Related Research Articles

Metallic bonding is a type of chemical bonding that arises from the electrostatic attractive force between conduction electrons and positively charged metal ions. It may be described as the sharing of free electrons among a structure of positively charged ions (cations). Metallic bonding accounts for many physical properties of metals, such as strength, ductility, thermal and electrical resistivity and conductivity, opacity, and lustre.
In physics, statistical mechanics is a mathematical framework that applies statistical methods and probability theory to large assemblies of microscopic entities. Sometimes called statistical physics or statistical thermodynamics, its applications include many problems in the fields of physics, biology, chemistry, neuroscience, computer science, information theory and sociology. Its main purpose is to clarify the properties of matter in aggregate, in terms of physical laws governing atomic motion.

In physics, a state of matter is one of the distinct forms in which matter can exist. Four states of matter are observable in everyday life: solid, liquid, gas, and plasma. Many intermediate states are known to exist, such as liquid crystal, and some states only exist under extreme conditions, such as Bose–Einstein condensates and Fermionic condensates, neutron-degenerate matter, and quark–gluon plasma. For a list of exotic states of matter, see the article List of states of matter.

An ideal gas is a theoretical gas composed of many randomly moving point particles that are not subject to interparticle interactions. The ideal gas concept is useful because it obeys the ideal gas law, a simplified equation of state, and is amenable to analysis under statistical mechanics. The requirement of zero interaction can often be relaxed if, for example, the interaction is perfectly elastic or regarded as point-like collisions.
Degenerate matter occurs when the Pauli exclusion principle significantly alters a state of matter at low temperature. The term is used in astrophysics to refer to dense stellar objects such as white dwarfs and neutron stars, where thermal pressure alone is not enough to avoid gravitational collapse. The term also applies to metals in the Fermi gas approximation.

Fermi liquid theory is a theoretical model of interacting fermions that describes the normal state of the conduction electrons in most metals at sufficiently low temperatures. The theory describes the behavior of many-body systems of particles in which the interactions between particles may be strong. The phenomenological theory of Fermi liquids was introduced by the Soviet physicist Lev Davidovich Landau in 1956, and later developed by Alexei Abrikosov and Isaak Khalatnikov using diagrammatic perturbation theory. The theory explains why some of the properties of an interacting fermion system are very similar to those of the ideal Fermi gas, and why other properties differ.
In physics, screening is the damping of electric fields caused by the presence of mobile charge carriers. It is an important part of the behavior of charge-carrying fluids, such as ionized gases, electrolytes, and charge carriers in electronic conductors . In a fluid, with a given permittivity ε, composed of electrically charged constituent particles, each pair of particles interact through the Coulomb force as
Density functional theory (DFT) is a computational quantum mechanical modelling method used in physics, chemistry and materials science to investigate the electronic structure of many-body systems, in particular atoms, molecules, and the condensed phases. Using this theory, the properties of a many-electron system can be determined by using functionals, i.e. functions of another function. In the case of DFT, these are functionals of the spatially dependent electron density. DFT is among the most popular and versatile methods available in condensed-matter physics, computational physics, and computational chemistry.
In condensed matter physics, a quasiparticle is a concept used to describe a collective behavior of a group of particles that can be treated as if they were a single particle. Formally, quasiparticles and collective excitations are closely related phenomena that arise when a microscopically complicated system such as a solid behaves as if it contained different weakly interacting particles in vacuum.

A Luttinger liquid, or Tomonaga–Luttinger liquid, is a theoretical model describing interacting electrons in a one-dimensional conductor. Such a model is necessary as the commonly used Fermi liquid model breaks down for one dimension.
In physics, the Einstein relation is a previously unexpected connection revealed independently by William Sutherland in 1904, Albert Einstein in 1905, and by Marian Smoluchowski in 1906 in their works on Brownian motion. The more general form of the equation in the classical case is
The classical-map hypernetted-chain method is a method used in many-body theoretical physics for interacting uniform electron liquids in two and three dimensions, and for non-ideal plasmas. The method extends the famous hypernetted-chain method (HNC) introduced by J. M. J van Leeuwen et al. to quantum fluids as well. The classical HNC, together with the Percus–Yevick approximation, are the two pillars which bear the brunt of most calculations in the theory of interacting classical fluids. Also, HNC and PY have become important in providing basic reference schemes in the theory of fluids, and hence they are of great importance to the physics of many-particle systems.
This glossary of chemistry terms is a list of terms and definitions relevant to chemistry, including chemical laws, diagrams and formulae, laboratory tools, glassware, and equipment. Chemistry is a physical science concerned with the composition, structure, and properties of matter, as well as the changes it undergoes during chemical reactions; it features an extensive vocabulary and a significant amount of jargon.

A liquid is a nearly incompressible fluid that conforms to the shape of its container but retains a nearly constant volume independent of pressure. It is one of the four fundamental states of matter, and is the only state with a definite volume but no fixed shape.

Gas is one of the four fundamental states of matter. The others are solid, liquid, and plasma. A pure gas may be made up of individual atoms, elemental molecules made from one type of atom, or compound molecules made from a variety of atoms. A gas mixture, such as air, contains a variety of pure gases. What distinguishes gases from liquids and solids is the vast separation of the individual gas particles. This separation usually makes a colorless gas invisible to the human observer.
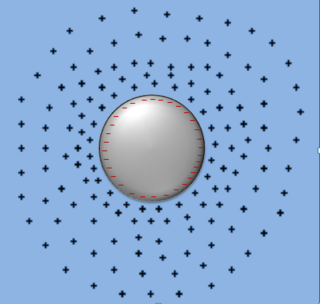
Friedel oscillations, named after French physicist Jacques Friedel, arise from localized perturbations in a metallic or semiconductor system caused by a defect in the Fermi gas or Fermi liquid. Friedel oscillations are a quantum mechanical analog to electric charge screening of charged species in a pool of ions. Whereas electrical charge screening utilizes a point entity treatment to describe the make-up of the ion pool, Friedel oscillations describing fermions in a Fermi fluid or Fermi gas require a quasi-particle or a scattering treatment. Such oscillations depict a characteristic exponential decay in the fermionic density near the perturbation followed by an ongoing sinusoidal decay resembling sinc function. In 2020, magnetic Friedel oscillations were observed on a metal surface.

Plasma is one of four fundamental states of matter characterized by the presence of a significant portion of charged particles in any combination of ions or electrons. It is the most abundant form of ordinary matter in the universe, mostly in stars, but also dominating the rarefied intracluster medium and intergalactic medium. Plasma can be artificially generated, for example, by heating a neutral gas or subjecting it to a strong electromagnetic field.
This glossary of engineering terms is a list of definitions about the major concepts of engineering. Please see the bottom of the page for glossaries of specific fields of engineering.
This glossary of physics is a list of definitions of terms and concepts relevant to physics, its sub-disciplines, and related fields, including mechanics, materials science, nuclear physics, particle physics, and thermodynamics. For more inclusive glossaries concerning related fields of science and technology, see Glossary of chemistry terms, Glossary of astronomy, Glossary of areas of mathematics, and Glossary of engineering.
References
- ↑ R. Balescu, Equilibrium and Nonequilibrium Statistical Mechanics, (John Wiley, 1975)