
Transport in Argentina is mainly based on a complex network of routes, crossed by relatively inexpensive long-distance buses and by cargo trucks. The country also has a number of national and international airports. The importance of the long-distance train is minor today, though in the past it was widely used and is now regaining momentum after the re-nationalisation of the country's commuter and freight networks. Fluvial transport is mostly used for cargo.

The EMD SW1504 is a 1,500 hp (1,119 kW) diesel-electric switcher locomotive built by General Motors' Electro-Motive Division. The type was sold only to Mexico's national railroad, Ferrocarriles Nacionales de México; 60 examples were built between May and August 1973. With the breakup of NdeM, the locomotives have been passed to the variety of successor railroad operators in Mexico; some have been sold to leasing companies in the USA.

Electro-Motive Diesel is a brand of diesel-electric locomotives, locomotive products and diesel engines for the rail industry. Formerly a division of General Motors, EMD has been owned by Progress Rail since 2010. Electro-Motive Diesel traces its roots to the Electro-Motive Engineering Corporation, founded in 1922 and purchased by General Motors in 1930. After purchase by GM, the company was known as GM's Electro-Motive Division. In 2005, GM sold EMD to Greenbriar Equity Group and Berkshire Partners, and in 2010, EMD was sold to Progress Rail. Upon the 2005 sale, the company was renamed to Electro-Motive Diesel.

Ferrocarriles Argentinos was a state-owned company that managed the entire Argentine railway system for nearly 45 years. It was formed in 1948 when all the private railway companies were nationalised during Juan Perón's first presidential term, and transformed into the Empresa de Ferrocarriles del Estado Argentino.

The EMD G12 is a class of export locomotive built by GM-EMD, and its Canadian affiliate General Motors Diesel. In addition, Australian licensee Clyde Engineering built ten locomotives for New Zealand in 1957, five for Hong Kong, 23 for Queensland, fourteen for Western Australia and seven for BHP. Australian licensee Commonwealth Engineering also built 42 for Queensland Rail in 1964–1966. Many examples were built in the 1950-1960s for railroads around the world.
The Rede Ferroviária Federal, Sociedade Anônima was the State-owned national railway company of Brazil created from Brazilian Federal Law #3.115 on March 16, 1957, after several railroads were nationalized by the Brazilian government. However, the railroad did not take full effect until September 30, 1957. The RFFSA linked 42 railways together, creating a regional system composed of 22 railroads. The goal of the RFFSA was to promote and advance the railroad sector of Brazil, creating a north-south-east-west rail network in all five regions of Brazil. But it failed and the RFFSA only served four of the five regions with a north-south rail network win 19 units of the federation of Brazil. By 1999, freight service of the railroad was liquidated and privatized, with the passenger service of the railroad liquidations occurring in 2007.

The General Manuel Belgrano Railway (FCGMB), named after the Argentine politician and military leader Manuel Belgrano, is a 1,000 mmmetre gauge railway and the longest of the Argentine system. It was one of the six State-owned Argentine railway companies formed after President Juan Perón's nationalisation of the railway network in 1948.

The General San Martín Railway (FCGSM), named after the former Argentine general José de San Martín, was one of the six state-owned Argentine railway companies formed after President Juan Perón's nationalisation of the railway network in 1948. The six companies were managed by Ferrocarriles Argentinos which was later broken up during the process of railway privatisation beginning in 1991 during Carlos Menem's presidency.

The Belgrano Norte line is a commuter rail service in Buenos Aires, Argentina run by the private company Ferrovías since 1 April 1994. This service had previously been run by the state-owned General Belgrano Railway since nationalisation of the railways in 1948. Ferrovías also formed part of the consortium Unidad de Gestión Operativa Ferroviaria de Emergencia (UGOFE) which operated other commuter rail services in Buenos Aires.
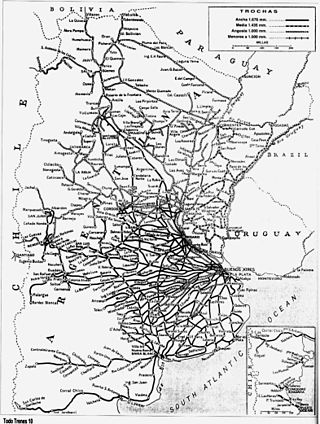
The Argentine railway network consisted of a 47,000 km (29,204 mi) network at the end of the Second World War and was, in its time, one of the most extensive and prosperous in the world. However, with the increase in highway construction, there followed a sharp decline in railway profitability, leading to the break-up in 1993 of Ferrocarriles Argentinos (FA), the state railroad corporation. During the period following privatisation, private and provincial railway companies were created and resurrected some of the major passenger routes that FA once operated.

The EMD GA8 was an export diesel locomotive designed by GM-EMD in the late 1950s as a simplified design for use on overseas railways with light rail and sharp curves. At the time of its introduction it was described as an extremely lightweight road locomotive capable of handling passenger or freight trains and switching. The locomotive is notable for its use of freight car trucks that are driven by cardan shafts and two traction motors attached to the underframe. Measuring 32 feet 6 inches, they are equipped with an 8-567C prime mover capable of producing 875 bhp or 800 hp traction. Late model GA8 locomotives were equipped with an 8-567E prime mover which is a 645 block fitted with 567 power assemblies. Due to the design, most servicing and maintenance could be done without removing the traction motors from the underframe or trucks of the locomotive. The units were built without multiple unit connection capability so electrical components are kept to a minimum.
Stadler Rail Valencia SAU is a Spanish company, mainly producing products for the railway industry, subsidiary of Stadler Rail.

The EMD G22 Locomotive Series made their debut in 1967 after the rise in popularity of the export EMD G12. Designed to meet most First World, Second World and Third World country requirements, the G22 Series was equipped with a naturally aspirated EMD 645 Series engine as well as four axle Flexicoil Type-B trucks which carried a low per-axle weight. Based on customer input, the G22 Series was defined by various designations that suited the customer's railway operations.

The EMD G22C Series were first introduced in 1968 to replace the popular G12 along with various improvements. They carried a low per axle weight on their Flexicoil Type-GC trucks and were the first model series to have a low nose as a standard option as well.

The EMD GT22 Series were first introduced in 1972 after the rise in popularity of six axle locomotives. The GT series now carried a turbocharger that increased the horsepower depending on customer input. The GT series also utilized six axle HTC Trucks, which allowed the locomotive to haul heavier loads at slower speeds with minimal wheelslip.

The South African Railways Class 35-200 of 1974 is a diesel-electric locomotive.

The South African Railways Class 35-600 of 1976 is a branch line diesel-electric locomotive.

Buenos Aires al Pacífico S. A. was an Argentine company that exploited the operation and infrastructure of the 1,676 mm San Martín Railway freight rail transport system.

The CSR EMU is a series of electric multiple unit cars manufactured by CSR Corporation Limited for use on Buenos Aires' commuter rail network. As of 2015, the trains operated on three of the city's lines and 705 cars were manufactured, with each line using a different number of cars per train. They were created for use on lines electrified using both third rail and overhead lines.

The NS locomotive series 2900 is a small series of five diesel-electric locomotives that were used by the Dutch Railways between 1970 and 1974. They were taken over by the NS from the State Mines in 1970. In 1975 they were sold to FEVE in Spain. They were built in 1956–1959 by Henschel & Son in Kassel under license from the Electro-Motive Division (EMD).




















