
Advanced Micro Devices, Inc. is an American multinational semiconductor company based in Santa Clara, California, that develops computer processors and related technologies for business and consumer markets.

ATI Technologies Inc. was a Canadian semiconductor technology corporation based in Markham, Ontario, that specialized in the development of graphics processing units and chipsets. Founded in 1985 as Array Technology Inc., the company listed publicly in 1993 and was acquired by AMD in 2006. As a major fabrication-less or fabless semiconductor company, ATI conducted research and development in-house and outsourced the manufacturing and assembly of its products. With the decline and eventual bankruptcy of 3dfx in 2000, ATI and its chief rival Nvidia emerged as the two dominant players in the graphics processors industry, eventually forcing other manufacturers into niche roles.

CES is an annual trade show organized by the Consumer Technology Association (CTA). Held in January at the Las Vegas Convention Center in Winchester, Nevada, United States, the event typically hosts presentations of new products and technologies in the consumer electronics industry.

High-Definition Multimedia Interface (HDMI) is a proprietary audio/video interface for transmitting uncompressed video data and compressed or uncompressed digital audio data from an HDMI-compliant source device, such as a display controller, to a compatible computer monitor, video projector, digital television, or digital audio device. HDMI is a digital replacement for analog video standards.

Analog Devices, Inc. (ADI), also known simply as Analog, is an American multinational semiconductor company specializing in data conversion, signal processing and power management technology, headquartered in Wilmington, Massachusetts.

Havok is a middleware software suite developed by the Irish company Havok. Havok provides a physics engine component and related functions to video games.
A home theater PC (HTPC) or media center computer is a convergent device that combines some or all the capabilities of a personal computer with a software application that focuses on video, photo, audio playback, and sometimes video recording functionality. Since the mid-2000s, other types of consumer electronics, including game consoles and dedicated media devices, have crossed over to manage video and music content. The term "media center" also refers to specialized application software designed to run on standard personal computers.
Wind River Systems, also known as Wind River, is an Alameda, California–based company, subsidiary of Aptiv PLC. The company develops embedded system and cloud software consisting of real-time operating systems software, industry-specific software, simulation technology, development tools and middleware.
Digital Living Network Alliance was founded by a group of PC and consumer electronics companies in June 2003 to develop and promote a set of interoperability guidelines for sharing digital media among multimedia devices under the auspices of a certification standard. DLNA certified devices include smartphones, tablets, PCs, TV sets and storage servers.

CableCARD is a special-use PC Card device that allows consumers in the United States to view and record digital cable television channels on digital video recorders, personal computers and television sets on equipment such as a set-top box not provided by a cable television company. The card is usually provided by the local cable operator, typically for a nominal monthly fee.
The Technology and Engineering Emmy Awards, or Technology and Engineering Emmys, are one of two sets of Emmy Awards that are presented for outstanding achievement in engineering development in the television industry. The Technology and Engineering Emmy Awards are presented by the National Academy of Television Arts and Sciences (NATAS), while the separate Primetime Engineering Emmy Awards are given by its sister organization the Academy of Television Arts & Sciences (ATAS).
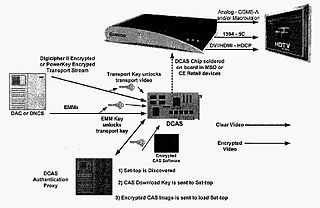
Downloadable Conditional Access System or DCAS was a proposal advanced by CableLabs for secure software download of a specific Conditional Access client which controls digital rights management (DRM) into an OCAP-compliant host consumer media device. The National Cable & Telecommunications Association (NCTA) proposed that DCAS be used as a substitute for physical CableCARDs, a standard also created by CableLabs for which products began appearing in August 2004 as part of industry compliance to the FCC mandate, which in turn is pursuant to the Telecommunications Act of 1996. DCAS is growing in popularity as a less expensive alternative for CableCARD, with major North American operator deployments from Cablevision and Charter. DCAS deployments can be expected to grow in the coming years, thanks to favorable regulatory view from the STELA Reauthorization Act of 2014 and FCC appointing a Downloadable Security Technical Advisory Committee, and wider support for key ladder (K-LAD) functionality from system-on-chip (SoC) vendors and set-top box manufacturers.

A flexible display or rollable display is an electronic visual display which is flexible in nature, as opposed to the traditional flat screen displays used in most electronic devices. In recent years there has been a growing interest from numerous consumer electronics manufacturers to apply this display technology in e-readers, mobile phones and other consumer electronics. Such screens can be rolled up like a scroll without the image or text being distorted. Technologies involved in building a rollable display include electronic ink, Gyricon, Organic LCD, and OLED.

Alcatel–Lucent S.A. was a multinational telecommunications equipment company, headquartered in Boulogne-Billancourt, France. It was formed in 2006 by the merger of France-based Alcatel and U.S.-based Lucent, the latter being a successor of AT&T's Western Electric and Bell Labs.
Tru2way is a brand name for interactive digital cable services delivered over the cable network. Services include interactive program guides, interactive ads, games, chat, web browsing, and t-commerce. The brand also appears as <tru2way> and is used to market cable services, applications, and devices that support the tru2way cable architecture. Tru2way is the successor name for technology known as OpenCable. Major cable operators committed to deploy the tru2way platform in service areas covering more than 90 million U.S. homes by the end of 2008.
G.hn is a specification for home networking with data rates up to 2 Gbit/s and operation over four types of legacy wires: telephone wiring, coaxial cables, power lines and plastic optical fiber. A single G.hn semiconductor device is able to network over any of the supported home wire types. Some benefits of a multi-wire standard are lower equipment development costs and lower deployment costs for service providers.
The Digital Entertainment Content Ecosystem was a consortium of major film studios, consumer electronics manufacturers and retailers, networking hardware vendors, systems integrators, and Digital Rights Management (DRM) vendors listed below. The consortium was announced in September 2008 by its president, Mitch Singer, who was also the chief technology officer (CTO) of Sony Pictures Entertainment at the time. DECE was chartered to develop a set of standards for the digital distribution of premium Hollywood content. The consortium created a set of rules and a back-end system for the management of those rules that enabled consumers to share purchased digital content among a domain of registered consumer electronics devices.
Thunderbolt is the brand name of a hardware interface for the connection of external peripherals to a computer. It has been developed by Intel, in collaboration with Apple. It was initially marketed under the name Light Peak, and first sold as part of an end-user product on 24 February 2011.
AllVid was a proposal to develop technology enabling smart broadband-connected video devices to access the content on the managed networks of cable operators, telcos, and satellite-TV operators. It was initially proposed in the U.S. Federal Communications Commission's (FCC) National Broadband Plan in 2010. The AllVid hardware would act as a universal adapter for all types of pay TV content such as video-on-demand and pay-per-view, as well as interactive programming guides, delivered through a wide variety of means, including cable TV, satellite TV, VDSL, IPTV, and Internet TV.











