A tax is a compulsory financial charge or some other type of levy imposed on a taxpayer by a governmental organization in order to collectively fund government spending, public expenditures, or as a way to regulate and reduce negative externalities. Tax compliance refers to policy actions and individual behaviour aimed at ensuring that taxpayers are paying the right amount of tax at the right time and securing the correct tax allowances and tax relief. The first known taxation took place in Ancient Egypt around 3000–2800 BC. Taxes consist of direct or indirect taxes and may be paid in money or as its labor equivalent.

In economics and political science, fiscal policy is the use of government revenue collection and expenditure to influence a country's economy. The use of government revenue expenditures to influence macroeconomic variables developed in reaction to the Great Depression of the 1930s, when the previous laissez-faire approach to economic management became unworkable. Fiscal policy is based on the theories of the British economist John Maynard Keynes, whose Keynesian economics theorised that government changes in the levels of taxation and government spending influence aggregate demand and the level of economic activity. Fiscal and monetary policy are the key strategies used by a country's government and central bank to advance its economic objectives. The combination of these policies enables these authorities to target inflation and to increase employment. In modern economies, inflation is conventionally considered "healthy" in the range of 2%–3%. Additionally, it is designed to try to keep GDP growth at 2%–3% and the unemployment rate near the natural unemployment rate of 4%–5%. This implies that fiscal policy is used to stabilise the economy over the course of the business cycle.

Public finance is the study of the role of the government in the economy. It is the branch of economics that assesses the government revenue and government expenditure of the public authorities and the adjustment of one or the other to achieve desirable effects and avoid undesirable ones. The purview of public finance is considered to be threefold, consisting of governmental effects on:
- The efficient allocation of available resources;
- The distribution of income among citizens; and
- The stability of the economy.

The government budget balance, also referred to as the general government balance, public budget balance, or public fiscal balance, is the difference between government revenues and spending. For a government that uses accrual accounting the budget balance is calculated using only spending on current operations, with expenditure on new capital assets excluded. A positive balance is called a government budget surplus, and a negative balance is a government budget deficit. A government budget presents the government's proposed revenues and spending for a financial year.

Publicly funded healthcare is a form of health care financing designed to meet the cost of all or most healthcare needs from a publicly managed fund. Usually this is under some form of democratic accountability, the right of access to which are set down in rules applying to the whole population contributing to the fund or receiving benefits from it.
In many states with political systems derived from the Westminster system, a consolidated fund or consolidated revenue fund is the main bank account of the government. General taxation is taxation paid into the consolidated fund, and general spending is paid out of the consolidated fund.
Universal health care is a health care system in which all residents of a particular country or region are assured access to health care. It is generally organized around providing either all residents or only those who cannot afford on their own, with either health services or the means to acquire them, with the end goal of improving health outcomes.

Two-tier healthcare is a situation in which a basic government-provided healthcare system provides basic care, and a secondary tier of care exists for those who can pay for additional, better quality or faster access. Most countries have both publicly and privately funded healthcare, but the degree to which it creates a quality differential depends on the way the two systems are managed, funded, and regulated.

Government spending or expenditure includes all government consumption, investment, and transfer payments. In national income accounting, the acquisition by governments of goods and services for current use, to directly satisfy the individual or collective needs of the community, is classed as government final consumption expenditure. Government acquisition of goods and services intended to create future benefits, such as infrastructure investment or research spending, is classed as government investment. These two types of government spending, on final consumption and on gross capital formation, together constitute one of the major components of gross domestic product.

The United States budget comprises the spending and revenues of the U.S. federal government. The budget is the financial representation of the priorities of the government, reflecting historical debates and competing economic philosophies. The government primarily spends on healthcare, retirement, and defense programs. The non-partisan Congressional Budget Office provides extensive analysis of the budget and its economic effects. CBO estimated in February 2024 that Federal debt held by the public is projected to rise from 99 percent of GDP in 2024 to 116 percent in 2034 and would continue to grow if current laws generally remained unchanged. Over that period, the growth of interest costs and mandatory spending outpaces the growth of revenues and the economy, driving up debt. Those factors persist beyond 2034, pushing federal debt higher still, to 172 percent of GDP in 2054.
A government budget or a budget is a projection of the government's revenues and expenditure for a particular period of time often referred to as a financial or fiscal year, which may or may not correspond with the calendar year. Government revenues mostly include taxes while expenditures consist of government spending. A government budget is prepared by the Central government or other political entity. In most parliamentary systems, the budget is presented to the legislature and often requires approval of the legislature. Through this budget, the government implements economic policy and realizes its program priorities. Once the budget is approved, the use of funds from individual chapters is in the hands of government ministries and other institutions. Revenues of the state budget consist mainly of taxes, customs duties, fees and other revenues. State budget expenditures cover the activities of the state, which are either given by law or the constitution. The budget in itself does not appropriate funds for government programs, hence need for additional legislative measures. The word budget comes from the Old French bougette.

Tax policy refers to the guidelines and principles established by a government for the imposition and collection of taxes. It encompasses both microeconomic and macroeconomic aspects, with the former focusing on issues of fairness and efficiency in tax collection, and the latter focusing on the overall quantity of taxes to be collected and its impact on economic activity. The tax framework of a country is considered a crucial instrument for influencing the country's economy.
The hidden welfare state is a term coined by Christopher Howard, professor of government at the College of William and Mary, to refer to tax expenditures with social welfare objectives that are often not included in discussions about the U.S. welfare state. Howard's terminology implies that "visible" social welfare programs are designed to help the neediest, but the "hidden" programs often offer benefits to wealthier individuals and companies.
The Road Fund was a British Government fund designated to pay for the building and maintenance of the United Kingdom road network. Its income came originally from Vehicle Excise Duty, until that ceased to be hypothecated for roads use in 1936, and then from government grants. It was created by the Roads Act 1920 and Finance Act 1920, and was wound up in the Miscellaneous Financial Provisions Act 1955.
Public budgeting is a field of public administration and a discipline in the academic study of public administration. Budgeting is characterized by its approaches, functions, formation, and type.
Tax expenditures are government revenue losses from tax exclusions, exemptions, deductions, credits, deferrals, and preferential tax rates. They are a counterpart to direct expenditures, in that they both are forms of government spending.
Examples of health care systems of the world, sorted by continent, are as follows.
The benefit principle is a concept in the theory of taxation from public finance. It bases taxes to pay for public-goods expenditures on a politically-revealed willingness to pay for benefits received. The principle is sometimes likened to the function of prices in allocating private goods. In its use for assessing the efficiency of taxes and appraising fiscal policy, the benefit approach was initially developed by Knut Wicksell (1896) and Erik Lindahl (1919), two economists of the Stockholm School. Wicksell's near-unanimity formulation of the principle was premised on a just income distribution. The approach was extended in the work of Paul Samuelson, Richard Musgrave, and others. It has also been applied to such subjects as tax progressivity, corporation taxes, and taxes on property or wealth. The unanimity-rule aspect of Wicksell's approach in linking taxes and expenditures is cited as a point of departure for the study of constitutional economics in the work of James Buchanan.
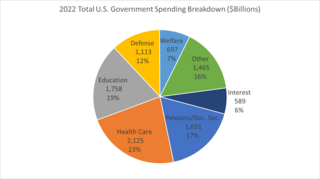
Government spending in the United States is the spending of the federal government of the United States and the spending of its state and local governments.





