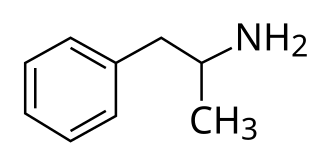
Amphetamine is a central nervous system (CNS) stimulant that is used in the treatment of attention deficit hyperactivity disorder (ADHD), narcolepsy, and obesity. Amphetamine was discovered as a chemical in 1887 by Lazăr Edeleanu, and then as a drug in the late 1920s. It exists as two enantiomers: levoamphetamine and dextroamphetamine. Amphetamine properly refers to a specific chemical, the racemic free base, which is equal parts of the two enantiomers in their pure amine forms. The term is frequently used informally to refer to any combination of the enantiomers, or to either of them alone. Historically, it has been used to treat nasal congestion and depression. Amphetamine is also used as an athletic performance enhancer and cognitive enhancer, and recreationally as an aphrodisiac and euphoriant. It is a prescription drug in many countries, and unauthorized possession and distribution of amphetamine are often tightly controlled due to the significant health risks associated with recreational use.
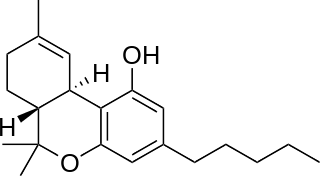
Tetrahydrocannabinol (THC) is the principal psychoactive constituent of cannabis and one of at least 113 total cannabinoids identified on the plant. Although the chemical formula for THC (C21H30O2) describes multiple isomers, the term THC usually refers to the delta-9-THC isomer with chemical name (−)-trans-Δ9-tetrahydrocannabinol. THC is a terpenoid found in cannabis and, like many pharmacologically active phytochemicals, it is assumed to be involved in the plant's evolutionary adaptation against insect predation, ultraviolet light, and environmental stress. THC was first discovered and isolated by Israeli chemist Raphael Mechoulam in Israel in 1964. It was found that, when smoked, THC is absorbed into the bloodstream and travels to the brain, attaching itself to endocannabinoid receptors located in the cerebral cortex, cerebellum, and basal ganglia. These are the parts of the brain responsible for thinking, memory, pleasure, coordination and movement.

Dextroamphetamine is a potent central nervous system (CNS) stimulant and enantiomer of amphetamine that is prescribed for the treatment of attention deficit hyperactivity disorder (ADHD) and narcolepsy. It is also used as an athletic performance and cognitive enhancer, and recreationally as an aphrodisiac and euphoriant.
An antimetabolite is a chemical that inhibits the use of a metabolite, which is another chemical that is part of normal metabolism. Such substances are often similar in structure to the metabolite that they interfere with, such as the antifolates that interfere with the use of folic acid; thus, competitive inhibition can occur, and the presence of antimetabolites can have toxic effects on cells, such as halting cell growth and cell division, so these compounds are used in chemotherapy for cancer.

Drug delivery refers to approaches, formulations, manufacturing techniques, storage systems, and technologies involved in transporting a pharmaceutical compound to its target site to achieve a desired therapeutic effect. Principles related to drug preparation, route of administration, site-specific targeting, metabolism, and toxicity are used to optimize efficacy and safety, and to improve patient convenience and compliance. Drug delivery is aimed at altering a drug's pharmacokinetics and specificity by formulating it with different excipients, drug carriers, and medical devices. There is additional emphasis on increasing the bioavailability and duration of action of a drug to improve therapeutic outcomes. Some research has also been focused on improving safety for the person administering the medication. For example, several types of microneedle patches have been developed for administering vaccines and other medications to reduce the risk of needlestick injury.
Targeted drug delivery, sometimes called smart drug delivery, is a method of delivering medication to a patient in a manner that increases the concentration of the medication in some parts of the body relative to others. This means of delivery is largely founded on nanomedicine, which plans to employ nanoparticle-mediated drug delivery in order to combat the downfalls of conventional drug delivery. These nanoparticles would be loaded with drugs and targeted to specific parts of the body where there is solely diseased tissue, thereby avoiding interaction with healthy tissue. The goal of a targeted drug delivery system is to prolong, localize, target and have a protected drug interaction with the diseased tissue. The conventional drug delivery system is the absorption of the drug across a biological membrane, whereas the targeted release system releases the drug in a dosage form. The advantages to the targeted release system is the reduction in the frequency of the dosages taken by the patient, having a more uniform effect of the drug, reduction of drug side-effects, and reduced fluctuation in circulating drug levels. The disadvantage of the system is high cost, which makes productivity more difficult, and the reduced ability to adjust the dosages.
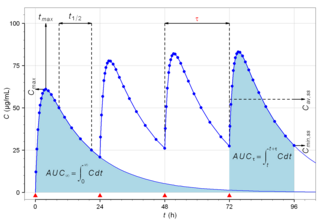
Pharmacokinetics, sometimes abbreviated as PK, is a branch of pharmacology dedicated to describing how the body affects a specific substance after administration. The substances of interest include any chemical xenobiotic such as pharmaceutical drugs, pesticides, food additives, cosmetics, etc. It attempts to analyze chemical metabolism and to discover the fate of a chemical from the moment that it is administered up to the point at which it is completely eliminated from the body. Pharmacokinetics is based on mathematical modeling that places great emphasis on the relationship between drug plasma concentration and the time elapsed since the drug's administration. Pharmacokinetics is the study of how an organism affects the drug, whereas pharmacodynamics (PD) is the study of how the drug affects the organism. Both together influence dosing, benefit, and adverse effects, as seen in PK/PD models.

Lisdexamfetamine, most commonly sold under the brand name Vyvanse and Elvanse among others, is a stimulant medication that is used to treat attention deficit hyperactivity disorder (ADHD) in children and adults and for moderate-to-severe binge eating disorder in adults. Lisdexamfetamine is taken by mouth. Its effects generally begin within two hours and last for up to 14 hours. In the United Kingdom, it is usually less preferred to methylphenidate for the treatment of children.
Thiolated polymers – designated thiomers – are functional polymers used in biotechnology product development with the intention to prolong mucosal drug residence time and to enhance absorption of drugs. The name thiomer was coined by Andreas Bernkop-Schnürch in 2000. Thiomers have thiol bearing side chains. Sulfhydryl ligands of low molecular mass are covalently bound to a polymeric backbone consisting of mainly biodegradable polymers, such as chitosan, hyaluronic acid, cellulose derivatives, pullulan, starch, gelatin, polyacrylates, cyclodextrins, or silicones.
Pharmacotoxicology entails the study of the consequences of toxic exposure to pharmaceutical drugs and agents in the health care field. The field of pharmacotoxicology also involves the treatment and prevention of pharmaceutically induced side effects. Pharmacotoxicology can be separated into two different categories: pharmacodynamics, and pharmacokinetics.
Polymer-drug conjugates are nano-medicine products under development for cancer diagnosis and treatment. There are more than 10 anticancer conjugates in clinical development. Polymer-drug conjugates are drug molecules held in polymer molecules, which act as the delivery system for the drug. Polymer drugs have passed multidrug resistance (MDR) testing and hence may become a viable treatment for endocrine-related cancers. A cocktail of pendant drugs could be delivered by water-soluble polymer platforms. The physical and chemical properties of the polymers used in polymer-drug conjugates are specially synthesized to flow through the kidneys and liver without being filtered out, allowing the drugs to be used more effectively. Traditional polymers used in polymer-drug conjugates can be degraded through enzymatic activity and acidity. Polymers are now being synthesized to be sensitive to specific enzymes that are apparent in diseased tissue. The drugs remain attached to the polymer and are not activated until the enzymes associated with the diseased tissue are present. This process significantly minimizes damage to healthy tissue.

Tetrahydrocannabinolic acid (THCA) synthase is an enzyme responsible for catalyzing the formation of THCA from cannabigerolic acid (CBGA). THCA is the direct precursor of tetrahydrocannabinol (THC), the principal psychoactive component of cannabis, which is produced from various strains of Cannabis sativa. Therefore, THCA synthase is considered to be a key enzyme controlling cannabis psychoactivity. Polymorphisms of THCA synthase result in varying levels of THC in Cannabis plants, resulting in "drug-type" and "fiber-type" C. sativa varieties.

In the field of drug discovery, retrometabolic drug design is a strategy for the design of safer drugs either using predictable metabolism to an inactive moiety or using targeted drug delivery approaches. The phrase retrometabolic drug design was coined by Nicholas Bodor. The method is analogous to retrosynthetic analysis where the synthesis of a target molecule is planned backwards. In retrometabolic drug design, metabolic reaction information of drugs is used to design parent drugs whose metabolism and distribution can be controlled to target and eliminate the drug to increase efficacy and minimize undesirable side effects. The new drugs thus designed achieve selective organ and/or therapeutic site drug targeting and produce safe therapeutic agents and safe environmental chemicals. These approaches represent systematic methodologies that thoroughly integrate structure-activity (SAR) and structure-metabolism (SMR) relationships and are aimed at designing safe, locally active compounds with improved therapeutic index.

Malcolm Rowland FBPhS is Emeritus Professor of Pharmacy, University of Manchester, and Adjunct Professor, University of California San Francisco. His research in pharmacology, has been particularly in physiologically based pharmacokinetics. He has written several textbooks on the subject.

Dextran drug delivery systems involve the use of the natural glucose polymer dextran in applications as a prodrug, nanoparticle, microsphere, micelle, and hydrogel drug carrier in the field of targeted and controlled drug delivery. According to several in vitro and animal research studies, dextran carriers reduce off-site toxicity and improve local drug concentration at the target tissue site. This technology has significant implications as a potential strategy for delivering therapeutics to treat cancer, cardiovascular diseases, pulmonary diseases, bone diseases, liver diseases, colonic diseases, infections, and HIV.
Conventional drug delivery is limited by the inability to control dosing, target specific sites, and achieve targeted permeability. Traditional methods of delivering therapeutics to the body experience challenges in achieving and maintaining maximum therapeutic effect while avoiding the effects of drug toxicity. Many drugs that are delivered orally or parenterally do not include mechanisms for sustained release, and as a result they require higher and more frequent dosing to achieve any therapeutic effect for the patient. As a result, the field of drug delivery systems developed into a large focus area for pharmaceutical research to address these limitations and improve quality of care for patients. Within the broad field of drug delivery, the development of stimuli-responsive drug delivery systems has created the ability to tune drug delivery systems to achieve more controlled dosing and targeted specificity based on material response to exogenous and endogenous stimuli.
Protein nanotechnology is a burgeoning field of research that integrates the diverse physicochemical properties of proteins with nanoscale technology. This field assimilated into pharmaceutical research to give rise to a new classification of nanoparticles termed protein nanoparticles (PNPs). PNPs garnered significant interest due to their favorable pharmacokinetic properties such as high biocompatibility, biodegradability, and low toxicity Together, these characteristics have the potential to overcome the challenges encountered with synthetic NPs drug delivery strategies. These existing challenges including low bioavailability, a slow excretion rate, high toxicity, and a costly manufacturing process, will open the door to considerable therapeutic advancements within oncology, theranostics, and clinical translational research.
pH-responsive tumor-targeted drug delivery is a specialized form of targeted drug delivery that utilizes nanoparticles to deliver therapeutic drugs directly to cancerous tumor tissue while minimizing its interaction with healthy tissue. Scientists have used drug delivery as a way to modify the pharmacokinetics and targeted action of a drug by combining it with various excipients, drug carriers, and medical devices. These drug delivery systems have been created to react to the pH environment of diseased or cancerous tissues, triggering structural and chemical changes within the drug delivery system. This form of targeted drug delivery is to localize drug delivery, prolongs the drug's effect, and protect the drug from being broken down or eliminated by the body before it reaches the tumor.

A ligand-targeted liposome (LTL) is a nanocarrier with specific ligands attached to its surface to enhance localization for targeted drug delivery. The targeting ability of LTLs enhances cellular localization and uptake of these liposomes for therapeutic or diagnostic purposes. LTLs have the potential to enhance drug delivery by decreasing peripheral systemic toxicity, increasing in vivo drug stability, enhancing cellular uptake, and increasing efficiency for chemotherapeutics and other applications. Liposomes are beneficial in therapeutic manufacturing because of low batch-to-batch variability, easy synthesis, favorable scalability, and strong biocompatibility. Ligand-targeting technology enhances liposomes by adding targeting properties for directed drug delivery.
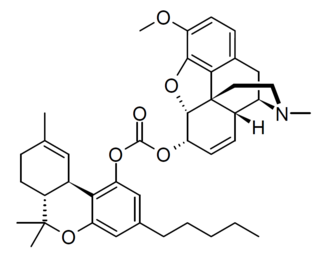
Cod-THC is a synthetic codrug formed by linking tetrahydrocannabinol with codeine via a carbonate bridge. It is well absorbed orally and shows superior analgesic effects in animal studies compared to a simple mixture of the two drugs.











