
In gamma-ray astronomy, gamma-ray bursts (GRBs) are immensely energetic explosions that have been observed in distant galaxies, being the brightest and most extreme explosive events in the entire universe, as NASA describes the bursts as the "most powerful class of explosions in the universe". They are the most energetic and luminous electromagnetic events since the Big Bang. Gamma-ray bursts can last from ten milliseconds to several hours. After the initial flash of gamma rays, an "afterglow" is emitted, which is longer lived and usually emitted at longer wavelengths.

The Fermi Gamma-ray Space Telescope, formerly called the Gamma-ray Large Area Space Telescope (GLAST), is a space observatory being used to perform gamma-ray astronomy observations from low Earth orbit. Its main instrument is the Large Area Telescope (LAT), with which astronomers mostly intend to perform an all-sky survey studying astrophysical and cosmological phenomena such as active galactic nuclei, pulsars, other high-energy sources and dark matter. Another instrument aboard Fermi, the Gamma-ray Burst Monitor, is being used to study gamma-ray bursts and solar flares.
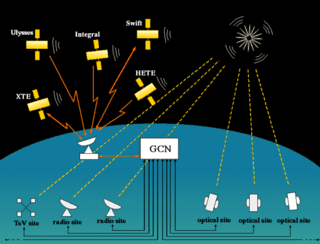
The General Coordinates Network (GCN), formerly known as the Gamma-ray burst Coordinates Network, is an open-source platform created by NASA to receive and transmit alerts about astronomical transient phenomena. This includes neutrino detections by observatories such as IceCube or Super-Kamiokande, gravitational wave events from the LIGO, Virgo and KAGRA interferometers, and gamma-ray bursts observed by Fermi, Swift or INTEGRAL. One of the main goals is to allow for follow-up observations of an event by other observatories, in hope to observe multi-messenger events.

GRB 080319B was a gamma-ray burst (GRB) detected by the Swift satellite at 06:12 UTC on March 19, 2008. The burst set a new record for the farthest object that was observable with the naked eye: it had a peak visual apparent magnitude of 5.7 and remained visible to human eyes for approximately 30 seconds. The magnitude was brighter than 9.0 for approximately 60 seconds. If viewed from 1 AU away, it would have had a peak apparent magnitude of −67.57. It had an absolute magnitude of −38.6, beaten by GRB 220101A with −39.4 in 2023.

GRB 080916C is a gamma-ray burst (GRB) that was recorded on September 16, 2008, in the Carina constellation and detected by NASA's Fermi Gamma-ray Space Telescope. The burst lasted for 23 minutes. It is one of the most extreme gamma-ray bursts ever recorded, and was the most energetic gamma-ray burst ever recorded, until GRB 221009A was recorded in 2022. The explosion had the energy of approximately 9000 type Ia supernovae if the emission was isotropically emitted, and the gas jets emitting the initial gamma rays moved at a minimum velocity of approximately 299,792,158 m/s, making this blast one of the most extreme recorded.

The Gamma-Ray Burst Optical/Near-Infrared Detector (GROND) is an imaging instrument used to investigate Gamma-Ray Burst afterglows and for doing follow-up observations on exoplanets using transit photometry. It is operated at the 2.2-metre MPG/ESO telescope at ESO's La Silla Observatory in the southern part of the Atacama desert, about 600 kilometres north of Santiago de Chile and at an altitude of 2,400 metres.
The history of gamma-ray began with the serendipitous detection of a gamma-ray burst (GRB) on July 2, 1967, by the U.S. Vela satellites. After these satellites detected fifteen other GRBs, Ray Klebesadel of the Los Alamos National Laboratory published the first paper on the subject, Observations of Gamma-Ray Bursts of Cosmic Origin. As more and more research was done on these mysterious events, hundreds of models were developed in an attempt to explain their origins.

GRB 990123 is a gamma-ray burst which was detected on January 23, 1999. It was the first GRB for which a simultaneous optical flash was detected. Astronomers first managed to obtain a visible-light image of a GRB as it occurred on January 23, 1999, using the ROTSE-I telescope in Los Alamos, New Mexico. The ROTSE-I was operated by a team under Dr. Carl W. Akerlof of the University of Michigan and included members from Los Alamos National Laboratory and Lawrence Livermore National Laboratory. The robotic telescope was fully automated, responding to signals from NASA's BATSE instrument aboard the Compton Gamma Ray Observatory within seconds, without human intervention. In the dark hours of the morning of January 23, 1999, the Compton satellite recorded a gamma-ray burst that lasted for about a minute and a half. There was a peak of gamma and X-ray emission 25 seconds after the event was first detected, followed by a somewhat smaller peak 40 seconds after the beginning of the event. The emission then fizzled out in a series of small peaks over the next 50 seconds, and eight minutes after the event had faded to a hundredth of its maximum brightness. The burst was so strong that it ranked in the top 2% of all bursts detected.
GRB 000131 was a gamma-ray burst (GRB) that was detected on 31 January 2000 at 14:59 UTC. A gamma-ray burst is a highly luminous flash associated with an explosion in a distant galaxy and producing gamma rays, the most energetic form of electromagnetic radiation, and often followed by a longer-lived "afterglow" emitted at longer wavelengths.
GRB 011211 was a gamma-ray burst (GRB) detected on December 11, 2001. A gamma-ray burst is a highly luminous flash associated with an explosion in a distant galaxy and producing gamma rays, the most energetic form of electromagnetic radiation, and often followed by a longer-lived "afterglow" emitted at longer wavelengths.
GRB 030329 was a gamma-ray burst (GRB) that was detected on 29 March 2003 at 11:37 UTC. A gamma-ray burst is a highly luminous flash associated with an explosion in a distant galaxy and producing gamma rays, the most energetic form of electromagnetic radiation, and often followed by a longer-lived "afterglow" emitted at longer wavelengths. GRB 030329 was the first burst whose afterglow definitively exhibited characteristics of a supernova, confirming the existence of a relationship between the two phenomena.
GRB 070714B was a gamma-ray burst (GRB) that was detected on 14 July 2007 at 04:59 UTC. A gamma-ray burst is a highly luminous flash associated with an explosion in a distant galaxy and producing gamma rays, the most energetic form of electromagnetic radiation, and often followed by a longer-lived "afterglow" emitted at longer wavelengths.

GRB 090429B was a gamma-ray burst observed on 29 April 2009 by the Burst Alert Telescope aboard the Swift satellite. The burst triggered a standard burst-response observation sequence, which started 106 seconds after the burst. The X-ray telescope aboard the satellite identified an uncatalogued fading source. No optical or UV counterpart was seen in the UV–optical telescope. Around 2.5 hours after the burst trigger, a series of observations was carried out by the Gemini North telescope, which detected a bright object in the infrared part of the spectrum. No evidence of a host galaxy was found either by Gemini North or by the Hubble Space Telescope. Though this burst was detected in 2009, it was not until May 2011 that its distance estimate of 13.14 billion light-years was announced. With 90% likelihood, the burst had a photometric redshift greater than z = 9.06, which would make it the most distant GRB known, although the error bar on this estimate is large, providing a lower limit of z > 7.

GRB 101225A, also known as the "Christmas burst", was a cosmic explosion first detected by NASA's Swift observatory on Christmas Day 2010. The gamma-ray emission lasted at least 28 minutes, which is unusually long. Follow-up observations of the burst's afterglow by the Hubble Space Telescope and ground-based observatories were unable to determine the object's distance using spectroscopic methods.

GRB 130427A was a record-setting gamma-ray burst, discovered starting on April 27, 2013. This GRB was associated to SN 2013cq, of which the appearance of optical signal was predicted on May 2, 2013 and detected on May 13, 2013. The Fermi space observatory detected a gamma-ray with an energy of at least 94 billion electron volts. It was simultaneously detected by the Burst Alert Telescope aboard the Swift telescope and was the brightest burst Swift had ever detected. It was one of the five closest GRBs, at about 3.6 billion light-years away, and was comparatively long-lasting.
Fermi's Large Area Telescope (LAT) recorded one gamma ray with an energy of at least 94 billion electron volts (GeV), or some 35 billion times the energy of visible light, and about three times greater than the LAT's previous record. The GeV emission from the burst lasted for hours, and it remained detectable by the LAT for the better part of a day, setting a new record for the longest gamma-ray emission from a GRB.

A kilonova is a transient astronomical event that occurs in a compact binary system when two neutron stars or a neutron star and a black hole merge. These mergers are thought to produce gamma-ray bursts and emit bright electromagnetic radiation, called "kilonovae", due to the radioactive decay of heavy r-process nuclei that are produced and ejected fairly isotropically during the merger process. The measured high sphericity of the kilonova AT2017gfo at early epochs was deduced from the blackbody nature of its spectrum.

NGC 4993 is a lenticular galaxy located about 140 million light-years away in the constellation Hydra. It was discovered on 26 March 1789 by William Herschel and is a member of the NGC 4993 Group.

GRB 221009A, also known as Swift J1913.1+1946, was an extraordinarily bright and long-lasting gamma-ray burst (GRB) jointly discovered by the Neil Gehrels Swift Observatory and the Fermi Gamma-ray Space Telescope on October 9, 2022. The gamma-ray burst was ten minutes long, but was detectable for more than ten hours following initial detection. Despite being around two billion light-years away, it was powerful enough to affect Earth's atmosphere, having the strongest effect ever recorded by a gamma-ray burst on the planet. The peak luminosity of GRB 221009A was measured by Konus-Wind to be ~ 2.1 × 1047 W and by Fermi Gamma-ray Burst Monitor to be ~ 1.0 × 1047 W over its 1.024s interval. A burst as energetic and as close to Earth as 221009A is thought to be a once-in-10,000-year event. It was the brightest and most energetic gamma-ray burst ever recorded, with some dubbing it the BOAT, or Brightest Of All Time.

GRB 230307A was an extremely bright, long duration gamma-ray burst (GRB), likely produced as a consequence of a neutron star merger or black hole - neutron star merger event. It lasted around three minutes, and was observed to have a gamma ray fluence of 3×10-4 erg cm-2 in the 10 to 1000 KeV (electronvolt) range making it second only to GRB 221009A, which was an extremely bright and long duration gamma ray burst deemed to be the Brightest Of All Time. The burst was around 1000 times more powerful than a typical gamma-ray burst. The burst had the second-highest gamma-ray fluence ever recorded. The James Webb Space Telescope (JWST) detected the chemical signature for tellurium (Te). The neutron stars were once part of a spiral galaxy (host galaxy) but were kicked out via gravitational interactions. Then while outside of the main galaxy at a distance of 120,000 light years, they merged, creating GRB 230307A.

















