
The afterlife or life after death is a purported existence in which the essential part of an individual's stream of consciousness or identity continues to exist after the death of their physical body. The surviving essential aspect varies between belief systems; it may be some partial element, or the entire soul or spirit, which carries with it one's personal identity.

Hades, in the ancient Greek religion and mythology, is the god of the dead and the king of the underworld, with which his name became synonymous. Hades was the eldest son of Cronus and Rhea, although this also made him the last son to be regurgitated by his father. He and his brothers, Zeus and Poseidon, defeated their father's generation of gods, the Titans, and claimed joint rulership over the cosmos. Hades received the underworld, Zeus the sky, and Poseidon the sea, with the solid earth available to all three concurrently. In artistic depictions, Hades is typically portrayed holding a bident and wearing his helm with Cerberus, the three-headed guard-dog of the underworld, standing at his side.

Jewish eschatology is the area of Jewish theology concerned with events that will happen in the end of days and related concepts. This includes the ingathering of the exiled diaspora, the coming of the Jewish Messiah, the afterlife, and the resurrection of the dead. In Judaism, the end times are usually called the "end of days", a phrase that appears several times in the Tanakh.
In philosophy, metempsychosis is the transmigration of the soul, especially its reincarnation after death. The term is derived from ancient Greek philosophy, and has been recontextualized by modern philosophers such as Arthur Schopenhauer, Kurt Gödel, Mircea Eliade, and Magdalena Villaba; otherwise, the term transmigration is more appropriate. The word plays a prominent role in James Joyce's Ulysses and is also associated with Nietzsche. Another term sometimes used synonymously is palingenesis.
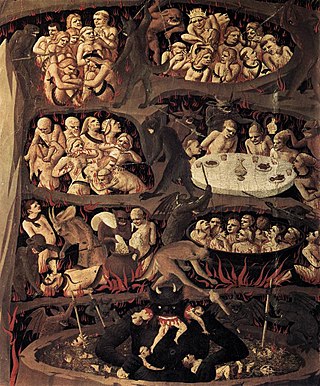
Damnation is the concept of divine punishment and torment in an afterlife for actions that were committed, or in some cases, not committed on Earth.

The Last Judgment, Final Judgment, Day of Reckoning, Day of Judgment, Judgment Day, Doomsday, Day of Resurrection or The Day of the Lord is a concept found across the Abrahamic religions and the Frashokereti of Zoroastrianism.

Christian mortalism is the Christian belief that the human soul is not naturally immortal and may include the belief that the soul is "sleeping" after death until the Resurrection of the Dead and the Last Judgment, a time known as the intermediate state. "Soul sleep" is often used as a pejorative term, so the more neutral term "mortalism" was also used in the nineteenth century, and "Christian mortalism" since the 1970s. Historically the term psychopannychism was also used, despite problems with the etymology and application. The term thnetopsychism has also been used; for example, Gordon Campbell (2008) identified John Milton as believing in the latter.
The problem of Hell is an ethical problem in the Abrahamic religions of Christianity, Islam and Judaism, in which the existence of Hell (Jahannam) for the punishment of souls in the Afterlife is regarded as inconsistent with the notion of a just, moral, and omnipotent, omnibenevolent, omniscient supreme being. Also regarded as inconsistent with such a just being is the combination of human free will, and the divine qualities of omniscience and omnipotence, as this would mean God would determine everything that has happened and will happen in the universe—including sinful human behavior.

Orphism is the name given to a set of religious beliefs and practices originating in the ancient Greek and Hellenistic world, associated with literature ascribed to the mythical poet Orpheus, who descended into the Greek underworld and returned. This type of journey is called a katabasis and is the basis of several hero worships and journeys. Orphics revered Dionysus and Persephone. Orphism has been described as a reform of the earlier Dionysian religion, involving a re-interpretation or re-reading of the myth of Dionysus and a re-ordering of Hesiod's Theogony, based in part on pre-Socratic philosophy.
The concept of an immaterial and immortal soul – distinct from the body – did not appear in Judaism before the Babylonian exile, but developed as a result of interaction with Persian and Hellenistic philosophies. Accordingly, the Hebrew word נֶ֫פֶשׁ, nephesh, although translated as "soul" in some older English-language Bibles, actually has a meaning closer to "living being". Nephesh was translated into Greek in the Septuagint as ψυχή (psūchê), using the Greek word for "soul". The New Testament also uses the word ψυχή, but with the Hebrew meaning and not the Greek.
The Discourse to the Greeks concerning Hades, also called Against Plato on the Cause of the Universe, is a short treatise believed to be the work of Hippolytus of Rome. It was erroneously attributed to the Jewish historian Josephus since at least the 9th century and was first published in a translation of Josephus' works by William Whiston. As Whiston's translation is in the public domain, it appears in many present-day English editions of Josephus' work without any noting of its erroneous attribution.

In religion and folklore, hell is a location or state in the afterlife in which souls are subjected to punitive suffering, most often through torture, as punishment after death. Religions with a linear divine history often depict hells as eternal destinations, the biggest examples of which are Christianity and Islam, whereas religions with reincarnation usually depict a hell as an intermediary period between incarnations, as is the case in the Dharmic religions. Religions typically locate hell in another dimension or under Earth's surface. Other afterlife destinations include heaven, paradise, purgatory, limbo, and the underworld.

Particular judgment, according to Christian eschatology, is the divine judgment that a departed (dead) person undergoes immediately after death, in contradistinction to the general judgment of all people at the end of the world.

Hades, according to various Christian denominations, is "the place or state of departed spirits", borrowing the name of Hades, the Greek god of the underworld. It is often associated with the Jewish concept of Sheol.

In some forms of Christianity the intermediate state or interim state is a person's existence between death and the universal resurrection. In addition, there are beliefs in a particular judgment right after death and a general judgment or last judgment after the resurrection.

The idea of purgatory has roots that date back into antiquity. A sort of proto-purgatory called the "celestial Hades" appears in the writings of Plato and Heraclides Ponticus and in many other pagan writers. This concept is distinguished from the Hades of the underworld described in the works of Homer and Hesiod. In contrast, the celestial Hades was understood as an intermediary place where souls spent an undetermined time after death before either moving on to a higher level of existence or being reincarnated back on earth. Its exact location varied from author to author. Heraclides of Pontus thought it was in the Milky Way; the Academicians, the Stoics, Cicero, Virgil, Plutarch, the Hermetical writings situated it between the Moon and the Earth or around the Moon; while Numenius and the Latin Neoplatonists thought it was located between the sphere of the fixed stars and the Earth.

Purgatory is a passing intermediate state after physical death for purifying or purging a soul. A common analogy is dross being removed from metal in a furnace.

Judgement in an afterlife, in which one's deeds and characteristics in life determine either punishment or reward, is a central theme of many religions. Almost all religions are greatly devoted to the afterlife, emphasizing that what you do in your current life affects what happens to you after death.

In Christianity, heaven is traditionally the location of the throne of God and the angels of God, and in most forms of Christianity it is the abode of the righteous dead in the afterlife. In some Christian denominations it is understood as a temporary stage before the resurrection of the dead and the saints' return to the New Earth.

Christian universalism was a theology prevalent in the early United States coinciding with the founding of the Latter Day Saint movement in 1830. Universalists believed that God would save all of humanity. Universalism peaked in popularity during the 1820s and 1830s, and the idea of universal salvation for all humanity was hotly debated. Several revelations of the founder of the Latter Day Saint movement, Joseph Smith, dealt with issues regarding Universalism, and it was a prominent heresy in the Book of Mormon. Smith's father was a Universalist, while his mother was a traditional Calvinist, creating strain in the Smith family home.


















