
Sustainable development is an organizing principle that aims to meet human development goals while also enabling natural systems to provide necessary natural resources and ecosystem services to humans. The desired result is a society where living conditions and resources meet human needs without undermining the planetary integrity and stability of the natural system. Sustainable development tries to find a balance between economic development, environmental protection, and social well-being. The Brundtland Report in 1987 defined sustainable development as "development that meets the needs of the present generation without compromising the ability of future generations to meet their own needs". The concept of sustainable development nowadays has a focus on economic development, social development and environmental protection for future generations.

Ecological economics, bioeconomics, ecolonomy, eco-economics, or ecol-econ is both a transdisciplinary and an interdisciplinary field of academic research addressing the interdependence and coevolution of human economies and natural ecosystems, both intertemporally and spatially. By treating the economy as a subsystem of Earth's larger ecosystem, and by emphasizing the preservation of natural capital, the field of ecological economics is differentiated from environmental economics, which is the mainstream economic analysis of the environment. One survey of German economists found that ecological and environmental economics are different schools of economic thought, with ecological economists emphasizing strong sustainability and rejecting the proposition that physical (human-made) capital can substitute for natural capital.
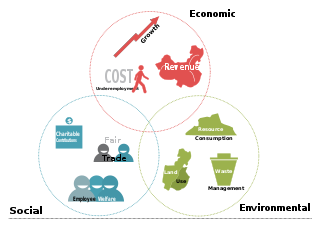
The triple bottom line is an accounting framework with three parts: social, environmental and economic. Some organizations have adopted the TBL framework to evaluate their performance in a broader perspective to create greater business value. Business writer John Elkington claims to have coined the phrase in 1994.

Laurence Jacob Kotlikoff is a professor of economics at Boston University, a William Warren Fairfield Professor at Boston University, a Fellow of the American Academy of Arts and Sciences, a Research Associate of the National Bureau of Economic Research, a Fellow of the Econometric Society, and a former Senior Economist on the President's Council of Economic Advisers.
The Stern Review on the Economics of Climate Change is a 700-page report released for the Government of the United Kingdom on 30 October 2006 by economist Nicholas Stern, chair of the Grantham Research Institute on Climate Change and the Environment at the London School of Economics (LSE) and also chair of the Centre for Climate Change Economics and Policy (CCCEP) at Leeds University and LSE. The report discusses the effect of global warming on the world economy. Although not the first economic report on climate change, it is significant as the largest and most widely known and discussed report of its kind.
Foundation for the Rights of Future Generations (FRFG), also known as Stiftung für die Rechte zukünftiger Generationen (SRzG), is a German think tank and activist group focused on intergenerational justice and sustainability. Established in 1997, the foundation is based in Stuttgart, Germany. The FRFG has been called the most important extra-parliamentary think tank on the topic of intergenerational justice in Germany, and has members from around the world. The organization rose to national prominence while campaigning to include a provision for sustainability and the protection of future generations into the German constitution. It has also campaigned for age-independent voting rights. FRFG publishes the English-language journal Intergenerational Justice Review in collaboration with the University of Tübingen and the Intergenerational Foundation.

Corporate sustainability is an approach aiming to create long-term stakeholder value through the implementation of a business strategy that focuses on the ethical, social, environmental, cultural, and economic dimensions of doing business. The strategies created are intended to foster longevity, transparency, and proper employee development within business organizations. Firms will often express their commitment to corporate sustainability through a statement of Corporate Sustainability Standards (CSS), which are usually policies and measures that aim to meet, or exceed, minimum regulatory requirements.

Climate justice is an approach to climate action that focuses on the unequal impacts of climate change on marginalized or otherwise vulnerable populations. Climate justice wants to achieve an equitable distribution of both the burdens of climate change and the efforts to mitigate climate change. Climate justice is a type of environmental justice.
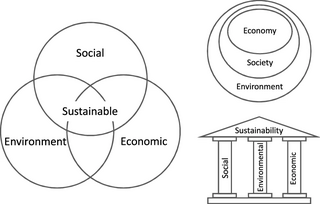
Sustainability is a social goal for people to co-exist on Earth over a long time. Definitions of this term are disputed and have varied with literature, context, and time. Experts sometimes describe sustainability as having three dimensions : environmental, economic, and social, or people, planet, and profit and many publications emphasize the environmental dimension. Many experts have also expanded the dimensions to account for notable aspects of sustainability, for example future generations or health, thereby using a quadruple bottom line (QBL). In everyday use, sustainability often focuses on countering major environmental problems, including climate change, loss of biodiversity, loss of ecosystem services, land degradation, and air and water pollution. The idea of sustainability can guide decisions at the global, national, and individual levels. A related concept is sustainable development, and the terms are often used to mean the same thing. UNESCO distinguishes the two like this: "Sustainability is often thought of as a long-term goal, while sustainable development refers to the many processes and pathways to achieve it."
Intergenerationality is interaction between members of different generations. Sociologists study many intergenerational issues, including equity, conflict, and mobility.

Sustainable gardening includes the more specific sustainable landscapes, sustainable landscape design, sustainable landscaping, sustainable landscape architecture, resulting in sustainable sites. It comprises a disparate group of horticultural interests that can share the aims and objectives associated with the international post-1980s sustainable development and sustainability programs developed to address that humans are now using natural biophysical resources faster than they can be replenished by nature.

The economics of climate change mitigation is a contentious part of climate change mitigation – action aimed to limit the dangerous socio-economic and environmental consequences of climate change.

Sustainability studies is an academic discipline that focuses on the interdisciplinary perspective of the concept of sustainability. Programs include instruction in sustainable development, geography, environmental policies, ethics, ecology, landscape architecture, city and regional planning, economics, natural resources, sociology, and anthropology. Sustainability studies also focuses on the importance of climate change, poverty, social justice and environmental justice. Many universities across the world currently offer sustainability studies as a degree program. The main goal of sustainability studies is for students to find ways to develop novel solutions to environmental problems.

Although related, sustainable development and sustainability are two different concepts. Weak sustainability is an idea within environmental economics which states that 'human capital' can substitute 'natural capital'. It is based upon the work of Nobel laureate Robert Solow, and John Hartwick. Contrary to weak sustainability, strong sustainability assumes that 'human capital' and 'natural capital' are complementary, but not interchangeable.
Fiscal sustainability, or public finance sustainability, is the ability of a government to sustain its current spending, tax and other policies in the long run without threatening government solvency or defaulting on some of its liabilities or promised expenditures. There is no consensus among economists on a precise operational definition for fiscal sustainability, rather different studies use their own, often similar, definitions. However, the European Commission defines public finance sustainability as: the ability of a government to sustain its current spending, tax and other policies in the long run without threatening the government's solvency or without defaulting on some of the government's liabilities or promised expenditures. Many countries and research institutes have published reports which assess the sustainability of fiscal policies based on long-run projections of country's public finances. These assessments attempt to determine whether an adjustment to current fiscal policies that is required to reconcile projected revenues with projected expenditures. The size of the required adjustment is given with measures such as the Fiscal gap. In empirical works, weak and strong fiscal sustainability are distinguished. Differences are related to both econometric techniques used for examination and variables involved.

The 2030 Agenda for Sustainable Development, adopted by all United Nations members in 2015, created 17 world Sustainable Development Goals (SDGs). They were created with the aim of "peace and prosperity for people and the planet..." – while tackling climate change and working to preserve oceans and forests. The SDGs highlight the connections between the environmental, social and economic aspects of sustainable development. Sustainability is at the center of the SDGs.

Future generations are cohorts of hypothetical people not yet born. Future generations are contrasted with current and past generations and evoked in order to encourage thinking about intergenerational equity. The moral patienthood of future generations has been argued for extensively among philosophers, and is thought of as an important, neglected cause by the effective altruism community. The term is often used in describing the conservation or preservation of cultural heritage or natural heritage.

Clive L. Spash is an ecological economist. He currently holds the Chair of Public Policy and Governance at Vienna University of Economics and Business, appointed in 2010. He is also Editor-in-Chief of the academic journal Environmental Values.

Climate change ethics is a field of study that explores the moral aspects of climate change. Climate change is often studied and addressed by scientists, economists, and policymakers in value neutral ways. However, philosophers such as Stephen M. Gardiner and the scientific authors of the Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change (IPCC), argue that decisions related to climate change are moral issues and involve value judgment. Climate change involves difficult moral questions relating to global inequality and human development, who bears responsibility for past emissions, as well as the role of future generations, personal responsibility and many more.
The Intergenerational Fairness Day (IFD) is celebrated annually on 16 November and was proclaimed as a worldwide day of action by an international network of non-partisan organisations that exist to protect the rights of younger and future generations. According to the organising network, the day was created with the goal of being recognised by the United Nations as an official international day. The UN observes various days to commemorate efforts in favour of human rights, climate, or youth.
















