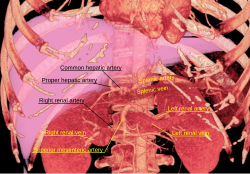
The portal vein or hepatic portal vein (HPV) is a blood vessel that carries blood from the gastrointestinal tract, gallbladder, pancreas and spleen to the liver. This blood contains nutrients and toxins extracted from digested contents. Approximately 75% of total liver blood flow is through the portal vein, with the remainder coming from the hepatic artery proper. The blood leaves the liver to the heart in the hepatic veins.

In human anatomy, the abdominal aorta is the largest artery in the abdominal cavity. As part of the aorta, it is a direct continuation of the descending aorta.
The common hepatic duct is the first part of the biliary tract. It joins the cystic duct coming from the gallbladder to form the common bile duct.

The celiacartery, also known as the celiac trunk or truncus coeliacus, is the first major branch of the abdominal aorta. It is about 1.25 cm in length. Branching from the aorta at thoracic vertebra 12 (T12) in humans, it is one of three anterior/ midline branches of the abdominal aorta.

In human anatomy, the splenic artery or lienal artery, an older term, is the blood vessel that supplies oxygenated blood to the spleen. It branches from the celiac artery, and follows a course superior to the pancreas. It is known for its tortuous path to the spleen.

In anatomy, the gastroduodenal artery is a small blood vessel in the abdomen. It supplies blood directly to the pylorus and proximal part of the duodenum. It also indirectly supplies the pancreatic head.

The lesser omentum is the double layer of peritoneum that extends from the liver to the lesser curvature of the stomach, and to the first part of the duodenum. The lesser omentum is usually divided into these two connecting parts: the hepatogastric ligament, and the hepatoduodenal ligament.

The hepatic artery proper is the artery that supplies the liver and gallbladder. It raises from the common hepatic artery, a branch of the celiac artery.

The cystic artery is (usually) a branch of the right hepatic artery that provides arterial supply to the gallbladder and contributes arterial supply to the extrahepatic bile ducts.

In human anatomy, the hepatic portal system or portal venous system is the system of veins comprising the portal vein and its tributaries. The other portal venous systems in the body are the renal portal system, and the hypophyseal portal system.

The left gastroepiploic artery, the largest branch of the splenic artery, runs from left to right about a finger's breadth or more from the greater curvature of the stomach, between the layers of the greater omentum, and anastomoses with the right gastroepiploic.

The right gastric artery usually arises from the proper hepatic artery. It descends to the pyloric end of the stomach before passing from right to left along its lesser curvature, supplying it with branches, and finally anastomosing with the left gastric artery.

The superior pancreaticoduodenal artery is an artery that supplies blood to the duodenum and pancreas.

In the anatomy of the human digestive tract, there are two colic flexures, or curvatures in the transverse colon. The right colic flexure is also known as the hepatic flexure, and the left colic flexure is also known as the splenic flexure. Note that "right" refers to the patient's anatomical right, which may be depicted on the left of a diagram.

The greater omentum is a large apron-like fold of visceral peritoneum that hangs down from the stomach. It extends from the greater curvature of the stomach, passing in front of the small intestines and doubles back to ascend to the transverse colon before reaching to the posterior abdominal wall. The greater omentum is larger than the lesser omentum, which hangs down from the liver to the lesser curvature. The common anatomical term "epiploic" derives from "epiploon", from the Greek epipleein, meaning to float or sail on, since the greater omentum appears to float on the surface of the intestines. It is the first structure observed when the abdominal cavity is opened anteriorly.

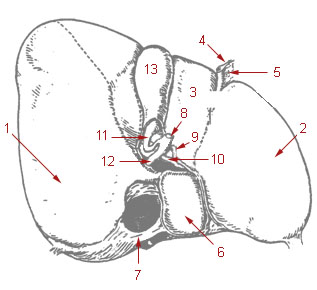
The porta hepatis or transverse fissure of the liver is a short but deep fissure, about 5 cm long, extending transversely beneath the left portion of the right lobe of the liver, nearer its posterior surface than its anterior border.

The hepatic plexus is a sympathetic and parasympathetic nerve plexus that provides innervation to the parenchyma of the liver as well as contributing innervation to some other abdominal structures.

The liver is a major metabolic organ only found in vertebrate animals, which performs many essential biological functions such as detoxification of the organism, and the synthesis of proteins and biochemicals necessary for digestion and growth. In humans, it is located in the right upper quadrant of the abdomen, below the diaphragm and mostly shielded by the lower right rib cage. Its other metabolic roles include carbohydrate metabolism, the production of hormones, conversion and storage of nutrients such as glucose and glycogen, and the decomposition of red blood cells.

A liver segment is one of eight segments of the liver as described in the widely used Couinaud classification in the anatomy of the liver. This system divides the lobes of the liver into eight segments based on a transverse plane through the bifurcation of the main portal vein, arranged in a clockwise manner starting from the caudate lobe.

In human anatomy, the liver is divided grossly into four parts or lobes: the right lobe, the left lobe, the caudate lobe, and the quadrate lobe. Seen from the front – the diaphragmatic surface – the liver is divided into two lobes: the right lobe and the left lobe. Viewed from the underside – the visceral surface – the other two smaller lobes, the caudate lobe and the quadrate lobe, are also visible. The two smaller lobes, the caudate lobe and the quadrate lobe, are known as superficial or accessory lobes, and both are located on the underside of the right lobe.