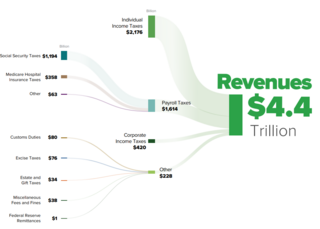
The United States has separate federal, state, and local governments with taxes imposed at each of these levels. Taxes are levied on income, payroll, property, sales, capital gains, dividends, imports, estates and gifts, as well as various fees. In 2020, taxes collected by federal, state, and local governments amounted to 25.5% of GDP, below the OECD average of 33.5% of GDP.
This aims to be a complete list of the articles on real estate.

Proposition 13 is an amendment of the Constitution of California enacted during 1978, by means of the initiative process, to cap property taxes and limit property reassessments to when the property changes ownership, as well as require a 2/3 majority for tax increases in the state legislature. The initiative was approved by California voters in a primary election on June 6, 1978 by a nearly two to one margin. It was upheld by the Supreme Court in 1992 in Nordlinger v. Hahn, 505 U.S. 1 (1992). Proposition 13 is embodied in Article XIII A of the Constitution of the State of California.

In finance, valuation is the process of determining the value of a (potential) investment, asset, or security. Generally, there are three approaches taken, namely discounted cashflow valuation, relative valuation, and contingent claim valuation.
A property tax is an ad valorem tax on the value of a property.

A taxpayer is a person or organization subject to pay a tax. Modern taxpayers may have an identification number, a reference number issued by a government to citizens or firms.
Market value or OMV is the price at which an asset would trade in a competitive auction setting. Market value is often used interchangeably with open market value, fair value or fair market value, although these terms have distinct definitions in different standards, and differ in some circumstances.
Real estate appraisal, property valuation or land valuation is the process of developing an opinion of value for real property. Real estate transactions often require appraisals because they occur infrequently and every property is unique, unlike corporate stocks, which are traded daily and are identical. The location also plays a key role in valuation. However, since property cannot change location, it is often the upgrades or improvements to the home that can change its value. Appraisal reports form the basis for mortgage loans, settling estates and divorces, taxation, and so on. Sometimes an appraisal report is used to establish a sale price for a property.
An ad valorem tax is a tax whose amount is based on the value of a transaction or of a property. It is typically imposed at the time of a transaction, as in the case of a sales tax or value-added tax (VAT). An ad valorem tax may also be imposed annually, as in the case of a real or personal property tax, or in connection with another significant event. In some countries, a stamp duty is imposed as an ad valorem tax.
Capitalization rate is a real estate valuation measure used to compare different real estate investments. Although there are many variations, the cap rate is generally calculated as the ratio between the annual rental income produced by a real estate asset to its current market value. Most variations depend on the definition of the annual rental income and whether it is gross or net of annual costs, and whether the annual rental income is the actual amount received, or the potential rental income that could be received if the asset was optimally rented.

In 2021, the economy of the State of Colorado was 16th largest in the United States with a gross state product of $421 billion.Colorado's per capita personal income in 2019 was $61,157, putting Colorado 12th in the nation.

Business rates in England, or non-domestic rates, are a tax on the occupation of non-domestic property. Rates are a property tax with ancient roots that was formerly used to fund local services that was formalised with the Vagabonds Act 1572 and superseded by the Poor Relief Act 1601. The Local Government Finance Act 1988 introduced business rates in England and Wales from 1990, repealing its immediate predecessor, the General Rate Act 1967. The act also introduced business rates in Scotland but as an amendment to the existing system, which had evolved separately to that in the rest of Great Britain. Since the establishment in 1997 of a Welsh Assembly able to pass legislation, the English and Welsh systems have been able to diverge. In 2015, business rates for Wales were devolved.
The view tax is a term for the fact that the appraisal of a piece of real estate in preparation for assessing property tax includes aspects of a property that are subjective, such as its view. It was also the informal name for a 2005 bill in the legislature of the U.S. state of New Hampshire.

A mortgage loan or simply mortgage, in civil law jurisdictions known also as a hypothec loan, is a loan used either by purchasers of real property to raise funds to buy real estate, or by existing property owners to raise funds for any purpose while putting a lien on the property being mortgaged. The loan is "secured" on the borrower's property through a process known as mortgage origination. This means that a legal mechanism is put into place which allows the lender to take possession and sell the secured property to pay off the loan in the event the borrower defaults on the loan or otherwise fails to abide by its terms. The word mortgage is derived from a Law French term used in Britain in the Middle Ages meaning "death pledge" and refers to the pledge ending (dying) when either the obligation is fulfilled or the property is taken through foreclosure. A mortgage can also be described as "a borrower giving consideration in the form of a collateral for a benefit (loan)".
In the United States, a special assessment is a charge that public authorities can assess against real estate parcels for certain public projects. This charge is levied in a specific geographic area known as a special assessment district (SAD). A special assessment may only be levied against parcels of real estate which have been identified as having received a direct and unique "benefit" from the public project.

The Municipal Property Assessment Corporation (MPAC) administers property assessments and appeals of assessment in the province of Ontario, Canada. MPAC determines the assessed value for all properties across Ontario. This is provided in the form of an Assessment Roll, which is delivered to municipalities throughout the province on the second Tuesday in December. Municipalities then take the assessment roll, and calculate property taxes for each individual property in their jurisdiction.

Warren Jones Company v. Commissioner of Internal Revenue, 524 F.2d 788 was a taxation decision by the United States Court of Appeals for the Ninth Circuit.

Most local governments in the United States impose a property tax, also known as a millage rate, as a principal source of revenue. This tax may be imposed on real estate or personal property. The tax is nearly always computed as the fair market value of the property, multiplied by an assessment ratio, multiplied by a tax rate, and is generally an obligation of the owner of the property. Values are determined by local officials, and may be disputed by property owners. For the taxing authority, one advantage of the property tax over the sales tax or income tax is that the revenue always equals the tax levy, unlike the other types of taxes. The property tax typically produces the required revenue for municipalities' tax levies. One disadvantage to the taxpayer is that the tax liability is fixed, while the taxpayer's income is not.
Taxes in Germany are levied at various government levels: the federal government, the 16 states (Länder), and numerous municipalities (Städte/Gemeinden). The structured tax system has evolved significantly, since the reunification of Germany in 1990 and the integration within the European Union, which has influenced tax policies. Today, income tax and Value-Added Tax (VAT) are the primary sources of tax revenue. These taxes reflect Germany's commitment to a balanced approach between direct and indirect taxation, essential for funding extensive social welfare programs and public infrastructure. The modern German tax system accentuate on fairness and efficiency, adapting to global economic trends and domestic fiscal needs.
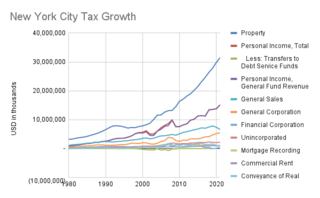
S.7000-A is the name given to the current dominant property tax law in effect in New York State affecting New York City. Surrounding areas such as Nassau County have similar laws. The bill was enacted in 1981 in response to the Hellerstein decision. The law is embodied in Article 18 of the New York State Real Property Law.












