
In male human anatomy, the glans penis, commonly referred to as the glans, is the bulbous structure at the distal end of the human penis that is the human male's most sensitive erogenous zone and their primary anatomical source of sexual pleasure. It is anatomically homologous to the clitoral glans. The glans penis is part of the male reproductive organs in humans and other mammals where it may appear smooth, spiny, elongated or divided. It is externally lined with mucosal tissue, which creates a smooth texture and glossy appearance. In humans, the glans is a continuation of the corpus spongiosum of the penis. At the summit appears the urinary meatus and at the base forms the corona glandis. An elastic band of tissue, known as the frenulum, runs on its ventral surface. In men who are not circumcised, it is completely or partially covered by the foreskin. In adults, the foreskin can generally be retracted over and past the glans manually or sometimes automatically during an erection.

Foreskin restoration is the process of expanding the skin on the penis to reconstruct an organ similar to the foreskin, which has been removed by circumcision or injury. Foreskin restoration is primarily accomplished by stretching the residual skin of the penis, but surgical methods also exist. Restoration creates a facsimile of the foreskin, but specialized tissues removed during circumcision cannot be reclaimed. Actual regeneration of the foreskin is experimental at this time. Some forms of restoration involve only partial regeneration in instances of a high-cut wherein the circumcisee feels that the circumciser removed too much skin and that there is not enough skin for erections to be comfortable.

The terms genital modification and genital mutilation can refer to permanent or temporary changes to human sex organs. Some forms of genital alteration are performed on adults with their informed consent at their own behest, usually for aesthetic reasons or to enhance stimulation. However, other forms are performed on people who do not give informed consent, including infants or children. Any of these procedures may be considered modifications or mutilations in different cultural contexts and by different groups of people.
The Gáe Bulg, meaning "spear of mortal pain/death", "gapped/notched spear", or "belly spear", was the name of the spear of Cúchulainn in the Ulster Cycle of Irish mythology. It was given to him by his martial arts teacher, the warrior woman Scáthach, and its technique was taught only to him.

Phimosis is a condition in which the foreskin of the penis cannot stretch to allow it to be pulled back past the glans. A balloon-like swelling under the foreskin may occur with urination. In teenagers and adults, it may result in pain during an erection, but is otherwise not painful. Those affected are at greater risk of inflammation of the glans, known as balanitis, and other complications.
A frenulum is a small fold of tissue that secures the motion of a mobile organ in the body.

A dydoe is a type of male genital body piercing that passes through the ridge of the glans on the head of the penis. They are often done in pairs. Less often, a "king's crown" is where several dydoes are placed around the head of the penis. The jewelry is usually a 12 gauge, straight barbell with a ball on either end, although a ring may be used at a higher chance of rejection. A deep dydoe is one that uses a longer barbell and exits near the tip of the penis.

Genital piercing is a form of body piercing that involves piercing a part of the genitalia, thus creating a suitable place for wearing different types of jewellery. Nevertheless, the term may also be used pars pro toto to indicate all body piercings in the area of anus, perineum, genitals and mons pubis, including piercings such as anal, guiche, and pubic that do not involve perforation of genitalia. Genital piercings can be done regardless of sex, with various forms of piercings available. The main motive is beautification and individualization; in addition, some piercings enhance sexual pleasure by increasing stimulation. Pre-modern genital piercings is most culturally widespread in Southeast Asia, where it has been part of traditional practice since ancient times. Records of genital piercing are found in the Kama Sutra.

Pearling or genital beading is a form of body modification, the practice of permanently inserting small beads made of various materials beneath the skin of the genitals—of the labia, or of the shaft or foreskin of the penis. As well as being an aesthetic practice, this is usually intended to enhance the sexual pleasure of partners during vaginal or anal intercourse.
Circumcision likely has ancient roots among several ethnic groups in sub-equatorial Africa, Egypt, and Arabia, though the specific form and extent of circumcision has varied. Ritual male circumcision is known to have been practiced by South Sea Islanders, Aboriginal peoples of Australia, Sumatrans, Incas, Aztecs, Mayans and Ancient Egyptians. Today it is still practiced by Jews, Muslims, Coptic Christians, Ethiopian Orthodox, Eritrean Orthodox, Druze, and some tribes in East and Southern Africa, as well as in the United States and Philippines.

Chastity piercings are types of genital piercings that can be used to impose chastity in males and females.
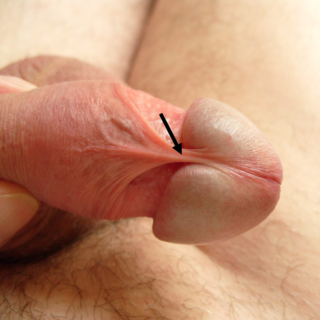
The frenulum of prepuce of penis, often known simply as the frenulum, is a highly erogenous elastic band of tissue under the glans penis that connects the foreskin to the vernal mucosa, and helps contract the foreskin over the glans. Along with the ridged bands at the tip of the foreskin, it is considered to be the most sensitive part of the penis to fine-touch.

Circumcision is a procedure that removes the foreskin from the human penis. In the most common form of the operation, the foreskin is extended with forceps, then a circumcision device may be placed, after which the foreskin is excised. Topical or locally injected anesthesia is generally used to reduce pain and physiologic stress. It is usually elective, performed as preventive healthcare, a religious rite, or cultural practice. It is also an option for cases of phimosis, other pathologies that do not resolve with other treatments, and chronic urinary tract infections (UTIs). The procedure is contraindicated in cases of certain genital structure abnormalities or poor general health.

The human penis is an external male intromittent organ that additionally serves as the urinary duct. The main parts are the root (radix); the body (corpus); and the epithelium of the penis including the shaft skin and the foreskin (prepuce) covering the glans penis. The body of the penis is made up of three columns of tissue: two corpora cavernosa on the dorsal side and corpus spongiosum between them on the ventral side. The human male urethra passes through the prostate gland, where it is joined by the ejaculatory duct, and then through the penis. The urethra traverses the corpus spongiosum, and its opening, the meatus, lies on the tip of the glans penis. It is a passage both for urination and ejaculation of semen

Body piercing, which is a form of body modification, is the practice of puncturing or cutting a part of the human body, creating an opening in which jewelry may be worn, or where an implant could be inserted. The word piercing can refer to the act or practice of body piercing, or to an opening in the body created by this act or practice. It can also, by metonymy, refer to the resulting decoration, or to the decorative jewelry used. Piercing implants alter body and/or skin profile and appearance. Although the history of body piercing is obscured by popular misinformation and by a lack of scholarly reference, ample evidence exists to document that it has been practiced in various forms by multiple sexes since ancient times throughout the world.Body piercing can be performed on people of all ages, although most minors are only permitted to have earlobe piercings.

In male human anatomy, the foreskin, also known as the prepuce, is the double-layered fold of skin, mucosal and muscular tissue at the distal end of the human penis that covers the glans and the urinary meatus. The foreskin is attached to the glans by an elastic band of tissue, known as the frenulum. The outer skin of the foreskin meets with the inner preputial mucosa at the area of the mucocutaneous junction. The foreskin is mobile, fairly stretchable and sustains the glans in a moist environment. Except for humans, a similar structure, known as penile sheath, appears in the male sexual organs of all primates and the vast majority of mammals.

Circumcision surgical procedure in males involves either a conventional "cut and stitch" surgical procedure or use of a circumcision instrument or device. In the newborn period, almost all circumcisions are done by generalist physicians using one of three surgical instruments. In the US, the Gomco clamp is the most utilized instrument, followed by the Mogen clamp and the Plastibell. They are also used worldwide.

A penile fibula is foremost a ring, attached with a pin through the foreskin to fasten it above the glans penis. It was mainly used by ancient Roman culture, though it may have originated earlier. This ring type of fibula has been described akin to a "large modern safety pin". Its usage may have had several reasons, for example to avoid intercourse, to promote modesty or the belief that it helped preserve a man's voice. Some Jews also utilized fibulas to hide that they were circumcised. The word fibula could also be used in general in Rome to denote any type of covering of the penis for the sake of voice preservation or sexual abstinence, it was often used by masters on their slaves for this purpose. Fibulas were frequent subject of ridicule among satirists in Rome.















