A photon is an elementary particle that is a quantum of the electromagnetic field, including electromagnetic radiation such as light and radio waves, and the force carrier for the electromagnetic force. Photons are massless, so they always move at the speed of light in vacuum when they are in vacuum. The photon belongs to the class of boson particles.
Spontaneous emission is the process in which a quantum mechanical system transits from an excited energy state to a lower energy state and emits a quantized amount of energy in the form of a photon. Spontaneous emission is ultimately responsible for most of the light we see all around us; it is so ubiquitous that there are many names given to what is essentially the same process. If atoms are excited by some means other than heating, the spontaneous emission is called luminescence. For example, fireflies are luminescent. And there are different forms of luminescence depending on how excited atoms are produced. If the excitation is effected by the absorption of radiation the spontaneous emission is called fluorescence. Sometimes molecules have a metastable level and continue to fluoresce long after the exciting radiation is turned off; this is called phosphorescence. Figurines that glow in the dark are phosphorescent. Lasers start via spontaneous emission, then during continuous operation work by stimulated emission.

Stimulated emission is the process by which an incoming photon of a specific frequency can interact with an excited atomic electron, causing it to drop to a lower energy level. The liberated energy transfers to the electromagnetic field, creating a new photon with a frequency, polarization, and direction of travel that are all identical to the photons of the incident wave. This is in contrast to spontaneous emission, which occurs at a characteristic rate for each of the atoms/oscillators in the upper energy state regardless of the external electromagnetic field.
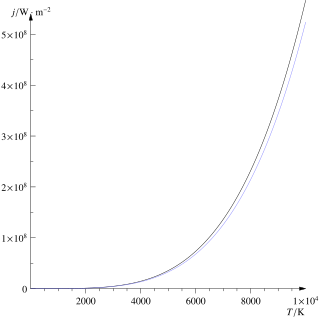
The Stefan–Boltzmann law, also known as Stefan's law, describes the intensity of the thermal radiation emitted by matter in terms of that matter's temperature. It is named for Josef Stefan, who empirically derived the relationship, and Ludwig Boltzmann who derived the law theoretically.

In particle physics, bremsstrahlung is electromagnetic radiation produced by the deceleration of a charged particle when deflected by another charged particle, typically an electron by an atomic nucleus. The moving particle loses kinetic energy, which is converted into radiation, thus satisfying the law of conservation of energy. The term is also used to refer to the process of producing the radiation. Bremsstrahlung has a continuous spectrum, which becomes more intense and whose peak intensity shifts toward higher frequencies as the change of the energy of the decelerated particles increases.
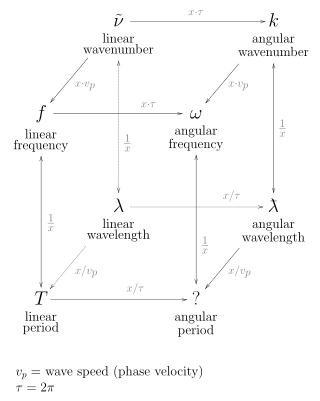
In the physical sciences, the wavenumber, also known as repetency, is the spatial frequency of a wave, measured in cycles per unit distance or radians per unit distance. It is analogous to temporal frequency, which is defined as the number of wave cycles per unit time or radians per unit time.

In physics, Planck's law describes the spectral density of electromagnetic radiation emitted by a black body in thermal equilibrium at a given temperature T, when there is no net flow of matter or energy between the body and its environment.

In thermodynamics and solid-state physics, the Debye model is a method developed by Peter Debye in 1912 to estimate phonon contribution to the specific heat in a solid. It treats the vibrations of the atomic lattice (heat) as phonons in a box in contrast to the Einstein photoelectron model, which treats the solid as many individual, non-interacting quantum harmonic oscillators. The Debye model correctly predicts the low-temperature dependence of the heat capacity of solids, which is proportional to – the Debye T 3 law. Similarly to the Einstein photoelectron model, it recovers the Dulong–Petit law at high temperatures. Due to simplifying assumptions, its accuracy suffers at intermediate temperatures.
In radiometry, radiance is the radiant flux emitted, reflected, transmitted or received by a given surface, per unit solid angle per unit projected area. Radiance is used to characterize diffuse emission and reflection of electromagnetic radiation, and to quantify emission of neutrinos and other particles. The SI unit of radiance is the watt per steradian per square metre. It is a directional quantity: the radiance of a surface depends on the direction from which it is being observed.
The fluctuation–dissipation theorem (FDT) or fluctuation–dissipation relation (FDR) is a powerful tool in statistical physics for predicting the behavior of systems that obey detailed balance. Given that a system obeys detailed balance, the theorem is a proof that thermodynamic fluctuations in a physical variable predict the response quantified by the admittance or impedance of the same physical variable, and vice versa. The fluctuation–dissipation theorem applies both to classical and quantum mechanical systems.

Black-body radiation is the thermal electromagnetic radiation within, or surrounding, a body in thermodynamic equilibrium with its environment, emitted by a black body. It has a specific, continuous spectrum of wavelengths, inversely related to intensity, that depend only on the body's temperature, which is assumed, for the sake of calculations and theory, to be uniform and constant.
Resolved sideband cooling is a laser cooling technique allowing cooling of tightly bound atoms and ions beyond the Doppler cooling limit, potentially to their motional ground state. Aside from the curiosity of having a particle at zero point energy, such preparation of a particle in a definite state with high probability (initialization) is an essential part of state manipulation experiments in quantum optics and quantum computing.
Quantum noise is noise arising from the indeterminate state of matter in accordance with fundamental principles of quantum mechanics, specifically the uncertainty principle and via zero-point energy fluctuations. Quantum noise is due to the apparently discrete nature of the small quantum constituents such as electrons, as well as the discrete nature of quantum effects, such as photocurrents.
Radiative transfer is the physical phenomenon of energy transfer in the form of electromagnetic radiation. The propagation of radiation through a medium is affected by absorption, emission, and scattering processes. The equation of radiative transfer describes these interactions mathematically. Equations of radiative transfer have application in a wide variety of subjects including optics, astrophysics, atmospheric science, and remote sensing. Analytic solutions to the radiative transfer equation (RTE) exist for simple cases but for more realistic media, with complex multiple scattering effects, numerical methods are required. The present article is largely focused on the condition of radiative equilibrium.
The linear attenuation coefficient, attenuation coefficient, or narrow-beam attenuation coefficient characterizes how easily a volume of material can be penetrated by a beam of light, sound, particles, or other energy or matter. A coefficient value that is large represents a beam becoming 'attenuated' as it passes through a given medium, while a small value represents that the medium had little effect on loss. The (derived) SI unit of attenuation coefficient is the reciprocal metre (m−1). Extinction coefficient is another term for this quantity, often used in meteorology and climatology. Most commonly, the quantity measures the exponential decay of intensity, that is, the value of downward e-folding distance of the original intensity as the energy of the intensity passes through a unit thickness of material, so that an attenuation coefficient of 1 m−1 means that after passing through 1 metre, the radiation will be reduced by a factor of e, and for material with a coefficient of 2 m−1, it will be reduced twice by e, or e2. Other measures may use a different factor than e, such as the decadic attenuation coefficient below. The broad-beam attenuation coefficient counts forward-scattered radiation as transmitted rather than attenuated, and is more applicable to radiation shielding. The mass attenuation coefficient is the attenuation coefficient normalized by the density of the material.
The McCumber relation is a relationship between the effective cross-sections of absorption and emission of light in the physics of solid-state lasers. It is named after Dean McCumber, who proposed the relationship in 1964.
Surface-extended X-ray absorption fine structure (SEXAFS) is the surface-sensitive equivalent of the EXAFS technique. This technique involves the illumination of the sample by high-intensity X-ray beams from a synchrotron and monitoring their photoabsorption by detecting in the intensity of Auger electrons as a function of the incident photon energy. Surface sensitivity is achieved by the interpretation of data depending on the intensity of the Auger electrons instead of looking at the relative absorption of the X-rays as in the parent method, EXAFS.
Heat transfer physics describes the kinetics of energy storage, transport, and energy transformation by principal energy carriers: phonons, electrons, fluid particles, and photons. Heat is thermal energy stored in temperature-dependent motion of particles including electrons, atomic nuclei, individual atoms, and molecules. Heat is transferred to and from matter by the principal energy carriers. The state of energy stored within matter, or transported by the carriers, is described by a combination of classical and quantum statistical mechanics. The energy is different made (converted) among various carriers. The heat transfer processes are governed by the rates at which various related physical phenomena occur, such as the rate of particle collisions in classical mechanics. These various states and kinetics determine the heat transfer, i.e., the net rate of energy storage or transport. Governing these process from the atomic level to macroscale are the laws of thermodynamics, including conservation of energy.
The Elliott formula describes analytically, or with few adjustable parameters such as the dephasing constant, the light absorption or emission spectra of solids. It was originally derived by Roger James Elliott to describe linear absorption based on properties of a single electron–hole pair. The analysis can be extended to a many-body investigation with full predictive powers when all parameters are computed microscopically using, e.g., the semiconductor Bloch equations or the semiconductor luminescence equations.
The Planck relation is a fundamental equation in quantum mechanics which states that the energy of a photon, E, known as photon energy, is proportional to its frequency, ν:










































































