
A stellarator is a device that confines plasma using external magnets. Scientists researching magnetic confinement fusion aim to use stellarator devices as a vessel for nuclear fusion reactions. The name refers to stars as fusion also occurs in stars such as the Sun. It is one of the earliest fusion power devices, along with the z-pinch and magnetic mirror.

A tokamak is a device which uses a powerful magnetic field generated by external magnets to confine plasma in the shape of an axially-symmetrical torus. The tokamak is one of several types of magnetic confinement devices being developed to produce controlled thermonuclear fusion power. The tokamak concept is currently one of the leading candidates for a practical fusion reactor.

In plasma physics, plasma stability concerns the stability properties of a plasma in equilibrium and its behavior under small perturbations. The stability of the system determines if the perturbations will grow, oscillate, or be damped out. It is an important consideration in topics such as nuclear fusion and astrophysical plasma.

Fusion power is a proposed form of power generation that would generate electricity by using heat from nuclear fusion reactions. In a fusion process, two lighter atomic nuclei combine to form a heavier nucleus, while releasing energy. Devices designed to harness this energy are known as fusion reactors. Research into fusion reactors began in the 1940s, but as of 2024, no device has reached net power, although net positive reactions have been achieved.

The Large Helical Device (LHD) is a fusion research device located in Toki, Gifu, Japan. It is operated by the National Institute for Fusion Science, and is the world's second-largest superconducting stellarator, after Wendelstein 7-X. The LHD employs a heliotron magnetic field originally developed in Japan.

Magnetic confinement fusion (MCF) is an approach to generate thermonuclear fusion power that uses magnetic fields to confine fusion fuel in the form of a plasma. Magnetic confinement is one of two major branches of controlled fusion research, along with inertial confinement fusion.
A field-reversed configuration (FRC) is a type of plasma device studied as a means of producing nuclear fusion. It confines a plasma on closed magnetic field lines without a central penetration. In an FRC, the plasma has the form of a self-stable torus, similar to a smoke ring.

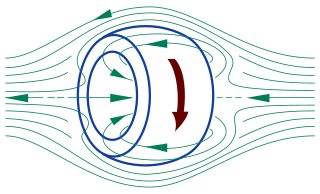
A spheromak is an arrangement of plasma formed into a toroidal shape similar to a smoke ring. The spheromak contains large internal electric currents and their associated magnetic fields arranged so the magnetohydrodynamic forces within the spheromak are nearly balanced, resulting in long-lived (microsecond) confinement times without external fields. Spheromaks belong to a type of plasma configuration referred to as the compact toroids. A spheromak can be made and sustained using magnetic flux injection, leading to a dynomak.
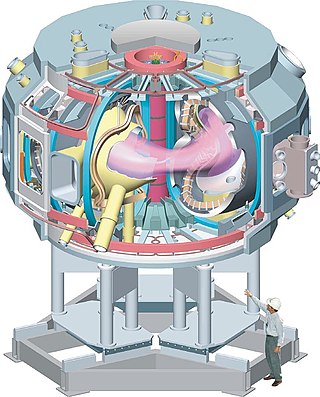
The National Compact Stellarator Experiment, NCSX in short, was a magnetic fusion energy experiment based on the stellarator design being constructed at the Princeton Plasma Physics Laboratory (PPPL).

The Wendelstein 7-X reactor is an experimental stellarator built in Greifswald, Germany, by the Max Planck Institute for Plasma Physics (IPP), and completed in October 2015. Its purpose is to advance stellarator technology: though this experimental reactor will not produce electricity, it is used to evaluate the main components of a future fusion power plant; it was developed based on the predecessor Wendelstein 7-AS experimental reactor.

The Helically Symmetric Experiment, is an experimental plasma confinement device at the University of Wisconsin–Madison, with design principles that are intended to be incorporated into a fusion reactor. The HSX is a modular coil stellarator which is a toroid-shaped pressure vessel with external electromagnets which generate a magnetic field for the purpose of containing a plasma. It began operation in 1999.
The Columbia Non-neutral Torus (CNT) is a small stellarator at the Columbia University Plasma Physics Laboratory designed by Thomas Sunn Pedersen with the aid of Wayne Reiersen and Fred Dahlgren of the Princeton Plasma Physics Laboratory to conduct the first investigation of non-neutral plasmas confined on magnetic surfaces. The experiment, which began operation in November 2004, is funded by the National Science Foundation and the United States Department of Energy in the form of a Faculty Early Career Development (CAREER) award.

In magnetic confinement fusion, a divertor or diverted configuration is a magnetic field configuration of a tokamak or a stellarator which separates the confined plasma from the material surface of the device. The plasma particles which diffuse across the boundary of the confined region are diverted by the open, wall-intersecting magnetic field lines to wall structures which are called the divertor targets, usually remote from the confined plasma. The magnetic divertor extracts heat and ash produced by the fusion reaction, minimizes plasma contamination, and protects the surrounding walls from thermal and neutronic loads.
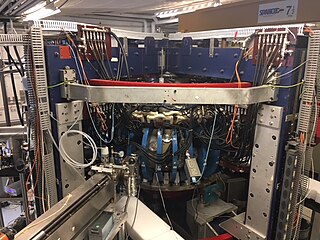
The Hybrid Illinois Device for Research and Applications (HIDRA) is a medium-sized toroidal magnetic fusion device housed in the Nuclear Radiation Laboratory and operated by the Center for Plasma-Material Interactions (CPMI) within the Department of Nuclear, Plasma and Radiological Engineering at the University of Illinois at Urbana–Champaign, United States. HIDRA had its first plasma at the end of April 2016 and started experimental campaigns by December of that year. HIDRA is the former WEGA classical stellarator that was operated at the Max Planck Institute for Plasma Physics in Greifswald Germany from 2001 to 2013.
The Model C stellarator was the first large-scale stellarator to be built, during the early stages of fusion power research. Planned since 1952, construction began in 1961 at what is today the Princeton Plasma Physics Laboratory (PPPL). The Model C followed the table-top sized Model A, and a series of Model B machines that refined the stellarator concept and provided the basis for the Model C, which intended to reach break-even conditions. Model C ultimately failed to reach this goal, producing electron temperatures of 400 eV when about 100,000 were needed. In 1969, after UK researchers confirmed that the USSR's T-3 tokamak was reaching 1000 eV, the Model C was converted to the Symmetrical Tokamak, and stellarator development at PPPL ended.

TJ-II is a flexible Heliac installed at Spain's National Fusion Laboratory.

The Compact Toroidal Hybrid (CTH) is an experimental device at Auburn University that uses magnetic fields to confine high-temperature plasmas. CTH is a torsatron type of stellarator with an external, continuously wound helical coil that generates the bulk of the magnetic field for containing a plasma.

Wendelstein 7-AS was an experimental stellarator which was in operation from 1988 to 2002 by the Max Planck Institute for Plasma Physics (IPP) in Garching. It was the first of a new class of advanced stellarators with modular coils, designed with the goal of developing a nuclear fusion reactor to generate electricity.
The history of nuclear fusion began early in the 20th century as an inquiry into how stars powered themselves and expanded to incorporate a broad inquiry into the nature of matter and energy, as potential applications expanded to include warfare, energy production and rocket propulsion.
















