
A lens is a transmissive optical device which focuses or disperses a light beam by means of refraction. A simple lens consists of a single piece of transparent material, while a compound lens consists of several simple lenses (elements), usually arranged along a common axis. Lenses are made from materials such as glass or plastic, and are ground and polished or molded to a desired shape. A lens can focus light to form an image, unlike a prism, which refracts light without focusing. Devices that similarly focus or disperse waves and radiation other than visible light are also called lenses, such as microwave lenses, electron lenses, acoustic lenses, or explosive lenses.
Star Trek: Enterprise, titled simply Enterprise for its first two seasons, is an American science fiction television series created by Rick Berman and Brannon Braga. It originally aired from September 26, 2001, to May 13, 2005 on UPN. The sixth series in the Star Trek franchise, it is a prequel to Star Trek: The Original Series. Set in the 22nd century, a hundred years before the events of The Original Series, it follows the adventures of the Enterprise, Earth's first starship capable of traveling at warp five, as it explores the galaxy and encounters various alien species.

A transporter is a fictional teleportation machine used in the Star Trek science fiction franchise. Transporters allow for teleportation by converting a person or object into an energy pattern, then send ("beam") it to a target location or else return it to the transporter, where it is reconverted into matter ("rematerialization"). Since then, the name and similar concepts have made their way to other science fiction scenarios, in literature, games (SimEarth), etc.
A warp drive is a fictional superluminal spacecraft propulsion system in many science fiction works, most notably Star Trek, and a subject of ongoing physics research. A spacecraft equipped with a warp drive may travel at speeds greater than that of light by many orders of magnitude. In contrast to some other fictitious faster-than-light technologies such as a jump drive, the warp drive does not permit instantaneous travel and transfers between two points, but rather involves a measurable passage of time which is pertinent to the concept. In contrast to hyperspace, spacecraft at warp velocity would continue to interact with objects in "normal space". The general concept of "warp drive" was introduced by John W. Campbell in his 1957 novel Islands of Space.
The focal length of an optical system is a measure of how strongly the system converges or diverges light; it is the inverse of the system's optical power. A positive focal length indicates that a system converges light, while a negative focal length indicates that the system diverges light. A system with a shorter focal length bends the rays more sharply, bringing them to a focus in a shorter distance or diverging them more quickly. For the special case of a thin lens in air, a positive focal length is the distance over which initially collimated (parallel) rays are brought to a focus, or alternatively a negative focal length indicates how far in front of the lens a point source must be located to form a collimated beam. For more general optical systems, the focal length has no intuitive meaning; it is simply the inverse of the system's optical power.
In mathematics, the harmonic series is the divergent infinite series
Section 31, in the fictional universe of Star Trek, is an autonomous intelligence and defense organization that carries out covert operations for the United Federation of Planets. Created by Ira Steven Behr for the Star Trek: Deep Space Nine episode "Inquisition", the organization was intended to act as a counterbalance to the utopian portrayal of the Federation.
Convergence may refer to:
The Mirror Universe is a parallel universe in which the plots of several Star Trek television episodes take place. It resembles the fictional universe in which the Star Trek television series takes place, but is separate from the main universe. The Mirror Universe has been visited in one episode of Star Trek: The Original Series, five episodes of Star Trek: Deep Space Nine, a two-part episode of Star Trek: Enterprise and a storyline in Star Trek: Discovery, as well as several non-canon Star Trek tie-in works. It is named after "Mirror, Mirror", the original series episode in which it first appeared.
In physics, an ultraviolet divergence or UV divergence is a situation in which an integral, for example a Feynman diagram, diverges because of contributions of objects with unbounded energy, or, equivalently, because of physical phenomena at infinitesimal distances.
"The Squire of Gothos" is the 17th episode of the first season of the American science-fiction television series, Star Trek. Written by Paul Schneider, and directed by Don McDougall, it first aired on January 12, 1967.
The Star Trek expanded universe is an unofficial, fan-created term to describe an extrapolation of events which occur in the Star Trek Universe outside the scope of the television series and feature films. Information from the Star Trek "Expanded Universe" typically fills "holes" in the Star Trek story and timeline, with explanations of events which have never been adequately explained through live action productions. The term was first used in 1966 by writer D.C. Fontana to describe information put forth in the backstory of Doctor Leonard McCoy.
"Divergence" is the sixteenth episode of the fourth season of the American science fiction television series Star Trek: Enterprise. It originally aired on February 25, 2005 in the United States on UPN. It was the fourth episode of Enterprise to be written by Judith and Garfield Reeves-Stevens, and was the first episode of a Star Trek series directed by David Barrett. "Divergence" is the second part of a two part story, following on from "Affliction".
Autocollimation is an optical setup where a collimated beam leaves an optical system and is reflected back into the same system by a plane mirror.
In statistics, probability theory, and information theory, a statistical distance quantifies the distance between two statistical objects, which can be two random variables, or two probability distributions or samples, or the distance can be between an individual sample point and a population or a wider sample of points.
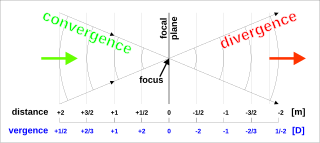
Vergence is the angle formed by rays of light that are not perfectly parallel to one another. Rays that move closer to the optical axis as they propagate are said to be converging, while rays that move away from the axis are diverging. These imaginary rays are always perpendicular to the wavefront of the light, thus the vergence of the light is directly related to the radii of curvature of the wavefronts. A convex lens or concave mirror will cause parallel rays to focus, converging toward a point. Beyond that focal point, the rays diverge. Conversely, a concave lens or convex mirror will cause parallel rays to diverge.
In computer science, a computation is said to diverge if it does not terminate or terminates in an exceptional state. Otherwise it is said to converge. In domains where computations are expected to be infinite, such as process calculi, a computation is said to diverge if it fails to be productive.

