic compound with the formula HBr. It is a hydrogen halide consisting of hydrogen and bromine. A colorless gas, it dissolves in water, forming hydrobromic acid, which is saturated at 68.85% HBr by weight at room temperature. Aqueous solutions that are 47.6% HBr by mass form a constant-boiling azeotrope mixture that boils at 124.3 °C (255.7 °F). Boiling less concentrated solutions releases H2O until the constant-boiling mixture composition is reached.
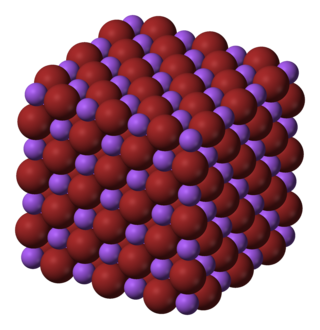
Sodium bromide is an inorganic compound with the formula NaBr. It is a high-melting white, crystalline solid that resembles sodium chloride. It is a widely used source of the bromide ion and has many applications.

Triphenylphosphine (IUPAC name: triphenylphosphane) is a common organophosphorus compound with the formula P(C6H5)3 and often abbreviated to PPh3 or Ph3P. It is versatile compound that is widely used as a reagent in organic synthesis and as a ligand for transition metal complexes, including ones that serve as catalysts in organometallic chemistry. PPh3 exists as relatively air stable, colorless crystals at room temperature. It dissolves in non-polar organic solvents such as benzene and diethyl ether.

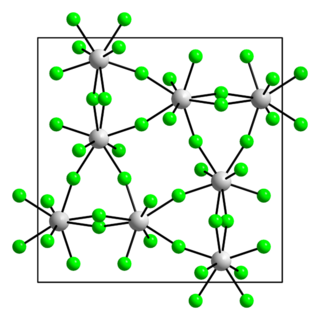
Carbon tetrabromide, CBr4, also known as tetrabromomethane, is a bromide of carbon. Both names are acceptable under IUPAC nomenclature.

Hypobromous acid is an inorganic compound with chemical formula of HOBr. It is a weak, unstable acid. It is mainly produced and handled in an aqueous solution. It is generated both biologically and commercially as a disinfectant. Salts of hypobromite are rarely isolated as solids.

Zinc bromide (ZnBr2) is an inorganic compound with the chemical formula ZnBr2. It is a colourless salt that shares many properties with zinc chloride (ZnCl2), namely a high solubility in water forming acidic solutions, and good solubility in organic solvents. It is hygroscopic and forms a dihydrate ZnBr2·2H2O.

Vanadium(III) bromide, also known as vanadium tribromide, describes the inorganic compounds with the formula VBr3 and its hydrates. The anhydrous material is a green-black solid. In terms of its structure, the compound is polymeric with octahedral vanadium(III) surrounded by six bromide ligands.

Copper(II) bromide (CuBr2) is a chemical compound that forms an unstable tetrahydrate CuBr2·4H2O. It is used in photographic processing as an intensifier and as a brominating agent in organic synthesis.
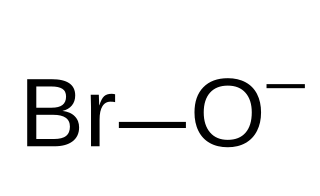
The hypobromite ion, also called alkaline bromine water, is BrO−. Bromine is in the +1 oxidation state. The Br–O bond length is 1.82 Å. Hypobromite is the bromine compound analogous to hypochlorites found in common bleaches, and in immune cells. In many ways, hypobromite functions in the same manner as hypochlorite, and is also used as a germicide and antiparasitic in both industrial applications, and in the immune system.
Tin(II) bromide is a chemical compound of tin and bromine with a chemical formula of SnBr2. Tin is in the +2 oxidation state. The stability of tin compounds in this oxidation state is attributed to the inert pair effect.
Bromine compounds are compounds containing the element bromine (Br). These compounds usually form the -1, +1, +3 and +5 oxidation states. Bromine is intermediate in reactivity between chlorine and iodine, and is one of the most reactive elements. Bond energies to bromine tend to be lower than those to chlorine but higher than those to iodine, and bromine is a weaker oxidising agent than chlorine but a stronger one than iodine. This can be seen from the standard electrode potentials of the X2/X− couples (F, +2.866 V; Cl, +1.395 V; Br, +1.087 V; I, +0.615 V; At, approximately +0.3 V). Bromination often leads to higher oxidation states than iodination but lower or equal oxidation states to chlorination. Bromine tends to react with compounds including M–M, M–H, or M–C bonds to form M–Br bonds.
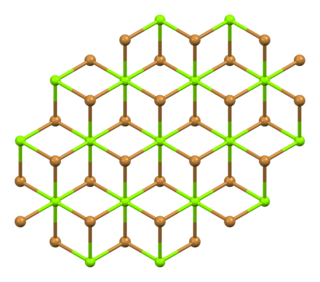
Magnesium bromide is a chemical compound of magnesium and bromine, with the chemical formula MgBr2. It is white and deliquescent crystalline solid. It is often used as a mild sedative and as an anticonvulsant for treatment of nervous disorders. It is water-soluble and somewhat soluble in alcohol. It can be found naturally in small amounts in some minerals such as: bischofite and carnallite, and in sea water, such as that of the Dead Sea.

Cobalt(II) bromide (CoBr2) is an inorganic compound. In its anhydrous form, it is a green solid that is soluble in water, used primarily as a catalyst in some processes.

Nickel(II) bromide is the name for the inorganic compounds with the chemical formula NiBr2(H2O)x. The value of x can be 0 for the anhydrous material, as well as 2, 3, or 6 for the three known hydrate forms. The anhydrous material is a yellow-brown solid which dissolves in water to give blue-green hexahydrate (see picture).

Bromous acid is the inorganic compound with the formula of HBrO2. It is an unstable compound, although salts of its conjugate base – bromites – have been isolated. In acidic solution, bromites decompose to bromine.
Scandium bromide, or ScBr3, is a trihalide, hygroscopic, water-soluble chemical compound of scandium and bromine.

Iron(II) nitrate is the nitrate salt of iron(II). It is commonly encountered as the green hexahydrate, Fe(NO3)2·6H2O, which is a metal aquo complex, however it is not commercially available unlike iron(III) nitrate due to its instability to air. The salt is soluble in water serves as a ready source of ferrous ions.
Protactinium(V) fluoride is a fluoride of protactinium with the chemical formula PaF5.