
The organized environmental movement is represented by a wide range of non-governmental organizations or NGOs that seek to address environmental issues in the United States. They operate on local, national, and international scales. Environmental NGOs vary widely in political views and in the ways they seek to influence the environmental policy of the United States and other governments.

David Ross Brower was a prominent environmentalist and the founder of many environmental organizations, including the John Muir Institute for Environmental Studies (1997), Friends of the Earth (1969), Earth Island Institute (1982), North Cascades Conservation Council, and Fate of the Earth Conferences. From 1952 to 1969, he served as the first Executive Director of the Sierra Club, and served on its board three times: from 1941–1953; 1983–1988; and 1995–2000 as a petition candidate enlisted by reform-activists known as the John Muir Sierrans. As a younger man, he was a prominent mountaineer.

The Diablo Canyon Power Plant is a nuclear power plant near Avila Beach in San Luis Obispo County, California. Following the permanent shutdown of the San Onofre Nuclear Generating Station in 2013, Diablo Canyon is now the only operational nuclear plant in California, as well as the state's largest single power station. It was the subject of controversy and protests during its construction, with nearly two thousand civil disobedience arrests in a two-week period in 1981.
The Abalone Alliance (1977–1985) was a nonviolent civil disobedience group formed to shut down the Pacific Gas and Electric Company's Diablo Canyon Power Plant near San Luis Obispo on the central California coast in the United States. They modeled their affinity group-based organizational structure after the Clamshell Alliance which was then protesting the Seabrook Nuclear Power Plant in coastal New Hampshire. The group of activists took the name "Abalone Alliance" referring to the tens of thousands of wild California Red Abalone that were killed in 1974 in Diablo Cove when the unit's plumbing had its first hot flush.

The anti-nuclear movement in the United States consists of more than 80 anti-nuclear groups that oppose nuclear power, nuclear weapons, and/or uranium mining. These have included the Abalone Alliance, Clamshell Alliance, Committee for Nuclear Responsibility, Nevada Desert Experience, Nuclear Information and Resource Service, Physicians for Social Responsibility, Plowshares Movement, United Steelworkers of America (USWA) District 31, Women Strike for Peace, Nukewatch, and Women's International League for Peace and Freedom. Some fringe aspects of the anti-nuclear movement have delayed construction or halted commitments to build some new nuclear plants, and have pressured the Nuclear Regulatory Commission to enforce and strengthen the safety regulations for nuclear power plants. Most groups in the movement focus on nuclear weapons.

Nuclear weapons testing, uranium mining and export, and nuclear power have often been the subject of public debate in Australia, and the anti-nuclear movement in Australia has a long history. Its origins date back to the 1972–1973 debate over French nuclear testing in the Pacific and the 1976–1977 debate about uranium mining in Australia.
The 1970s proved to be a pivotal period for the anti-nuclear movement in California. Opposition to nuclear power in California coincided with the growth of the country's environmental movement. Opposition to nuclear power increased when President Richard Nixon called for the construction of 1000 nuclear plants by the year 2000.

Critical Masses: Opposition to Nuclear Power in California, 1958–1978 is the first detailed history of the anti-nuclear movement in the United States, written by Thomas Wellock. It is also the first state-level research on the subject with a focus on California. Reviewer Paula Garb has said:
The book is rich with vivid verbal pictures and the passionate voices of participants on all sides of the controversy around the peaceful atom. It is based on interviews, documents from state and federal archives, and activist papers. Wellock brings to this project the expertise of a former engineer for civilian and navy nuclear reactors, a thorough archivist, and a sensitive interviewer.

More than 80 anti-nuclear groups are operating, or have operated, in the United States. These include Abalone Alliance, Clamshell Alliance, Greenpeace USA, Institute for Energy and Environmental Research, Musicians United for Safe Energy, Nevada Desert Experience, Nuclear Control Institute, Nuclear Information and Resource Service, Public Citizen Energy Program, Shad Alliance, and the Sierra Club. These are direct action, environmental, health, and public interest organizations who oppose nuclear weapons and/or nuclear power. In 1992, the chairman of the Nuclear Regulatory Commission said that "his agency had been pushed in the right direction on safety issues because of the pleas and protests of nuclear watchdog groups".

The Sundesert Nuclear Power Plant was a proposed California nuclear power station, formally submitted in 1976. Facing firm opposition from the state's Governor Jerry Brown and denied a permit by a state agency, plans for the construction of the power facility were rejected in 1978 after 100 million dollars had been spent towards its construction. The Sundesert proposal was the last major attempt to build a nuclear plant in California.

The Bodega Bay Nuclear Power Plant was a proposed Northern California nuclear power facility that was stopped by local activism in the 1960s and never built. The foundations, located 2 miles (3.2 km) west of the active San Andreas Fault, were being dug at the time the plant was cancelled. The action has been termed "the birth of the anti-nuclear movement."
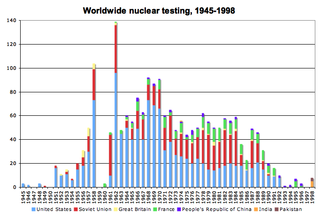
The application of nuclear technology, both as a source of energy and as an instrument of war, has been controversial.

The United States Government Accountability Office reported more than 150 incidents from 2001 to 2006 of nuclear plants not performing within acceptable safety guidelines. According to a 2010 survey of energy accidents, there have been at least 56 accidents at nuclear reactors in the United States. The most serious of these was the Three Mile Island accident in 1979. Davis-Besse Nuclear Power Plant has been the source of two of the top five most dangerous nuclear incidents in the United States since 1979. Relatively few accidents have involved fatalities.

Dark Circle is a 1982 American documentary film directed and produced by Judy Irving, Christopher Beaver and Ruth Landy that focuses on the connections between the nuclear weapons and the nuclear power industries, with a strong emphasis on the individual human and protracted U.S. environmental costs involved. A clear point made by the film is that while only two bombs were dropped on Japan, many hundreds were exploded in the United States.
San Luis Obispo Mothers for Peace (SLOMFP) is a participant in the anti-nuclear movement in California which is depicted in the anti-nuclear documentary film Dark Circle during the early years of protest opposing the Diablo Canyon Power Plant (DCPP). In Dark Circle, Mothers for Peace takes credit for delays which prevented the plant from going online prior to the discovery of the errors.
Alliance for Nuclear Responsibility is a non-profit, anti-nuclear, public interest organization founded in 2005, and based in San Luis Obispo, California. It is focused on public citizen activism and public participation with regard to the Diablo Canyon Power Plant, also known as the Diablo Canyon Nuclear Power Plant. The focus of the group is primarily on using leverage at the level of state agencies such as the California Public Utilities Commission. Concurrent jurisdiction of their concern also includes the California Coastal Commission, which certifies compliance of all action within the coastal zone which thus includes the plant. Their posture is primarily oppositional. Other venues for activism include the Nuclear Regulatory Commission, California Energy Commission, Regional Water Quality Control Board, SLO County, the California legislature, the office of the state attorney general, and the US Congress, of which they are in the 23rd District.
Diablo Canyon (Nuclear) Power Plant, located in San Luis Obispo County California, was originally designed to withstand a 6.75 magnitude earthquake from four faults, including the nearby San Andreas and Hosgri faults, but was later upgraded to withstand a 7.5 magnitude quake. It has redundant seismic monitoring and a safety system designed to shut it down promptly in the event of significant ground motion.

Anti-nuclear protests in the United States have occurred since the development of nuclear power plants in the United States. Examples include Clamshell Alliance protests at Seabrook Station Nuclear Power Plant, Abalone Alliance protests at Diablo Canyon Power Plant, and those following the Three Mile Island accident in 1979.













