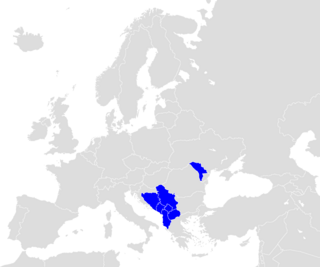
The Central European Free Trade Agreement (CEFTA) is an international trade agreement between countries mostly located in Southeastern Europe. Founded by representatives of Poland, Hungary and Czechoslovakia, CEFTA in 2006 expanded to Albania, Bosnia and Herzegovina, Bulgaria, Croatia, Moldova, Montenegro, North Macedonia, Romania, Serbia, Slovenia and the UNMIK.
Europe, the westernmost portion of Eurasia, is often divided into regions and subregions based on geographical, cultural or historical factors. Since there is no universal agreement on Europe's regional composition, the placement of individual countries may vary based on criteria being used. For instance, the Balkans is a distinct geographical region within Europe, but individual countries may alternatively be grouped into South-eastern Europe or Southern Europe.

Southeast Europe or Southeastern Europe (SEE) is a geographical sub-region of Europe, consisting primarily of the cultural region of the Balkans, as well as adjacent regions and archipelagos. There are overlapping and conflicting definitions of the region, due to political, economic, historical, cultural, and geographical considerations.

The Southeast European Cooperative Initiative (SECI) is a multilateral regional initiative that has been initiated by the European Union, the United States of America and the countries of Southeast Europe within the framework of the Organization for Security and Cooperation in Europe (OSCE) as a support to the implementation of the Dayton Accords in December 1996 at the inaugural session at Geneva on the basis of Final Points of Common EU-USA Understanding.
South East Europe Media Organisation (SEEMO) is a regional non-governmental, non-profit network of editors, media executives and leading journalists in Southeast, South, East and Central Europe. The organization aims to create a bridge between international media activities and the media developments in the region. It has headquarters and national committees in several countries. In total 33 member states or territories are included in SEEMO: Albania, Armenia, Azerbaijan, Belarus, Bosnia-Herzegovina, Bulgaria, Croatia, Cyprus, Czech Republic, Estonia, Georgia, Greece, Hungary, Kazakhstan, Kosovo, Kyrgyzstan, Latvia, Lithuania, Malta, Moldova, Montenegro, North Macedonia, Poland, Romania, Russia, Serbia, Slovakia, Slovenia, Tajikistan, Turkmenistan, Turkey, Ukraine and Uzbekistan
Languages of Yugoslavia are all languages spoken in former Yugoslavia. They are mainly Indo-European languages and dialects, namely dominant South Slavic varieties as well as Albanian, Aromanian, Bulgarian, Czech, German, Italian, Venetian, Balkan Romani, Romanian, Pannonian Rusyn, Slovak and Ukrainian languages. There are also pockets where varieties of non-Indo-European languages, such as those of Hungarian and Turkish, are spoken.
As a member of FIFA and UEFA, the Montenegro national football team has been playing official matches since March 2007. Montenegro plays in the qualifiers for the FIFA World Cup and UEFA European Championship, as well as partaking in the UEFA Nations League. Apart from that, the team participates in friendly matches.
East-Central Europe is the region between German-, Hungarian-, and West Slavic-speaking Europe and the East Slavic countries of Belarus, Russia, and Ukraine. Those lands are described as situated "between two": "between two worlds, between two stages, between two futures".
This article lists all the Bosnia and Herzegovina national football team results between 1995 and 2019.

This is a list of the Romania national football team results from 2000 to 2019:
ATP (formally, the Agreement on the International Carriage of Perishable Foodstuffs and on the Special Equipment to be used for such Carriage (ATP)) is a 1970 United Nations treaty that establishes standards for the international transport of perishable food between the states that ratify the treaty. It has been updated through amendment a number of times and as of 2016 has 50 state parties, most of which are in Europe or Central Asia. It is open to ratification by states that are members of the United Nations Economic Commission for Europe (UNECE) and states that otherwise participate in UNECE activities. "ATP" is derived from the French name of the treaty: Accord relatif aux transports internationaux de denrées périssables et aux engins spéciaux à utiliser pour ces transports.
This is a list of all Slovakia national football team results against other national teams to the present day.

The sixth European Athletics Team Championships took place on 20 and 21 June 2015.
The 2019 FIBA Basketball World Cupqualification for the FIBA Europe region, began in August 2017 and concluded in February 2019. Contrary to previous years, no teams were automatically placed into the World Cup, so all FIBA Europe nations had to participate in qualification.
The Slovenia national football team represents Slovenia in association football and is controlled by the Football Association of Slovenia, the governing body for football in Slovenia. It competes as a member of the Union of European Football Associations (UEFA), which encompasses the countries of Europe. Slovenia joined UEFA and the International Federation of Association Football (FIFA) in 1992, a year after the country gained independence from the Socialist Federal Republic of Yugoslavia.
This page describes the qualification procedure for FIBA Women's EuroBasket 2021. 14 teams joined the co-hosts France and Spain.

These are all the matches played by the Macedonia national football team from 1993 to 2018:

The Lithuania national football team represents Lithuania in association football and is controlled by the Lithuanian Football Federation (LFF), the governing body of the sport in the country.

This is a list of the Norway national football team results from 2000 to 2019.
The EuroBasket Women 2023 qualification was held from November 2021 to February 2023 to decide the 14 teams to join the co-hosts Israel and Slovenia. It featured 38 teams split in ten groups of three or four teams. The ten group winners and the four best second-ranked teams qualified for the final tournament.











