Related Research Articles
In information science, an ontology encompasses a representation, formal naming, and definitions of the categories, properties, and relations between the concepts, data, or entities that pertain to one, many, or all domains of discourse. More simply, an ontology is a way of showing the properties of a subject area and how they are related, by defining a set of terms and relational expressions that represent the entities in that subject area. The field which studies ontologies so conceived is sometimes referred to as applied ontology.
The Gene Ontology (GO) is a major bioinformatics initiative to unify the representation of gene and gene product attributes across all species. More specifically, the project aims to: 1) maintain and develop its controlled vocabulary of gene and gene product attributes; 2) annotate genes and gene products, and assimilate and disseminate annotation data; and 3) provide tools for easy access to all aspects of the data provided by the project, and to enable functional interpretation of experimental data using the GO, for example via enrichment analysis. GO is part of a larger classification effort, the Open Biomedical Ontologies, being one of the Initial Candidate Members of the OBO Foundry.
BRENDA is an information system representing one of the most comprehensive enzyme repositories. It is an electronic resource that comprises molecular and biochemical information on enzymes that have been classified by the IUBMB. Every classified enzyme is characterized with respect to its catalyzed biochemical reaction. Kinetic properties of the corresponding reactants are described in detail. BRENDA contains enzyme-specific data manually extracted from primary scientific literature and additional data derived from automatic information retrieval methods such as text mining. It provides a web-based user interface that allows a convenient and sophisticated access to the data.
The Protein Information Resource (PIR), located at Georgetown University Medical Center, is an integrated public bioinformatics resource to support genomic and proteomic research, and scientific studies. It contains protein sequences databases
The Unified Medical Language System (UMLS) is a compendium of many controlled vocabularies in the biomedical sciences. It provides a mapping structure among these vocabularies and thus allows one to translate among the various terminology systems; it may also be viewed as a comprehensive thesaurus and ontology of biomedical concepts. UMLS further provides facilities for natural language processing. It is intended to be used mainly by developers of systems in medical informatics.
Chemical Entities of Biological Interest, also known as ChEBI, is a chemical database and ontology of molecular entities focused on 'small' chemical compounds, that is part of the Open Biomedical Ontologies (OBO) effort at the European Bioinformatics Institute (EBI). The term "molecular entity" refers to any "constitutionally or isotopically distinct atom, molecule, ion, ion pair, radical, radical ion, complex, conformer, etc., identifiable as a separately distinguishable entity". The molecular entities in question are either products of nature or synthetic products which have potential bioactivity. Molecules directly encoded by the genome, such as nucleic acids, proteins and peptides derived from proteins by proteolytic cleavage, are not as a rule included in ChEBI.
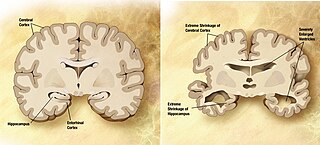
A neurodegenerative disease is caused by the progressive loss of structure or function of neurons, in the process known as neurodegeneration. Such neuronal damage may ultimately involve cell death. Neurodegenerative diseases include amyotrophic lateral sclerosis, multiple sclerosis, Parkinson's disease, Alzheimer's disease, Huntington's disease, multiple system atrophy, tauopathies, and prion diseases. Neurodegeneration can be found in the brain at many different levels of neuronal circuitry, ranging from molecular to systemic. Because there is no known way to reverse the progressive degeneration of neurons, these diseases are considered to be incurable; however research has shown that the two major contributing factors to neurodegeneration are oxidative stress and inflammation. Biomedical research has revealed many similarities between these diseases at the subcellular level, including atypical protein assemblies and induced cell death. These similarities suggest that therapeutic advances against one neurodegenerative disease might ameliorate other diseases as well.
The Open Biological and Biomedical Ontologies (OBO) Foundry is a group of people dedicated to build and maintain ontologies related to the life sciences. The OBO Foundry establishes a set of principles for ontology development for creating a suite of interoperable reference ontologies in the biomedical domain. Currently, there are more than a hundred ontologies that follow the OBO Foundry principles.
Gideon Dreyfuss is an American biochemist, the Isaac Norris Professor of Biochemistry and Biophysics at the University of Pennsylvania School of Medicine, and an investigator of the Howard Hughes Medical Institute. He was elected to the National Academy of Sciences in 2012.
Europe PubMed Central is an open-access repository that contains millions of biomedical research works. It was known as UK PubMed Central until 1 November 2012.
Plant ontology (PO) is a collection of ontologies developed by the Plant Ontology Consortium. These ontologies describe anatomical structures and growth and developmental stages across Viridiplantae. The PO is intended for multiple applications, including genetics, genomics, phenomics, and development, taxonomy and systematics, semantic applications and education.
The Gene Wiki is a project within Wikipedia that aims to describe the relationships and functions of all human genes. It was established to transfer information from scientific resources to Wikipedia stub articles.

Therapeutic Target Database (TTD) is a pharmaceutical and medical repository constructed by the Innovative Drug Research and Bioinformatics Group (IDRB) at Zhejiang University, China and the Bioinformatics and Drug Design Group at the National University of Singapore. It provides information about known and explored therapeutic protein and nucleic acid targets, the targeted disease, pathway information and the corresponding drugs directed at each of these targets. Detailed knowledge about target function, sequence, 3D structure, ligand binding properties, enzyme nomenclature and drug structure, therapeutic class, and clinical development status. TTD is freely accessible without any login requirement at https://idrblab.org/ttd/.
The Human Phenotype Ontology (HPO) is a formal ontology of human phenotypes. Developed as part of the Monarch Initiative in collaboration with members of the Open Biomedical Ontologies Foundry, HPO currently contains over 13,000 terms and over 156,000 annotations to hereditary diseases. Data from Online Mendelian Inheritance in Man and medical literature were used to generate the terms currently in the HPO. The ontology contains over 50,000 annotations between phenotypes and hereditary disease.
The Monarch Initiative is a large scale bioinformatics web resource focused on leveraging existing biomedical knowledge to connect genotypes with phenotypes in an effort to aid research that combats genetic diseases. Monarch does this by integrating multi-species genotype, phenotype, genetic variant and disease knowledge from various existing biomedical data resources into a centralized and structured database. While this integration process has been traditionally done manually by basic researchers and clinicians on a case-by-case basis, The Monarch Initiative provides an aggregated and structured collection of data and tools that make biomedical knowledge exploration more efficient and effective.
PathoPhenoDB is a biological database. The database connects pathogens to their phenotypes using multiple databases such as NCBI, Human Disease Ontology Human Phenotype Ontology, Mammalian Phenotype Ontology, PubChem, SIDER and CARD. Pathogen-disease associations were gathered mainly through the CDC and the List of Infectious Diseases page on Wikipedia. The manner by which they assigned taxonomy was semi-automatic. When mapped against NCBI Taxonomy, if the pathogen was not an exact match, it was then mapped to the parent class. PathoPhenoDB employs NPMI in order to filter pairs based on their co-occurrence statistics.
Biocuration is the field of life sciences dedicated to organizing biomedical data, information and knowledge into structured formats, such as spreadsheets, tables and knowledge graphs. The biocuration of biomedical knowledge is made possible by the cooperative work of biocurators, software developers and bioinformaticians and is at the base of the work of biological databases.

Erika L F. Holzbaur is an American biologist who is the William Maul Measey Professor of Physiology at University of Pennsylvania Perelman School of Medicine. Her research considers the dynamics of organelle motility along cytoskeleton of cells. She is particularly interested in the molecular mechanisms that underpin neurodegenerative diseases.

Susanna-Assunta Sansone is a British-Italian data scientist who is professor of data readiness at the University of Oxford where she leads the data readiness group and serves as associate director of the Oxford e-Research Centre. Her research investigates techniques for improving the interoperability, reproducibility and integrity of data.
References
- ↑ Schriml, Lynn Marie; Arze, Cesar; Nadendla, Suvama; Chang, Yu-Wei Wayne; Mazaitis, Mark; Felix, Victor; Feng, Gang; Kibbe, Warren Alden (Jan 2012). "Disease Ontology: a backbone for disease semantic integration". Nucleic Acids Research . 40 (Database issue): D940–D946. doi:10.1093/nar/gkr972. PMC 3245088 . PMID 22080554.
- ↑ Osborne, John D; Flatow, Jared; Holko, Michelle; Lin, Simon M; Kibbe, Warren A; Zhu, Lihua (Julie); Danila, Maria I; Feng, Gang; Chisholm, Rex L (Jul 7, 2009). "Annotating the human genome with Disease Ontology". BMC Genomics . 10 (Suppl 1): S6. doi: 10.1186/1471-2164-10-s1-s6 . PMC 2709267 . PMID 19594883.
- ↑ Kibbe, Warren A.; Arze, Cesar; Felix, Victor; Mitraka, Elvira; Bolton, Evan; Fu, Gang; Mungall, Christopher J.; Binder, Janos X.; Malone, James; Vasant, Drashtti; Parkinson, Helen; Schriml, Lynn M. (Jan 2015). "Disease Ontology 2015 update: an expanded and updated database of human diseases for linking biomedical knowledge through disease data". Nucleic Acids Research . 43 (Database issue): D1071–D1078. doi:10.1093/nar/gku1011. PMC 4383880 . PMID 25348409.