Cuneiform is an ancient writing system originating in Mesopotamia.

The Colosseum is an oval amphitheatre in the centre of the city of Rome, Italy, just east of the Roman Forum. It is the largest ancient amphitheatre ever built, and is still the largest standing amphitheatre in the world today, despite its age. Construction began under the emperor Vespasian in 72 and was completed in 80 AD under his successor and heir, Titus. Further modifications were made during the reign of Domitian. The three emperors that were patrons of the work are known as the Flavian dynasty, and the amphitheatre was named the Flavian Amphitheatre by later classicists and archaeologists for its association with their family name (Flavius).
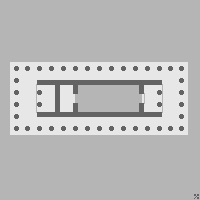
A cella or naos is the inner chamber of an ancient Greek or Roman temple in classical antiquity. Its enclosure within walls has given rise to extended meanings, of a hermit's or monk's cell, and since the 17th century, of a biological cell in plants or animals.

A flying wedge is a configuration created from a body moving forward in a triangular formation. This V-shaped arrangement began as a successful military strategy in ancient times when infantry units would move forward in wedge formations to smash through an enemy's lines. This principle was later used by Medieval European armies, as well as modern armed forces, which have adapted the V-shaped wedge for armored assault.

The Theatre of Pompey was a structure in Ancient Rome built during the latter part of the Roman Republican era by Pompey the Great. Completed in 55 BC, it was the first permanent theatre to be built in Rome. Its ruins are located at Largo di Torre Argentina.

A theater, theatre or playhouse, is a structure where theatrical works or plays are performed, or other performances such as musical concerts may be produced. A theatre used for opera performances is called an opera house. While a theater is not required for performance, a theater serves to define the performance and audience spaces. The facility is traditionally organized to provide support areas for performers, the technical crew and the audience members.

The Ludus Magnus was the largest of the gladiatorial schools in Rome. It was built by the emperor Domitian in the late first century C.E., alongside other building projects undertaken by him such as three other gladiatorial schools across the Roman Empire. The training school is situated directly east of the Colosseum in the valley between the Esquiline and the Caelian hills, an area already occupied by Republican and Augustan structures. While there are remains that are visible today, they belong to a reconstruction that took place under the emperor Trajan where the Ludus plane was raised by about 1.5 metres. The Ludus Magnus was essentially a gladiatorial arena where gladiators from across the Roman Empire would live, eat, and practice while undergoing gladiatorial training in preparation for fighting at the gladiatorial games held at the Colosseum.

The Roman theatre of Philippopolis is one of the world's best-preserved ancient Roman theatres, located in the city center of modern Plovdiv, Bulgaria. It was constructed in the 90s of the 1st century AD, probably during the reign of Domitian. The theatre can host between 5,000 and 7,000 spectators and it is currently in use.

The Stadiumof Philippopolis was the ancient Roman stadium of Philippopolis, built in the 2nd century AD, during the Roman imperial period. It is among the largest and best preserved buildings from the time of the Roman Empire in the Balkan peninsula. At the time the stadium was built, Philippopolis was the capital of the Roman province of Thracia.

Roman amphitheatres are Roman theatres – large, circular or oval open-air venues with raised seating – built by the ancient Romans. They were used for events such as gladiator combats, venationes and executions. About 230 Roman amphitheatres have been found across the area of the Roman Empire. Early amphitheatres date from the Republican period, though they became more monumental during the Imperial era.

The Amphitheatre of Mérida is a ruined Roman amphitheatre situated in the Roman colony of Emerita Augusta, present-day Mérida, in Spain. The city itself, Emerita Augusta, was founded in 25 BC by Augustus, to resettle emeritus soldiers discharged from the Roman army from two veteran legions of the Cantabrian Wars. The amphitheatre itself was completed in 8 BC. The term emeritus refers to the soldiers, all of whom had been honorably discharged from service. The city became the capital of the Roman province of Lusitania.

The Roman Theatre of Mérida is a construction promoted by the consul Vipsanius Agrippa in the Roman city of Emerita Augusta, capital of Lusitania. It was constructed in the years 16 to 15 B.C.E. One of the most famous and visited landmarks in Spain, the Roman Theatre of Mérida is regarded as a Spanish cultural icon and was chosen as one of the 12 Treasures of Spain.

The Roman Theatre is an ancient Roman theatre in Cartagena, Spain.

The Roman Theatre at Palmyra is a Roman theatre in ancient Palmyra in the Syrian Desert. The unfinished theatre dates back to the second-century CE Severan period. The theatre's remains have since been restored. It was occupied by the Islamic State of Iraq and the Levant (ISIL) in May 2015 and recaptured by the government forces in March 2016 with the support of Russian airstrikes.

The Greek theatre of Syracuse lies on the south slopes of the Temenite hill, overlooking the modern city of Syracuse in southeastern Sicily. It was first built in the 5th century BC, rebuilt in the 3rd century BC and renovated again in the Roman period. Today, it is a part of the Unesco World Heritage Site of "Syracuse and the Rocky Necropolis of Pantalica".
Despite its abandoned state, it remains one of the most beautiful locations in the world, offering the most grandiose and picturesque spectacle that there is.
Cuneus is part of the brain.

The Tours amphitheater is a Roman amphitheatre located in the historic city center of Tours, France, immediately behind the well known Tours cathedral. It was built in the 1st century when the city was called Caesarodunum. It was built atop a small hill on the outskirts of the ancient urban area, making it safe from floods, convenient for crowds and visitors, and demonstrating the power of the city from a distance. The structure was an enormous, elliptical structure approximately 122 meters by 94 meters. According to its design it is classified as a "primitive" amphitheatre. Unlike the famous Colosseum that was made mostly of masonry and built above-ground, the Tours amphitheatre was made mostly of earth and created by moving soil and rock into a bowl shape. Spectators likely sat directly on the grassy slopes, while the masonry was primarily used for the vomitoria and retaining walls.

The Roman amphitheatre of Italica is a ruined Roman amphitheatre situated in the Roman settlement of Italica, present-day Santiponce, in Andalusia, Spain.
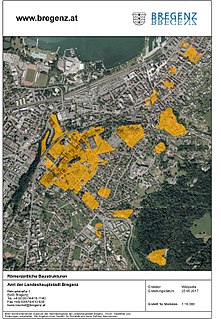
The Roman theatre in Bregenz, Vorarlberg, Austria, is located in the quarter of Thalbach in Bregenz. Bregenz was called Brigantium by the Romans. The theatre was excavated by archaeologists specifically in 2013 and 2019 in the name of the Vorarlberg provincial museum.

The Roman Theater of Catania consists of site with the ruins of two open air semicircular Ancient Roman theaters, located between Piazza San Francesco, via Vittorio Emanuele, via Timeo and via Teatro Greco in the center of Catania, region of Sicily, southern Italy. The site consists of the larger theater and a smaller semicircular theater, an Odeon. The structure is part of the Parco archeologico greco-romano di Catania.


















