Related Research Articles
A verb is a word that in syntax generally conveys an action, an occurrence, or a state of being. In the usual description of English, the basic form, with or without the particle to, is the infinitive. In many languages, verbs are inflected to encode tense, aspect, mood, and voice. A verb may also agree with the person, gender or number of some of its arguments, such as its subject, or object. Verbs have tenses: present, to indicate that an action is being carried out; past, to indicate that an action has been done; future, to indicate that an action will be done.
In language, a clause is a constituent that comprises a semantic predicand and a semantic predicate. A typical clause consists of a subject and a syntactic predicate, the latter typically a verb phrase composed of a verb with any objects and other modifiers. However, the subject is sometimes unvoiced if it is retrievable from context, especially in null-subject language but also in other languages, including English instances of the imperative mood.

The grammar of Standard Chinese or Mandarin shares many features with other varieties of Chinese. The language almost entirely lacks inflection; words typically have only one grammatical form. Categories such as number and verb tense are frequently not expressed by any grammatical means, but there are several particles that serve to express verbal aspect and, to some extent, mood.
Denaʼina, also Tanaina, is the Athabaskan language of the region surrounding Cook Inlet. It is geographically unique in Alaska as the only Alaska Athabaskan language to include territory which borders salt water. Four dialects are usually distinguished:
- Upper Inlet, spoken in Eklutna, Knik, Susitna, Tyonek
- Outer Inlet, spoken in Kenai, Kustatan, Seldovia
- Iliamna, spoken in Pedro Bay, Old Iliamna, Lake Iliamna area
- Inland, spoken in Nondalton, Lime Village

Zarma is one of the Songhay languages. It is the leading indigenous language of the southwestern lobe of the West African nation of Niger, where the Niger River flows and the capital city, Niamey, is located. Zarma is the second-most common language in the country, after Hausa, which is spoken in south-central Niger. With over 2 million speakers, Zarma is easily the most widely spoken Songhay language.
The perfect tense or aspect is a verb form that indicates that an action or circumstance occurred earlier than the time under consideration, often focusing attention on the resulting state rather than on the occurrence itself. An example of a perfect construction is I have made dinner. Although this gives information about a prior action, the focus is likely to be on the present consequences of that action. The word perfect in this sense means "completed".
The continuous and progressive aspects are grammatical aspects that express incomplete action or state in progress at a specific time: they are non-habitual, imperfective aspects.

Tzeltal or Tseltal is a Mayan language spoken in the Mexican state of Chiapas, mostly in the municipalities of Ocosingo, Altamirano, Huixtán, Tenejapa, Yajalón, Chanal, Sitalá, Amatenango del Valle, Socoltenango, Las Rosas, Chilón, San Juan Cancuc, San Cristóbal de las Casas and Oxchuc. Tzeltal is one of many Mayan languages spoken near this eastern region of Chiapas, including Tzotzil, Chʼol, and Tojolabʼal, among others. There is also a small Tzeltal diaspora in other parts of Mexico and the United States, primarily as a result of unfavorable economic conditions in Chiapas.
The Kaska language originated from the family of Athabaskan languages. Traditionally Kaska is an oral aboriginal language that is used by the Kaska Dena people. The Kaska Dene region consists of a small area in the Southwestern part of the Northwest Territories, the Southeastern part of Yukon Territory, and the Northern part of British Columbia. The communities that are in the Kaska Dene region are Fort Ware in N.W.T.; Ross River and Watson Lake in Y.T.; Dease Lake, Good Hope Lake, Lower Post, Fireside, and Muncho Lake in B.C. Kaska is made up of eight dialects, all of which have similar pronunciations and expressional terms. The town of Watson Lake was established around the period of the second World War when the Alaska Highway was first built in 1942. A major consequence of colonization was Kaska language loss. Another major cause of Kaska language loss was due to the residential school. The effect that these schools had on the Kaska language have caused a language gap between two generations resulting in few young speakers.
In linguistics, telicity is the property of a verb or verb phrase that presents an action or event as having a specific endpoint. A verb or verb phrase with this property is said to be telic; if the situation it describes is not heading for any particular endpoint, it is said to be atelic.

Tuscarora, sometimes called Skarò˙rə̨ˀ, was the Iroquoian language of the Tuscarora people, spoken in southern Ontario, Canada, North Carolina and northwestern New York around Niagara Falls, in the United States, before its extinction in late 2020. The historic homeland of the Tuscarora was in eastern North Carolina, in and around the Goldsboro, Kinston, and Smithfield areas.

Maidu, also Northeastern Maidu or Mountain Maidu, is an extinct Maiduan language spoken by Maidu peoples traditionally in the mountains east and south of Lassen Peak in the American River and Feather River basins. These river regions include such valleys in the northern Sierra Nevada mountains of California as: Indian Valley, American Valley, Butte Valley, and Big Meadows. Maidu may also refer to the related Konkow and Nisenan languages.
This article is a description of the morphology, syntax, and semantics of Korean. For phonetics and phonology, see Korean phonology. See also Korean honorifics, which play a large role in the grammar.
Araki is a nearly extinct language spoken in the small island of Araki, south of Espiritu Santo Island in Vanuatu. Araki is gradually being replaced by Tangoa, a language from a neighbouring island.
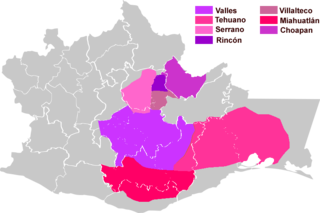
Yatzachi Zapotec is an Oto-Manguean language of the Zapotecan branch, spoken in northern central Oaxaca, Mexico. 2,500 self-reported being Yatzachi speakers for the 1990 Mexican census, but the actual number of speakers is unknown. The Yatzachi dialect belongs to the Villa Alta group of Zapotec dialects, of which the main dialect is San Bartolomé Zoogocho. The degree of mutual intelligibility between Yatzachi and the San Bartolomé Zoogocho dialect is estimated to be around 90 percent.

This article describes the uses of various verb forms in modern standard English language. This includes:
Teiwa is a Papuan language spoken on the Pantar island in eastern Indonesia. The island is the second largest in the Alor archipelago, lying just west of the largest island Alor.
Neverver (Nevwervwer), also known as Lingarak, is an Oceanic language. Neverver is spoken in Malampa Province, in central Malekula, Vanuatu. The names of the villages on Malekula Island where Neverver is spoken are Lingarakh and Limap.
Saliba is an Oceanic language spoken on the islets off the southeastern tip of Papua New Guinea. There are approximately 2,500 speakers of Saliba. Significant documentation of the language was undertaken by the Saliba-Logea documentation project, and hundreds of audio-video resources can be found in the project archive.
Navajo is a "verb-heavy" language – it has a great preponderance of verbs but relatively few nouns. In addition to verbs and nouns, Navajo has other elements such as pronouns, clitics of various functions, demonstratives, numerals, postpositions, adverbs, and conjunctions, among others. Harry Hoijer grouped all of the above into a word-class he called particles. Navajo has no words that would correspond to adjectives in English grammar: verbs provide the adjectival functionality.