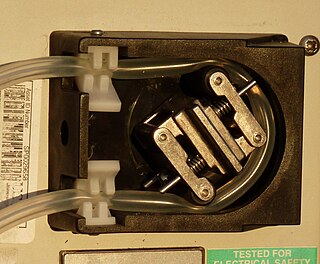
A peristaltic pump, also commonly known as a roller pump, is a type of positive displacement pump used for pumping a variety of fluids. The fluid is contained in a flexible tube fitted inside a circular pump casing. Most peristaltic pumps work through rotary motion, though linear peristaltic pumps have also been made. The rotor has a number of "wipers" or "rollers" attached to its external circumference, which compress the flexible tube as they rotate by. The part of the tube under compression is closed, forcing the fluid to move through the tube. Additionally, as the tube opens to its natural state after the rollers pass, more fluid is drawn into the tube. This process is called peristalsis and is used in many biological systems such as the gastrointestinal tract. Typically, there will be two or more rollers compressing the tube, trapping a body of fluid between them. The body of fluid is transported through the tube, toward the pump outlet. Peristaltic pumps may run continuously, or they may be indexed through partial revolutions to deliver smaller amounts of fluid.

A fire hydrant, fireplug, or firecock (archaic) is a connection point by which firefighters can tap into a water supply. It is a component of active fire protection. Underground fire hydrants have been used in Europe and Asia since at least the 18th century. Above-ground pillar-type hydrants are a 19th-century invention.

A paper machine is an industrial machine which is used in the pulp and paper industry to create paper in large quantities at high speed. Modern paper-making machines are based on the principles of the Fourdrinier Machine, which uses a moving woven mesh to create a continuous paper web by filtering out the fibres held in a paper stock and producing a continuously moving wet mat of fibre. This is dried in the machine to produce a strong paper web.

Storz is a type of hose coupling invented by Carl August Guido Storz in 1882 and patented in Switzerland in 1890, and patented in the U.S. in 1893 that connects using interlocking hooks and flanges. It was first specified in standard FEN 301-316, and has been used by German fire brigades since 1933. Amongst other uses, it has been widely employed on fire hoses in firefighting applications. It is the standard coupling on fire hoses in Portugal, Denmark, Slovenia, Germany, Austria, Switzerland, Sweden, the Netherlands, Poland, Czechia, Israel, Croatia, Serbia, Bosnia & Herzegovina, Macedonia, Montenegro and Greece. It is also one of the standard couplings on fire hoses in Australia and the United States.

A hose is a flexible hollow tube designed to carry fluids from one location to another. Hoses are also sometimes called pipes, or more generally tubing. The shape of a hose is usually cylindrical.

A draft is the use of suction to move a liquid such as water from a vessel or body of water below the intake of a suction pump. A rural fire department or farmer might draft water from a pond as the first step in moving the water elsewhere. A suction pump creates a partial vacuum and the atmospheric pressure on the water's surface forces the water into the pump, usually via a rigid pipe or a semi-rigid hard suction hose.
This is a glossary of firefighting equipment.

A garden hose, hosepipe, or simply hose is a flexible tube used to convey water. There are a number of common attachments available for the end of the hose, such as sprayers and sprinklers. Hoses are usually attached to a hose spigot or tap.

A hose coupling is a connector on the end of a hose to connect it with another hose or with a tap or a hose appliance, such as an irrigation sprinkler. It is usually made of steel, brass, stainless steel, aluminium or plastic.

Pneumatic tires are manufactured according to relatively standardized processes and machinery, in around 455 tire factories in the world. With over 1 billion tires manufactured worldwide annually, the tire industry is a major consumer of natural rubber. Tire factories start with bulk raw materials such as synthetic rubber, carbon black, and chemicals and produce numerous specialized components that are assembled and cured.

A fitting or adapter is used in pipe systems to connect sections of pipe or tube, adapt to different sizes or shapes, and for other purposes such as regulating fluid flow. These fittings are used in plumbing to manipulate the conveyance of fluids such as water for potatory, irrigational, sanitary, and refrigerative purposes, gas, petroleum, liquid waste, or any other liquid or gaseous substances required in domestic or commercial environments, within a system of pipes or tubes, connected by various methods, as dictated by the material of which these are made, the material being conveyed, and the particular environmental context in which they will be used, such as soldering, mortaring, caulking, Plastic welding, welding, friction fittings, threaded fittings, and compression fittings.
Injection molding of liquid silicone rubber (LSR) is a process to produce pliable, durable parts in high volume.
Heat setting is a term used in the textile industry to describe a thermal process usually taking place in either a steam atmosphere or a dry heat environment. The effect of the process gives fibers, yarns or fabric dimensional stability and, very often, other desirable attributes like higher volume, wrinkle resistance or temperature resistance. Very often, heat setting is also used to improve attributes for subsequent processes.
Thermoplastic vulcanizates (TPV) are dynamically vulcanized alloys consisting mostly of fully cured EPDM rubber particles encapsulated in a polypropylene (PP) matrix. They are part of the thermoplastic elastomer (TPE) family of polymers but are closest in elastomeric properties to EPDM thermoset rubber, combining the characteristics of vulcanized rubber with the processing properties of thermoplastics. There are almost 100 grades in the S portfolio that are used globally in the automotive, household appliance, electrical, construction, and healthcare markets. The name Santoprene was trademarked in 1977 by Monsanto, and the trademark is now owned by Celanese. Similar material is available from Elastron and others.

Flexible suction hose, not to be confused with hard suction hose in U.S., is a specific type of fire hose used in drafting operations, when a fire engine uses a vacuum to draw water from a portable water tank, pool, or other static water source. It is built to withstand vacuum, rather than pressure, abrasion, and heat. Conversely, hard suction is capable of withstanding up to 200 PSIG, as well as vacuum. In the United States, it is standard equipment according to the National Fire Protection Association standards for fire engines. It is used in both structural and wildland firefighting throughout the world, and is made in various diameters and connection types.
The Venus for Men, previously sold as the Venus 2000, is a self-actuated masturbation aid for men that applies sexual stimulation using a mechanism outwardly similar to a milking machine. The machine works with or without an erection. Metro has described it as a sex toy "for the serious onanist". In addition to masturbation, the machine may also be used for orgasm control practices such as edging or forced orgasm.
A slurry pump is a type of pump designed for pumping liquid containing solid particles. Slurry pumps changes in design and construction to adjust to multiple type of slurry which varies in concentration of solids, size of solid particles, shape of solid particles, and composition of solution. Slurry pump are more robust than liquid pumps; they have added sacrificial material and replaceable wear parts to withstand wear due to abrasion.

A gasoline pump or fuel dispenser is a machine at a filling station that is used to pump gasoline (petrol), diesel, or other types of liquid fuel into vehicles. Gasoline pumps are also known as bowsers or petrol bowsers, petrol pumps, or gas pumps.
Despite fire hose and hydrant coupler standardization efforts that are at least 144 years old, there remain significant areas in Canada, the United States, and Mexico that use fire hose and hydrant threads and other couplings that are incompatible with those used by neighboring fire departments. This is notable because the first fire hydrant was invented by Manhattan fire fighter George Smith in 1817, making these devices 200 years old.

















