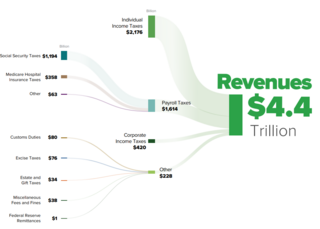
The United States has separate federal, state, and local governments with taxes imposed at each of these levels. Taxes are levied on income, payroll, property, sales, capital gains, dividends, imports, estates and gifts, as well as various fees. In 2020, taxes collected by federal, state, and local governments amounted to 25.5% of GDP, below the OECD average of 33.5% of GDP.
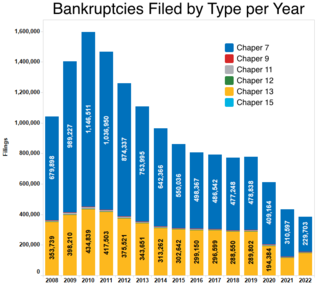
Chapter 7 of Title 11 U.S. Code is the bankruptcy code that governs the process of liquidation under the bankruptcy laws of the U.S. In contrast to bankruptcy under Chapter 11 and Chapter 13, which govern the process of reorganization of a debtor, Chapter 7 bankruptcy is the most common form of bankruptcy in the U.S.

Proposition 13 is an amendment of the Constitution of California enacted during 1978, by means of the initiative process. The initiative was approved by California voters on June 6, 1978 by a nearly two to one margin. It was upheld as constitutional by the United States Supreme Court in the case of Nordlinger v. Hahn, 505 U.S. 1 (1992). Proposition 13 is embodied in Article XIII A of the Constitution of the State of California.
A property tax is an ad valorem tax on the value of a property.
An individual retirement account (IRA) in the United States is a form of pension provided by many financial institutions that provides tax advantages for retirement savings. It is a trust that holds investment assets purchased with a taxpayer's earned income for the taxpayer's eventual benefit in old age. An individual retirement account is a type of individual retirement arrangement as described in IRS Publication 590, Individual Retirement Arrangements (IRAs). Other arrangements include employer-established benefit trusts and individual retirement annuities, by which a taxpayer purchases an annuity contract or an endowment contract from a life insurance company.
Garnishment is a legal process for collecting a monetary judgment on behalf of a plaintiff from a defendant. Garnishment allows the plaintiff to take the money or property of the debtor from the person or institution that holds that property. A similar legal mechanism called execution allows the seizure of money or property held directly by the debtor.
Tax exemption is the reduction or removal of a liability to make a compulsory payment that would otherwise be imposed by a ruling power upon persons, property, income, or transactions. Tax-exempt status may provide complete relief from taxes, reduced rates, or tax on only a portion of items. Examples include exemption of charitable organizations from property taxes and income taxes, veterans, and certain cross-border or multi-jurisdictional scenarios.
An ad valorem tax is a tax whose amount is based on the value of a transaction or of a property. It is typically imposed at the time of a transaction, as in the case of a sales tax or value-added tax (VAT). An ad valorem tax may also be imposed annually, as in the case of a real or personal property tax, or in connection with another significant event. In some countries, a stamp duty is imposed as an ad valorem tax.
In the United States, bankruptcy is largely governed by federal law, commonly referred to as the "Bankruptcy Code" ("Code"). The United States Constitution authorizes Congress to enact "uniform Laws on the subject of Bankruptcies throughout the United States". Congress has exercised this authority several times since 1801, including through adoption of the Bankruptcy Reform Act of 1978, as amended, codified in Title 11 of the United States Code and the Bankruptcy Abuse Prevention and Consumer Protection Act of 2005 (BAPCPA).

The Bankruptcy Abuse Prevention and Consumer Protection Act of 2005 (BAPCPA) is a legislative act that made several significant changes to the United States Bankruptcy Code.
Exempt property, under the law of property in many jurisdictions, is property that can neither be passed by will nor claimed by creditors of the deceased in the event that a decedent leaves a surviving spouse or surviving descendants. Typically, exempt property includes a family car, and a certain amount of cash, or the equivalent value in personal property.
The homestead exemption in Florida may refer to three different types of homestead exemptions under Florida law:
- exemption from forced sale before and at death per Art. X, Section 4(a)-(b) of the Florida Constitution;
- restrictions on devise and alienation, Art. X, Section 4(c) of the Florida Constitution;
- and exemption from taxation per Art. VII, Section 6 of the Florida Constitution.

The United States federal government and most state governments impose an income tax. They are determined by applying a tax rate, which may increase as income increases, to taxable income, which is the total income less allowable deductions. Income is broadly defined. Individuals and corporations are directly taxable, and estates and trusts may be taxable on undistributed income. Partnerships are not taxed, but their partners are taxed on their shares of partnership income. Residents and citizens are taxed on worldwide income, while nonresidents are taxed only on income within the jurisdiction. Several types of credits reduce tax, and some types of credits may exceed tax before credits. Most business expenses are deductible. Individuals may deduct certain personal expenses, including home mortgage interest, state taxes, contributions to charity, and some other items. Some deductions are subject to limits, and an Alternative Minimum Tax (AMT) applies at the federal and some state levels.
Tax deferral refers to instances where a taxpayer can delay paying taxes to some future period. In theory, the net taxes paid should be the same. Taxes can sometimes be deferred indefinitely, or may be taxed at a lower rate in the future, particularly for deferral of income taxes.

The 2007 Texas constitutional amendment election took place 6 November 2007.
Asset protection is a set of legal techniques and a body of statutory and common law dealing with protecting assets of individuals and business entities from civil money judgments. The goal of asset protection planning is to insulate assets from claims of creditors without perjury or tax evasion.
Taxes in Switzerland are levied by the Swiss Confederation, the cantons and the municipalities.
The New York State School Tax Relief Program, or New York State Real Property Tax Law §425, is a school tax rebate program offered in New York State aimed at reducing school district property taxes on the primary residences of New York residents. In New York City, the STAR Program is a tax exemption for those who applied before Fiscal Year 2015-2016 and a tax credit there after for new applicants. The program, which acts similarly to homestead exemptions in other states, was enacted on August 7, 1997, a product of the annual budget of then-Governor George Pataki.

Most local governments in the United States impose a property tax, also known as a millage rate, as a principal source of revenue. This tax may be imposed on real estate or personal property. The tax is nearly always computed as the fair market value of the property, multiplied by an assessment ratio, multiplied by a tax rate, and is generally an obligation of the owner of the property. Values are determined by local officials, and may be disputed by property owners. For the taxing authority, one advantage of the property tax over the sales tax or income tax is that the revenue always equals the tax levy, unlike the other types of taxes. The property tax typically produces the required revenue for municipalities' tax levies. One disadvantage to the taxpayer is that the tax liability is fixed, while the taxpayer's income is not.
Taxes in Germany are levied by the federal government, the states (Länder) as well as the municipalities (Städte/Gemeinden). Many direct and indirect taxes exist in Germany; income tax and VAT are the most significant.







