
The Treaty of Trianon often referred to as the PeaceDictate of Trianon or Dictate of Trianon in Hungary, was prepared at the Paris Peace Conference and was signed in the Grand Trianon château in Versailles on 4 June 1920. It formally ended World War I between most of the Allies of World War I and the Kingdom of Hungary. French diplomats played the major role in designing the treaty, with a view to establishing a French-led coalition of the newly formed states.

The Kingdom of Yugoslavia was a country in Southeast and Central Europe that existed from 1918 until 1941. From 1918 to 1929, it was officially called the Kingdom of Serbs, Croats, and Slovenes, but the term "Yugoslavia" was its colloquial name due to its origins. The official name of the state was changed to "Kingdom of Yugoslavia" by King Alexander I on 3 October 1929.

Alexander I, also known as Alexander the Unifier, was King of the Serbs, Croats and Slovenes from 16 August 1921 to 3 October 1929 and King of Yugoslavia from 3 October 1929 until his assassination in 1934. His reign of 13 years is the longest of the three monarchs of the Kingdom of Yugoslavia.

The Treaty of Rapallo was an agreement between the Kingdom of Italy and the Kingdom of Serbs, Croats and Slovenes in the aftermath of the First World War. It was intended to settle the Adriatic question, which referred to Italian claims over territories promised to the country in return for its entry into the war against Austria-Hungary, claims that were made on the basis of the 1915 Treaty of London. The wartime pact promised Italy large areas of the eastern Adriatic. The treaty, signed on 12 November 1920 in Rapallo, Italy, generally redeemed the promises of territorial gains in the former Austrian Littoral by awarding Italy territories generally corresponding to the peninsula of Istria and the former Princely County of Gorizia and Gradisca, with the addition of the Snežnik Plateau, in addition to what was promised by the London treaty. The articles regarding Dalmatia were largely ignored. Instead, in Dalmatia, Italy received the city of Zadar and several islands. Other provisions of the treaty contained safeguards for the rights of Italian nationals remaining in the Kingdom of Serbs, Croats and Slovenes, and provisions for commissions to demarcate the new border, and facilitate economic and educational cooperation. The treaty also established the Free State of Fiume, the city-state consisting of the former Austro-Hungarian Corpus separatum that consisted of Rijeka and a strip of coast giving the new state a land border with Italy at Istria.

The Treaty of Saint-Germain-en-Laye was signed on 10 September 1919 by the victorious Allies of World War I on the one hand and by the Republic of German-Austria on the other. Like the Treaty of Trianon with Hungary and the Treaty of Versailles with the Weimar Republic, it contained the Covenant of the League of Nations and as a result was not ratified by the United States but was followed by the US–Austrian Peace Treaty of 1921.

The Treaty of Neuilly-sur-Seine required Bulgaria to cede various territories, after Bulgaria had been one of the Central Powers defeated in World War I. The treaty was signed on 27 November 1919 at Neuilly-sur-Seine, France.

Milan Stojadinović was a Serbian and Yugoslav politician and economist who served as the Prime Minister of Yugoslavia from 1935 to 1939. He also served as Foreign Minister from 1935 to 1939 and as Minister of Finance three times.

The Yugoslav Committee was a World War I-era, unelected, ad-hoc committee that largely consisting of émigré Croat, Slovene, and Bosnian Serb politicians and political activists, whose aim was the detachment of Austro-Hungarian lands inhabited by South Slavs and unification of those lands with the Kingdom of Serbia. The group was formally established in 1915 and it last met in 1919, shortly after the breakup of Austria-Hungary and the establishment of the Kingdom of Serbs, Croats and Slovenes, which was later renamed Yugoslavia. The Yugoslav Committee was led by it president the Croat lawyer Ante Trumbić and, until 1916, by Croat politician Frano Supilo as its vice president.

The Treaty of London or the Pact of London was a secret agreement concluded on 26 April 1915 by the United Kingdom, France, and Russia on the one part, and Italy on the other, in order to entice the latter to enter World War I on the side of the Triple Entente. The agreement involved promises of Italian territorial expansion against Austria-Hungary, the Ottoman Empire and in Africa where it was promised enlargement of its colonies. The Entente countries hoped to force the Central Powers – particularly Germany and Austria-Hungary – to divert some of their forces away from existing battlefields. The Entente also hoped that Romania and Bulgaria would be encouraged to join them after Italy did the same.

The Balkan Pact, or Balkan Entente, was a treaty signed by Greece, Romania, Turkey and Yugoslavia on 9 February 1934 in Athens, aimed at maintaining the geopolitical status quo in the region after the end of World War I. To present a united front against Bulgarian designs on their territories, the signatories agreed to suspend all disputed territorial claims against one another and their immediate neighbours following the aftermath of the war and a rise in various regional irredentist tensions.

The Free State of Fiume was an independent free state that existed between 1920 and 1924. Its territory of 28 km2 (11 sq mi) comprised the city of Fiume and rural areas to its north, with a corridor to its west connecting it to the Kingdom of Italy.

There was a period of revolutions and interventions in Hungary between 1918 and 1920. The First Hungarian Republic was founded from the ruins of the Austro-Hungarian Empire by Mihály Károlyi during the Aster Revolution in 1918, at the end of World War I. In March 1919, the republic was overturned by another revolution, and the Hungarian Soviet Republic was created. Unresolved conflicts led to wars between Hungary and its neighbor states in 1919. The Hungarian Soviet Republic ceased to exist after the Romanian occupation. The 1920 Treaty of Trianon in Versailles created the Kingdom of Hungary.
The Polish–Romanian alliance was a series of treaties signed in the interwar period by the Second Polish Republic and the Kingdom of Romania. The first of them was signed in 1921 and, together, the treaties formed a basis for good foreign relations between the two countries that lasted until World War II began in 1939.

The Minority Treaties[a] are treaties, League of Nations mandates, and unilateral declarations made by countries applying for membership in the League of Nations that conferred basic rights on all the inhabitants of the country without distinction of birth, nationality, language, race or religion. The country concerned had to acknowledge the clauses of the treaty as fundamental laws of state and as obligations of international concern placed under the guarantee of the League of Nations. Most of the treaties entered into force after the Paris Peace Conference.
At the outbreak of World War I in August 1914, Hungary was part of the Dual Monarchy of Austria-Hungary. Although there are no significant battles specifically connected to Hungarian regiments, the troops suffered high losses throughout the war as the Empire suffered defeat after defeat. The result was the breakup of the Empire and eventually, Hungary suffered severe territorial losses by the closing Trianon Peace Treaty.

Béla Linder, Hungarian colonel of artillery, Secretary of War of Mihály Károlyi government, minister without portfolio of Dénes Berinkey government, military attaché of Hungarian Soviet Republic based in Vienna, finally the mayor of Pécs during the period of Serb occupation.
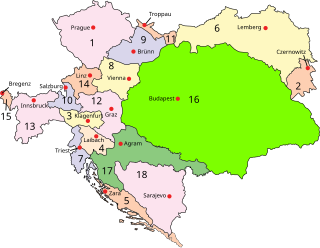
The dissolution of Austria-Hungary was a major geopolitical event that occurred as a result of the growth of internal social contradictions and the separation of different parts of Austria-Hungary. The more immediate reasons for the collapse of the state were World War I, the 1918 crop failure, general starvation and the economic crisis. The Austro-Hungarian Empire had additionally been weakened over time by a widening gap between Hungarian and Austrian interests. Furthermore, a history of chronic overcommitment rooted in the 1815 Congress of Vienna in which Metternich pledged Austria to fulfill a role that necessitated unwavering Austrian strength and resulted in overextension. Upon this weakened foundation, additional stressors during World War I catalyzed the collapse of the empire. The 1917 October Revolution and the Wilsonian peace pronouncements from January 1918 onward encouraged socialism on the one hand, and nationalism on the other, or alternatively a combination of both tendencies, among all peoples of the Habsburg monarchy.
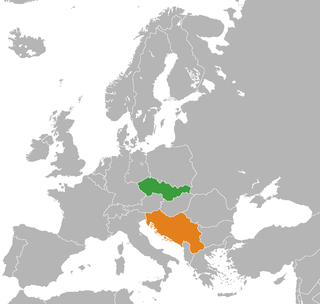
Czechoslovakia–Yugoslavia relations were historical foreign relations between Czechoslovakia and Yugoslavia, both of which are now-defunct states. Czechoslovakia and the Kingdom of Serbs, Croats and Slovenes were both created as union states of smaller Slavic ethnic groups. Both were created after the dissolution of Austria-Hungary, itself a multinational empire unable to appease its Slavic populations or implement a trialist reform in its final years.
The armistice of Belgrade was an agreement on the termination of World War I hostilities between the Triple Entente and the Kingdom of Hungary concluded in Belgrade on 13 November 1918. It was largely negotiated by General Louis Franchet d'Espèrey, as the commanding officer of the Allied Army of the Orient, and Hungarian Prime Minister Mihály Károlyi, on 7 November. It was signed by General Paul Prosper Henrys and vojvoda Živojin Mišić, as representatives of the Allies, and by the former Hungarian Minister of War, Béla Linder.

Austria–Yugoslavia relations were historical foreign relations between Austria and now broken up Yugoslavia. Both countries were created following the dissolution of Austria-Hungary in 1918. First Austrian Republic was a successor state of the empire while Yugoslavia was created after the unification of pre-World War I Kingdom of Serbia with the State of Slovenes, Croats and Serbs. In the days before this unification Kingdom of Serbia merged with the Banat, Bačka and Baranja and the Kingdom of Montenegro. During the interwar period of European history relations between the First Austrian Republic and the Kingdom of Yugoslavia were marked by the Austro-Slovene conflict in Carinthia, 1920 Carinthian plebiscite, 1920 establishment of pro-status quo Little Entente, 1934 Rome Protocols between revanchist Austria, Hungary and Fascist Italy and 1938 Anschluss.























