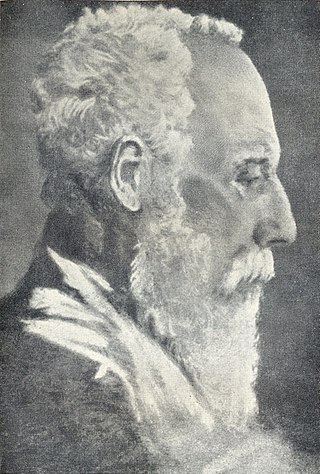Raja Ram Mohan Roy was an Indian reformer who was one of the founders of the Brahmo Sabha in 1828, the precursor of the Brahmo Samaj, a social-religious reform movement in the Indian subcontinent. He was given the title of Raja by Akbar II, the Mughal emperor. His influence was apparent in the fields of politics, public administration, education and religion. He was known for his efforts to abolish the practices of sati and child marriage. Roy is considered to be the "Father of Indian Renaissance" by many historians.

Dayanand Saraswati, also known as Maharshi Dayanand, was an Indian philosopher, social leader and founder of the Arya Samaj, a reform movement of Hinduism. His magnum opus is the book Satyarth Prakash, which has remained a highly influential text on the philosophy of the Vedas and clarifications of various ideas and duties of human beings. He was the first to give the call for Swaraj as "India for Indians" in 1876, a call later taken up by Lokmanya Tilak. Denouncing the idolatry and ritualistic worship, he worked towards reviving Vedic ideologies. Subsequently, the philosopher and President of India, S. Radhakrishnan, called him one of the "makers of Modern India", as did Sri Aurobindo.

Arya Samaj is considered a monotheistic Indian Hindu reform movement that promotes values and practices based on the belief in the infallible authority of the Vedas. The samaj was founded by the sannyasi (ascetic) Dayanand Saraswati in the 1870s.

The Gāyatrī Mantra, also known as the Sāvitri Mantra, is a highly revered mantra from the Rig Veda, dedicated to the Vedic deity Savitr. Gāyatrī is the name of the Goddess of the Vedic meter in which the verse is composed. Its recitation is traditionally preceded by oṃ and the formula bhūr bhuvaḥ svaḥ, known as the mahāvyāhṛti, or "great (mystical) utterance". The Gayatri mantra is cited widely in Hindu texts, such as the mantra listings of the Śrauta liturgy, and classical Hindu texts such as the Bhagavad Gita, Harivamsa, and Manusmṛti. The mantra and its associated metric form was known by the Buddha. The mantra is an important part of the upanayana ceremony. Modern Hindu reform movements spread the practice of the mantra to everyone and its use is now very widespread.
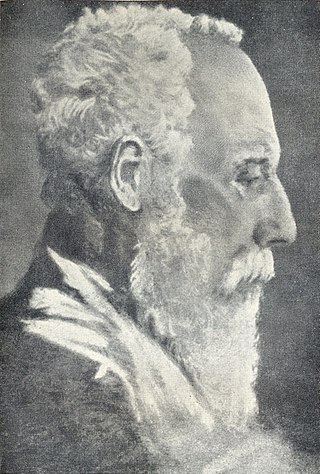
Debendranath Tagore was an Indian philosopher and religious reformer, active in the Brahmo Samaj. He joined Brahmo samaj in 1842. He was the founder in 1848 of the Brahmo religion, which today is synonymous with Brahmoism. Born in Shilaidaha, his father was the industrialist Dwarkanath Tagore; he himself had 14 children, many of whom, including Nobel-prize winning poet Rabindranath Tagore, made significant artistic or literary contributions to society.
Brahmo Samaj is the societal component of Brahmoism, which began as a monotheistic reformist movement that appeared during the Bengal Renaissance.
Bengali Brahmos are those who adhere to Brahmoism, the philosophy of Brahmo Samaj which was founded by Raja Rammohan Roy. A recent publication describes the disproportionate influence of Brahmos on India's development post-19th Century as unparalleled in recent times.

The Bengal Renaissance, also known as the Bengali Renaissance, was a cultural, social, intellectual, and artistic movement that took place in the Bengal region of the British Raj, from the late 18th century to the early 20th century. Historians have traced the beginnings of the movement to the victory of the British East India Company at the 1757 Battle of Plassey, as well as the works of reformer Raja Rammohan Roy, considered the "Father of the Bengal Renaissance," born in 1772. Nitish Sengupta stated that the movement "can be said to have … ended with Rabindranath Tagore," Asia's first Nobel laureate.

Keshub Chandra Sen was a Hindu philosopher and social reformer who attempted to incorporate Christian theology within the framework of Hindu thought. Born a Hindu in the Bengal Presidency of British India, he became a member of the Brahmo Samaj in 1857 but established his own breakaway "Bharatvarshiya Brahmo Samaj" in 1866 while the Brahmo Samaj remained under the leadership of Debendranath Tagore. In 1878, his followers abandoned him after the underage child marriage of his daughter which exposed his campaign against child marriage as hollow. Later in his life he came under the influence of Ramakrishna and founded a syncretic "New Dispensation" inspired by Christianity, and Vaishnavbhakti, and Hindu practices.

Pandit Shiv Narayan Agnihotri was a Hindu social reformer who emerged as a leading member of the Brahmo Samaj, a Hindu reform movement. He broke from Brahmoism in 1886 to form his own religious group, the Dev Samaj.
India has been home to a large number of religious thinkers and spiritualists. The most important of such religious thinkers include Buddha, Guru Nanak, and Mahavira. Buddha and Guru Nanak were the founders of the Buddhist and Sikh religions respectively. Mahavira was the last Jain Tirthankara.
Brahmoism is a Hindu religious movement which originated from the mid-19th century Bengali Renaissance, the nascent Indian independence movement. Adherents, known as Brahmos, are mainly of Indian or Bangladeshi origin or nationality.
The modern religious philosophy of Brahmoism is based in part on the foundations of reformer Raja Ram Mohan Roy's humanitarian philosophy, as exemplified by the Trust Deed of Brahmo Sabha, known to Brahmos as the 1830 Brahmo Trust Deed.
Adi Dharm refers to the religion of Adi Brahmo Samaj the first development of Brahmoism and includes those Sadharan Brahmo Samajists who were reintegrated into Brahmoism after the second schism of 1878 at the instance of Devendranath Tagore. This was the first organised casteless movement in British India and reverberated from its heart of Bengal to Assam, Bombay State, Punjab and Madras, Hyderabad, and Bangalore.
The Tattwabodhinī Sabhā was a group founded in Calcutta on 6 October 1839 as a splinter group of the Brahmo Samaj, reformers of Hinduism and Indian Society. The founding member was Debendranath Tagore, previously of the Brahmo Samaj, eldest son of influential entrepreneur Dwarkanath Tagore, and eventually father to renowned polymath Rabindranath Tagore. In 1859, the Tattwabodhinī Sabhā were dissolved back into the Brāhmo Samāj by Debendranath Tagore.
Gora is a novel by Rabindranath Tagore, set in Calcutta, in the 1880s during the British Raj. It is the fifth in order of writing and the longest of Tagore’s twelve novels. It is rich in philosophical debate on politics and religion. Other themes include liberation, universalism, brotherhood, gender, feminism, caste, class, tradition versus modernity, urban elite versus rural peasants, colonial rule, nationalism and the Brahmo Samaj.
Below is a timeline of Adi Dharm or Adi Brahmo Samaj.

Rao Sahib Ayyathan Gopalan, popularly known as Darsarji and Darsar Sahib, was an Indian doctor, surgeon, professor, writer, philanthropist, social reformer, and Renaissance leader from Kerala. He is the founder of the Sugunavardhini movement (1900) and Depressed classes mission (1909) and also the leader and propagandist of Brahmo Samaj (1893) in Kerala. He denounced idol worship and fought to end those social practices in Kerala that he thought were unethical. Among his followers were Brahmananda Swami Sivayogi, Vaghbatananda, and Brahmavadhi P. Kunhiraman. Gopalan titled P. Kunhiraman as "Brahmavadhi" and Sivayogi as "Brahmananda Swami".

Dr. Ayyathan Janaki Ammal (1878 –1945) was the first female doctor in Kerala and also in Malabar region which was an administrative district of Madras Presidency during British rule in India. She was also the first female doctor from the Thiyya community and also hailed with the title as the first Malayali lady doctor and surgeon. and the sister to Ayyathan Gopalan. a social reformer of Kerala, the founder of the Sugunavardhini movement (1900), Depressed Classes Mission (1909) and the leader and propagandist of Brahmo Samaj in Kerala.
Sanātanī is a term used to describe Hindu duties that incorporate teachings from the Vedas, Upanishads, Puranas, and other Hindu religious texts and scriptures such as the Ramayana and its many versions, as well as the Mahabharata, which itself is often described as a concise guide to Hindu philosophy and a practical, self-contained guide to life. The word Sanātanī is coined from Sanātana Dharma which refers to the idea that its origins lie beyond human history, as revealed in the Hindu texts.