Related Research Articles

Easter Island is an island and special territory of Chile in the southeastern Pacific Ocean, at the southeasternmost point of the Polynesian Triangle in Oceania. The island is most famous for its nearly 1,000 extant monumental statues, called moai, which were created by the early Rapa Nui people. In 1995, UNESCO named Easter Island a World Heritage Site, with much of the island protected within Rapa Nui National Park.

Jared Mason Diamond is an American scientist, historian, and author best known for his popular science and history books and articles. Originally trained in biochemistry and physiology, Diamond is commonly referred to as a polymath, stemming from his knowledge in many fields including anthropology, ecology, geography, and evolutionary biology. He is a professor of geography at UCLA.

Guns, Germs, and Steel: The Fates of Human Societies is a 1997 transdisciplinary non-fiction book by the American author Jared Diamond. The book attempts to explain why Eurasian and North African civilizations have survived and conquered others, while arguing against the idea that Eurasian hegemony is due to any form of Eurasian intellectual, moral, or inherent genetic superiority. Diamond argues that the gaps in power and technology between human societies originate primarily in environmental differences, which are amplified by various positive feedback loops. When cultural or genetic differences have favored Eurasians, he asserts that these advantages occurred because of the influence of geography on societies and cultures and were not inherent in the Eurasian genomes.

The boiling frog is an apologue describing a frog being slowly boiled alive. The premise is that if a frog is put suddenly into boiling water, it will jump out, but if the frog is put in tepid water which is then brought to a boil slowly, it will not perceive the danger and will be cooked to death. The story is often used as a metaphor for the inability or unwillingness of people to react to or be aware of sinister threats that arise gradually rather than suddenly.

In materials science, creep is the tendency of a solid material to undergo slow deformation while subject to persistent mechanical stresses. It can occur as a result of long-term exposure to high levels of stress that are still below the yield strength of the material. Creep is more severe in materials that are subjected to heat for long periods and generally increase as they near their melting point.

Mass wasting, also known as mass movement, is a general term for the movement of rock or soil down slopes under the force of gravity. It differs from other processes of erosion in that the debris transported by mass wasting is not entrained in a moving medium, such as water, wind, or ice. Types of mass wasting include creep, solifluction, rockfalls, debris flows, and landslides, each with its own characteristic features, and taking place over timescales from seconds to hundreds of years. Mass wasting occurs on both terrestrial and submarine slopes, and has been observed on Earth, Mars, Venus, Jupiter's moon Io, and on many other bodies in the Solar System.

Rose Madder is a horror/fantasy novel by American writer Stephen King, published in 1995. It deals with the effects of domestic violence and, unusually for a King novel, relies for its fantastic element on Greek mythology. In his memoir, On Writing, King states that Rose Madder and Insomnia are "stiff, trying-too-hard novels."

Collapse: How Societies Choose to Fail or Succeed is a 2005 book by academic and popular science author Jared Diamond, in which the author first defines collapse: "a drastic decrease in human population size and/or political/economic/social complexity, over a considerable area, for an extended time." He then reviews the causes of historical and pre-historical instances of societal collapse—particularly those involving significant influences from environmental changes, the effects of climate change, hostile neighbors, trade partners, and the society's response to the foregoing four challenges. It also considers why societies might not perceive a problem, might not decide to attempt a solution, and why an attempted solution might fail.
Salami slicing tactics, also known as salami slicing, salami tactics, the salami-slice strategy, or salami attacks, is the practice of using a series of many small actions to produce a much larger action or result that would be difficult or unlawful to perform all at once.

The Third Chimpanzee: The Evolution and Future of the Human Animal is a 1991 book by academic and popular science author Jared Diamond, in which the author explores concepts relating to the animal origins of human behavior. The book follows a series of articles published by Diamond, a physiologist, examining the evidence and its interpretation in earlier treatments of the related species, including cultural characteristics or features often regarded as particularly unique to humans. The book was released in the United Kingdom in 1991 by Radius under the title The Rise and Fall of the Third Chimpanzee: How Our Animal Heritage Affects the Way We Live and in the United States in 1992 by HarperCollins under the title The Third Chimpanzee: The Evolution and Future of the Human Animal. In 2014, Diamond published an adapted version for young people with Seven Stories Press titled, The Third Chimpanzee for Young People.

Soil consolidation refers to the mechanical process by which soil changes volume gradually in response to a change in pressure. This happens because soil is a two-phase material, comprising soil grains and pore fluid, usually groundwater. When soil saturated with water is subjected to an increase in pressure, the high volumetric stiffness of water compared to the soil matrix means that the water initially absorbs all the change in pressure without changing volume, creating excess pore water pressure. As water diffuses away from regions of high pressure due to seepage, the soil matrix gradually takes up the pressure change and shrinks in volume. The theoretical framework of consolidation is therefore closely related to the concept of effective stress, and hydraulic conductivity. The early theoretical modern models were proposed one century ago, according to two different approaches, by Karl Terzaghi and Paul Fillunger. The Terzaghi’s model is currently the most utilized in engineering practice and is based on the diffusion equation.
The camel's nose is a metaphor for a situation where the permitting of a small, seemingly innocuous act will open the door for larger, clearly undesirable actions.
Instruction creep or rule creep occurs when instructions or rules accumulate over time until they are unmanageable or inappropriate. It is a type of scope creep. The accumulation of bureaucratic requirements results in overly complex procedures that are often misunderstood, irritating, time-wasting, or ignored.
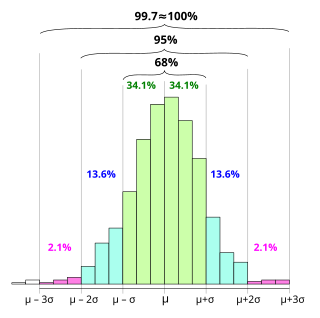
In statistics, the 68–95–99.7 rule, also known as the empirical rule, is a shorthand used to remember the percentage of values that lie within an interval estimate in a normal distribution: 68%, 95%, and 99.7% of the values lie within one, two, and three standard deviations of the mean, respectively.
Moving the goalposts is a metaphor, derived from goal-based sports such as football and hockey, that means to change the rule or criterion (goal) of a process or competition while it is still in progress, in such a way that the new goal offers one side an advantage or disadvantage.
In geology, a deformation mechanism is a process occurring at a microscopic scale that is responsible for changes in a material's internal structure, shape and volume. The process involves planar discontinuity and/or displacement of atoms from their original position within a crystal lattice structure. These small changes are preserved in various microstructures of materials such as rocks, metals and plastics, and can be studied in depth using optical or digital microscopy.

In phenology, season creep refers to observed changes in the timing of the seasons, such as earlier indications of spring widely observed in temperate areas across the Northern Hemisphere. Phenological records analyzed by climate scientists have shown significant temporal trends in the observed time of seasonal events, from the end of the 20th century and continuing into the 21st century. In Europe, season creep has been associated with the arrival of spring moving up by approximately one week in a recent 30-year period. Other studies have put the rate of season creep measured by plant phenology in the range of 2–3 days per decade advancement in spring, and 0.3–1.6 days per decade delay in autumn, over the past 30–80 years.
The tyranny of small decisions is a phenomenon in which a number of decisions, individually small and insignificant in size and time perspective, cumulatively result in a larger and significant outcome which is neither optimal nor desired. The concept was first explored in an essay of the same name, published in 1966 by the American economist Alfred E. Kahn. The article describes a situation where a series of small, individually rational decisions can negatively change the context of subsequent choices, even to the point where desired alternatives are irreversibly destroyed. Kahn described the problem as a common issue in market economics which can lead to market failure. The concept has since been extended to areas other than economic ones, such as environmental degradation, political elections and health outcomes.
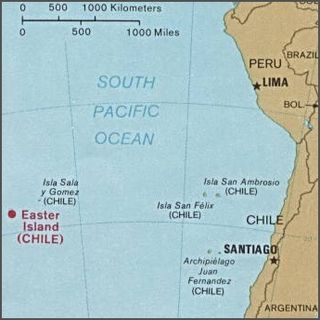
Easter Island is one of the world's most isolated inhabited islands. Its closest inhabited neighbours are the Chilean Juan Fernandez Islands, 1,850 km (1,150 mi) to the east, with approximately 850 inhabitants. The nearest continental point lies in central Chile near Concepción, at 3,512 kilometres (2,182 mi). Easter Island's latitude is similar to that of Caldera, Chile, and it lies 3,510 km (2,180 mi) west of continental Chile at its nearest point. Isla Salas y Gómez, 415 km (258 mi) to the east, is closer but is uninhabited. The Tristan da Cunha archipelago in the southern Atlantic competes for the title of the most remote island, lying 2,430 km (1,510 mi) from Saint Helena island and 2,816 km (1,750 mi) from the South African coast.
The term collapsology is a neologism used to designate the transdisciplinary study of the risks of collapse of industrial civilization. It is concerned with the general collapse of societies induced by climate change, as well as "scarcity of resources, vast extinctions, and natural disasters." Although the concept of civilizational or societal collapse had already existed for many years, collapsology focuses its attention on contemporary, industrial, and globalized societies.
References
- ↑ Fogg GE, LaBolle EM (14 March 2006). "Motivation of synthesis, with an example on groundwater quality sustainability". Water Resources Research. 42 (3): W03S05. Bibcode:2006WRR....42.3S05F. doi: 10.1029/2005WR004372 .
- ↑ Diamond, Jared (1995-08-01). "Easter's End". Discover magazine. Retrieved 2014-08-03.