
Espionage, spying, or intelligence gathering is the act of obtaining secret or confidential information (intelligence). A person who commits espionage is called an espionage agent or spy. Any individual or spy ring, in the service of a government, company, criminal organization, or independent operation, can commit espionage. The practice is clandestine, as it is by definition unwelcome. In some circumstances, it may be a legal tool of law enforcement and in others, it may be illegal and punishable by law.
A numbers station is a shortwave radio station characterized by broadcasts of formatted numbers, which are believed to be addressed to intelligence officers operating in foreign countries. Most identified stations use speech synthesis to vocalize numbers, although digital modes such as phase-shift keying and frequency-shift keying, as well as Morse code transmissions, are not uncommon. Most stations have set time schedules, or schedule patterns; however, some appear to have no discernible pattern and broadcast at random times. Stations may have set frequencies in the high-frequency band.

Robert Philip Hanssen was an American Federal Bureau of Investigation (FBI) agent who spied for Soviet and Russian intelligence services against the United States from 1979 to 2001. His espionage was described by the Department of Justice as "possibly the worst intelligence disaster in U.S. history".

The Main Directorate of the General Staff of the Armed Forces of the Russian Federation, formerly the Main Intelligence Directorate, and still commonly known by its previous abbreviation GRU, is the foreign military intelligence agency of the General Staff of the Armed Forces of the Russian Federation. The GRU controls the military intelligence service and maintains its own special forces units.

The Directorate-General for External Security is France's foreign intelligence agency, equivalent to the British MI6 and the American CIA, established on 2 April 1982. The DGSE safeguards French national security through intelligence gathering and conducting paramilitary and counterintelligence operations abroad, as well as economic espionage. It is headquartered in the 20th arrondissement of Paris.
A sleeper agent is a spy or operative who is placed in a target country or organization, not to undertake an immediate mission, but instead to act as a potential asset on short notice if activated. Even if not activated, the "sleeper agent" is still an asset and can still play an active role in sedition, espionage, or possibly treason by virtue of agreeing to act if activated. A team of sleeper agents may be referred to as a sleeper cell. A sleeper cell or agent may possibly be working with others in a clandestine cell system.

Oleg Vladimirovich Penkovsky, codenamed Hero and Yoga was a Soviet military intelligence (GRU) colonel during the late 1950s and early 1960s. Penkovsky informed the United States and the United Kingdom about Soviet military secrets, including the appearance and footprint of Soviet intermediate-range ballistic missile installations and the weakness of the Soviet intercontinental ballistic missile program. This information was decisive in allowing the US to recognize that the Soviets were placing missiles in Cuba before most of them were operational. It also gave US President John F. Kennedy, during the Cuban Missile Crisis that followed, valuable information about Soviet weakness that allowed him to face down Soviet leader Nikita Khrushchev and resolve the crisis without a nuclear war.

The International Spy Museum is an independent non-profit history museum which documents the tradecraft, history, and contemporary role of espionage. It holds the largest collection of international espionage artifacts on public display. The museum opened in 2002 in the Penn Quarter neighborhood of Washington, D.C., and relocated to L'Enfant Plaza in 2019.

The Falcon and the Snowman is a 1985 American spy drama film directed by John Schlesinger. The screenplay by Steven Zaillian is based on the 1979 book The Falcon and the Snowman: A True Story of Friendship and Espionage by Robert Lindsey, and tells the true story of two young American men, Christopher Boyce and Andrew Daulton Lee, who sold US security secrets to the Soviet Union.
The Office of Technical Service is a component of the U.S. Central Intelligence Agency, responsible for supporting CIA's clandestine operations with gadgets, disguises, forgeries, secret writings, and weapons. The OTS traces its history to October 1942, when OSS director William J. Donovan created the OSS Research and Development Branch, a technical group tasked with creating "dirty tricks and deadly weapons" to combat the US's World War II enemies. Donovan named Cornell University-trained chemist and executive Stanley Platt Lovell as the branch's first head, a man whom the CIA remembers as the "founding father" of the OTS. In the 1950s and early 1960s it also researched, investigated, and experimented with the use of drugs, chemicals, hypnosis, and isolation to extract information during interrogation, as well as to make it easier for American captives to resist interrogation. OTS is part of CIA's Directorate of Science and Technology.

Tradecraft, within the intelligence community, refers to the techniques, methods, and technologies used in modern espionage (spying) and generally as part of the activity of intelligence assessment. This includes general topics or techniques, or the specific techniques of a nation or organization.

William Weisband, Sr. was a Ukrainian-American cryptanalyst and NKVD agent, best known for his role in revealing U.S. decryptions of Soviet diplomatic and intelligence codes to Soviet intelligence.
H. Keith Melton is a graduate of the U.S. Naval Academy, an intelligence historian, and a specialist in clandestine technology and espionage tradecraft. Melton is the author of many spy books. He also is a founding member of the Board of Directors for the International Spy Museum in Washington, D.C.
Geoffrey Arthur Prime is a former British spy who worked for the Royal Air Force as well as the Government Communications Headquarters (GCHQ). While working for these organizations, Prime disclosed information to the Soviet Union. He was convicted in the early 1980s under charges of espionage and child sexual abuse. He was sentenced to a total of 38 years imprisonment, but was released from prison in 2001.
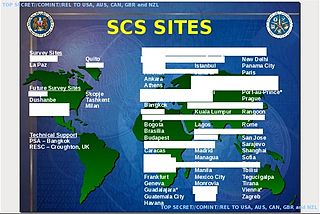
The Special Collection Service (SCS), codenamed F6, is a highly classified joint U.S. Central Intelligence Agency–National Security Agency program charged with inserting eavesdropping equipment in difficult-to-reach places, such as foreign embassies, communications centers, and foreign government installations. Established in the late 1970s and headquartered in Beltsville, Maryland, the SCS has been involved in operations ranging from the Cold War to the Global War on Terrorism.
The Clandestine HUMINT page adheres to the functions within the discipline, including espionage and active counterintelligence.

John Chris Kiriakou is an American author, journalist and former intelligence officer. Kiriakou is a columnist with Reader Supported News and co-host of Political Misfits on Sputnik Radio.

The Directorate of Science & Technology (DS&T) is the branch of the United States Central Intelligence Agency (CIA) tasked with collecting and analyzing information through technological means and developing technical systems in order to advance the CIA’s intelligence gathering.
Cyber spying, cyber espionage, or cyber-collection is the act or practice of obtaining secrets and information without the permission and knowledge of the holder of the information using methods on the Internet, networks or individual computers through the use of proxy servers, cracking techniques and malicious software including Trojan horses and spyware. Cyber espionage can be used to target various actors- individuals, competitors, rivals, groups, governments, and others- in order to obtain personal, economic, political or military advantages. It may wholly be perpetrated online from computer desks of professionals on bases in far away countries or may involve infiltration at home by computer trained conventional spies and moles or in other cases may be the criminal handiwork of amateur malicious hackers and software programmers.
Short range agent communications (SRAC) are one-way or two-way short-range wireless communications used for intelligence purposes. This communications technology became possible with the arrival of the transistor and small scale integrated circuits. In the late 2000s computer WiFi technology and USB Flash Drives had evolved into technologies that ordinary people can buy – yet can be used in a similar way to SRAC systems.













