
Coronary artery disease (CAD), also called coronary heart disease (CHD), ischemic heart disease (IHD), myocardial ischemia, or simply heart disease, involves the reduction of blood flow to the cardiac muscle due to build-up of atherosclerotic plaque in the arteries of the heart. It is the most common of the cardiovascular diseases. Types include stable angina, unstable angina, and myocardial infarction.
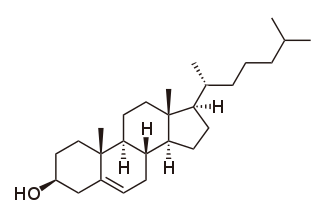
Cholesterol is the principal sterol of all higher animals, distributed in body tissues, especially the brain and spinal cord, and in animal fats and oils.

In nutrition, biology, and chemistry, fat usually means any ester of fatty acids, or a mixture of such compounds, most commonly those that occur in living beings or in food.
High-density lipoprotein (HDL) is one of the five major groups of lipoproteins. Lipoproteins are complex particles composed of multiple proteins which transport all fat molecules (lipids) around the body within the water outside cells. They are typically composed of 80–100 proteins per particle. HDL particles enlarge while circulating in the blood, aggregating more fat molecules and transporting up to hundreds of fat molecules per particle.

Low-density lipoprotein (LDL) is one of the five major groups of lipoprotein that transport all fat molecules around the body in extracellular water. These groups, from least dense to most dense, are chylomicrons, very low-density lipoprotein (VLDL), intermediate-density lipoprotein (IDL), low-density lipoprotein (LDL) and high-density lipoprotein (HDL). LDL delivers fat molecules to cells. LDL is involved in atherosclerosis, a process in which it is oxidized within the walls of arteries.

Atherosclerosis is a pattern of the disease arteriosclerosis, characterized by development of abnormalities called lesions in walls of arteries. These lesions may lead to narrowing of the arterial walls due to buildup of atheromatous plaques. At onset there are usually no symptoms, but if they develop, symptoms generally begin around middle age. In severe cases, it can result in coronary artery disease, stroke, peripheral artery disease, or kidney disorders, depending on which body part(s) the affected arteries are located in the body.

Statins are a class of medications that reduce illness and mortality in people who are at high risk of cardiovascular disease. They are the most commonly prescribed cholesterol-lowering drugs.
A saturated fat is a type of fat in which the fatty acid chains have all single bonds. A fat known as a glyceride is made of two kinds of smaller molecules: a short glycerol backbone and fatty acids that each contain a long linear or branched chain of carbon (C) atoms. Along the chain, some carbon atoms are linked by single bonds (-C-C-) and others are linked by double bonds (-C=C-). A double bond along the carbon chain can react with a pair of hydrogen atoms to change into a single -C-C- bond, with each H atom now bonded to one of the two C atoms. Glyceride fats without any carbon chain double bonds are called saturated because they are "saturated with" hydrogen atoms, having no double bonds available to react with more hydrogen.

The French paradox is an apparently paradoxical epidemiological observation that French people have a relatively low incidence of coronary heart disease (CHD), while having a diet relatively rich in saturated fats, in apparent contradiction to the widely held belief that the high consumption of such fats is a risk factor for CHD. The paradox is that if the thesis linking saturated fats to CHD is valid, the French ought to have a higher rate of CHD than comparable countries where the per capita consumption of such fats is lower.

Cardiovascular disease (CVD) is any disease involving the heart or blood vessels. CVDs constitute a class of diseases that includes: coronary artery diseases, heart failure, hypertensive heart disease, rheumatic heart disease, cardiomyopathy, arrhythmia, congenital heart disease, valvular heart disease, carditis, aortic aneurysms, peripheral artery disease, thromboembolic disease, and venous thrombosis.

Hypercholesterolemia, also called high cholesterol, is the presence of high levels of cholesterol in the blood. It is a form of hyperlipidemia, hyperlipoproteinemia, and dyslipidemia.
Dyslipidemia is a metabolic disorder characterized by abnormally high or low amounts of any or all lipids or lipoproteins in the blood. Dyslipidemia is a risk factor for the development of atherosclerotic cardiovascular diseases (ASCVD), which include coronary artery disease, cerebrovascular disease, and peripheral artery disease. Although dyslipidemia is a risk factor for ASCVD, abnormal levels don't mean that lipid lowering agents need to be started. Other factors, such as comorbid conditions and lifestyle in addition to dyslipidemia, is considered in a cardiovascular risk assessment. In developed countries, most dyslipidemias are hyperlipidemias; that is, an elevation of lipids in the blood. This is often due to diet and lifestyle. Prolonged elevation of insulin resistance can also lead to dyslipidemia. Likewise, increased levels of O-GlcNAc transferase (OGT) may cause dyslipidemia.

The American Heart Association (AHA) is a nonprofit organization in the United States that funds cardiovascular medical research, educates consumers on healthy living and fosters appropriate cardiac care in an effort to reduce disability and deaths caused by cardiovascular disease and stroke. They are known for publishing guidelines on cardiovascular disease and prevention, standards on basic life support, advanced cardiac life support (ACLS), pediatric advanced life support (PALS), and in 2014 issued the first guidelines for preventing strokes in women. The American Heart Association is also known for operating a number of highly visible public service campaigns starting in the 1970s, and also operates several fundraising events.
Hyperlipidemia is abnormally high levels of any or all lipids or lipoproteins in the blood. The term hyperlipidemia refers to the laboratory finding itself and is also used as an umbrella term covering any of various acquired or genetic disorders that result in that finding. Hyperlipidemia represents a subset of dyslipidemia and a superset of hypercholesterolemia. Hyperlipidemia is usually chronic and requires ongoing medication to control blood lipid levels.

The National Heart Foundation of Australia is a charity established in 1959. Its activities have been funding cardiovascular research, supporting health professionals in their practice, developing health promotion activities, informing and educating the public and assisting people with cardiovascular disease. It describes its mission as "to reduce heart disease and improve the heart health and quality of life of all Australians through our work in Risk Reduction, Support, Care and Research."

The Ride for Heart is a charity bicycle ride organized by the Heart and Stroke Foundation of Ontario. For more than 20 years it was sponsored by margarine brand Becel. In November 2017, Manulife was announced as the new title sponsor starting in 2018.
The Dietary Approaches to Stop Hypertension or the DASH diet is a diet to control hypertension promoted by the U.S.-based National Heart, Lung, and Blood Institute, part of the National Institutes of Health (NIH), an agency of the United States Department of Health and Human Services. The DASH diet is rich in fruits, vegetables, whole grains, and low-fat dairy foods. It includes meat, fish, poultry, nuts, and beans, and is limited in sugar-sweetened foods and beverages, red meat, and added fats. In addition to its effect on blood pressure, it is designed to be a well-balanced approach to eating for the general public. DASH is recommended by the United States Department of Agriculture (USDA) as a healthy eating plan. The DASH diet is one of three healthy diets recommended in the 2015–20 U.S. Dietary Guidelines, which also include the Mediterranean diet and a vegetarian diet. The American Heart Association (AHA) considers the DASH diet "specific and well-documented across age, sex and ethnically diverse groups."

The Seven Countries Study is an epidemiological longitudinal study directed by Ancel Keys at what is today the University of Minnesota Laboratory of Physiological Hygiene & Exercise Science (LPHES). Begun in 1956 with a yearly grant of US$200,000 from the U.S. Public Health Service, the study was first published in 1978 and then followed up on its subjects every five years thereafter.
This article provides a global overview of the current trends and distribution of metabolic syndrome. Metabolic syndrome refers to a cluster of related risk factors for cardiovascular disease that includes abdominal obesity, diabetes, hypertension, and elevated cholesterol.
Cardiovascular disease in women is an integral area of research in the ongoing studies of women's health. Cardiovascular disease (CVD) is an umbrella term for a wide range of diseases affecting the heart and blood vessels, including but not limited to, coronary artery disease, stroke, cardiomyopathy, myocardial infarctions, and aortic aneurysms.















