Related Research Articles

The Data Encryption Standard is a symmetric-key algorithm for the encryption of digital data. Although its short key length of 56 bits makes it too insecure for applications, it has been highly influential in the advancement of cryptography.
Differential cryptanalysis is a general form of cryptanalysis applicable primarily to block ciphers, but also to stream ciphers and cryptographic hash functions. In the broadest sense, it is the study of how differences in information input can affect the resultant difference at the output. In the case of a block cipher, it refers to a set of techniques for tracing differences through the network of transformation, discovering where the cipher exhibits non-random behavior, and exploiting such properties to recover the secret key.

In cryptography, the International Data Encryption Algorithm (IDEA), originally called Improved Proposed Encryption Standard (IPES), is a symmetric-key block cipher designed by James Massey of ETH Zurich and Xuejia Lai and was first described in 1991. The algorithm was intended as a replacement for the Data Encryption Standard (DES). IDEA is a minor revision of an earlier cipher Proposed Encryption Standard (PES).
In cryptography, linear cryptanalysis is a general form of cryptanalysis based on finding affine approximations to the action of a cipher. Attacks have been developed for block ciphers and stream ciphers. Linear cryptanalysis is one of the two most widely used attacks on block ciphers; the other being differential cryptanalysis.
A5/1 is a stream cipher used to provide over-the-air communication privacy in the GSM cellular telephone standard. It is one of seven algorithms which were specified for GSM use. It was initially kept secret, but became public knowledge through leaks and reverse engineering. A number of serious weaknesses in the cipher have been identified.

Serpent is a symmetric key block cipher that was a finalist in the Advanced Encryption Standard (AES) contest, where it was ranked second to Rijndael. Serpent was designed by Ross Anderson, Eli Biham, and Lars Knudsen.

The GOST block cipher (Magma), defined in the standard GOST 28147-89, is a Soviet and Russian government standard symmetric key block cipher with a block size of 64 bits. The original standard, published in 1989, did not give the cipher any name, but the most recent revision of the standard, GOST R 34.12-2015, specifies that it may be referred to as Magma. The GOST hash function is based on this cipher. The new standard also specifies a new 128-bit block cipher called Kuznyechik.
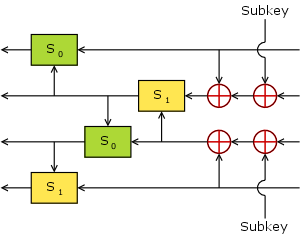
In cryptography, FEAL is a block cipher proposed as an alternative to the Data Encryption Standard (DES), and designed to be much faster in software. The Feistel based algorithm was first published in 1987 by Akihiro Shimizu and Shoji Miyaguchi from NTT. The cipher is susceptible to various forms of cryptanalysis, and has acted as a catalyst in the discovery of differential and linear cryptanalysis.

In cryptography, DES-X is a variant on the DES symmetric-key block cipher intended to increase the complexity of a brute-force attack using a technique called key whitening.
In cryptography, Khufu and Khafre are two block ciphers designed by Ralph Merkle in 1989 while working at Xerox's Palo Alto Research Center. Along with Snefru, a cryptographic hash function, the ciphers were named after the Egyptian Pharaohs Khufu, Khafre and Sneferu.
In cryptography, LOKI89 and LOKI91 are symmetric-key block ciphers designed as possible replacements for the Data Encryption Standard (DES). The ciphers were developed based on a body of work analysing DES, and are very similar to DES in structure. The LOKI algorithms were named for Loki, the god of mischief in Norse mythology.
In cryptography, Madryga is a block cipher published in 1984 by W. E. Madryga. It was designed to be easy and efficient for implementation in software. Serious weaknesses have since been found in the algorithm, but it was one of the first encryption algorithms to make use of data-dependent rotations, later used in other ciphers, such as RC5 and RC6.
In cryptography, REDOC II and REDOC III are block ciphers designed by Michael Wood (cryptographer) for Cryptech Inc and are optimised for use in software. Both REDOC ciphers are patented.
The slide attack is a form of cryptanalysis designed to deal with the prevailing idea that even weak ciphers can become very strong by increasing the number of rounds, which can ward off a differential attack. The slide attack works in such a way as to make the number of rounds in a cipher irrelevant. Rather than looking at the data-randomizing aspects of the block cipher, the slide attack works by analyzing the key schedule and exploiting weaknesses in it to break the cipher. The most common one is the keys repeating in a cyclic manner.

In cryptography, the boomerang attack is a method for the cryptanalysis of block ciphers based on differential cryptanalysis. The attack was published in 1999 by David Wagner, who used it to break the COCONUT98 cipher.
Introduced by Martin Hellman and Susan K. Langford in 1994, the differential-linear attack is a mix of both linear cryptanalysis and differential cryptanalysis.
In cryptography, impossible differential cryptanalysis is a form of differential cryptanalysis for block ciphers. While ordinary differential cryptanalysis tracks differences that propagate through the cipher with greater than expected probability, impossible differential cryptanalysis exploits differences that are impossible at some intermediate state of the cipher algorithm.
In cryptography, Ladder-DES is a block cipher designed in 1994 by Terry Ritter. It is a 4-round Feistel cipher with a block size of 128 bits, using DES as the round function. It has no actual key schedule, so the total key size is 4×56=224 bits.
In cryptography, COCONUT98 is a block cipher designed by Serge Vaudenay in 1998. It was one of the first concrete applications of Vaudenay's decorrelation theory, designed to be provably secure against differential cryptanalysis, linear cryptanalysis, and even certain types of undiscovered cryptanalytic attacks.
In cryptography, M8 is a block cipher designed by Hitachi in 1999. The algorithm negotiates introduced in 1997 M6, with the modified key length, which is enlarged to 64 bits or more. This cipher operates with Feistel network and designed to reach high performance on small implementation or 32 bits devices. For instance, by using round numbers = 10 it present encryption speed at 32 Mbps for dedicated hardware of 6K gates and 25 MHz clock or 208 Mbps for program, that uses C-language and Pentium-I 266 MHz. Due to the openness of description, it should not be used in open or multivendor software.
References
- Donald Davies, Sean Murphy (20 September 1993). "Pairs and Triplets of DES S-boxes" (PDF). Journal of Cryptology . 8 (1): 1–25. ISSN 0933-2790 . Retrieved 28 September 2018.
- Eli Biham, Alex Biryukov (May 1994). An Improvement of Davies' Attack on DES (gzipped PostScript). Advances in Cryptology — Eurocrypt '94. Perugia: Springer-Verlag. pp. 461–467. Retrieved 24 January 2007.
- Thomas Pornin (October 1998). Optimal Resistance Against the Davies and Murphy Attack (PDF). Advances in Cryptology — ASIACRYPT '98. Beijing: Springer-Verlag. pp. 148–159. Retrieved 28 September 2018.
| | This cryptography-related article is a stub. You can help Wikipedia by expanding it. |