Related Research Articles

The American Revolution was an ideological and political revolution that occurred in British America between 1765 and 1791. The Americans in the Thirteen Colonies formed independent states that defeated the British in the American Revolutionary War (1775–1783), gaining independence from the British Crown, establishing the constitution and establishing the United States of America, the first modern constitutional liberal democracy.

The French Revolution was a period of radical political and societal change in France that began with the Estates General of 1789 and ended with the formation of the French Consulate in November 1799. Many of its ideas are considered fundamental principles of liberal democracy, while phrases like Liberté, égalité, fraternité reappeared in other revolts, such as the 1917 Russian Revolution, and inspired campaigns for the abolition of slavery and universal suffrage. The values and institutions it created dominate French politics to this day.
Marxism–Leninism is a communist ideology which was the main communist movement throughout the 20th century. It was the formal name of the official state ideology adopted by the Soviet Union, its satellite states in the Eastern Bloc, and various self-declared scientific socialist regimes in the Non-Aligned Movement and Third World during the Cold War as well as the Communist International after Bolshevisation. Today, Marxism–Leninism is the ideology of several communist parties and remains the official ideology of the ruling parties of China, Cuba, Laos, and Vietnam as unitary one-party socialist republics, and of Nepal in a multiparty democracy. Generally, Marxist–Leninists support proletarian internationalism and socialist democracy, and oppose anarchism, fascism, imperialism, and liberal democracy. Marxism–Leninism holds that a two-stage communist revolution is needed to replace capitalism. A vanguard party, organised hierarchically through democratic centralism, would seize power "on behalf of the proletariat", and establish a communist party-led socialist state, which it claims to represent the dictatorship of the proletariat. The state controls the economy and means of production, suppresses the bourgeoisie, counter-revolution, and opposition, promotes collectivism in society, and paves the way for an eventual communist society, which would be both classless and stateless. Due to its state-oriented approach, Marxist–Leninist states have been commonly referred to by Western academics as Communist states.

The Russian Revolution was a period of political and social revolution that took place in the former Russian Empire which began during the First World War. This period saw Russia abolish its monarchy and adopt a socialist form of government following two successive revolutions and a bloody civil war. The Russian Revolution can also be seen as the precursor for the other European revolutions that occurred during or in the aftermath of WWI, such as the German Revolution of 1918.

In political science, a revolution is a fundamental and relatively sudden change in political power and political organization which occurs when the population revolts against the government, typically due to perceived oppression or political incompetence.

The 18th century lasted from January 1, 1701 (MDCCI) to December 31, 1800 (MDCCC). During the 18th century, elements of Enlightenment thinking culminated in the American, French, and Haitian revolutions. During the century, slave trading and human trafficking expanded on a global scale. Revolutions began to challenge the legitimacy of monarchical and aristocratic power structures, including the structures and beliefs that supported the slave trade. The British Industrial Revolution began, leading to radical changes in human society and the environment.

The Thirteen Colonies, also known as the Thirteen British Colonies or the Thirteen American Colonies, were a group of British colonies on the Atlantic coast of North America. Founded in the 17th and 18th centuries, they began fighting the American Revolutionary War in April 1775 and formed the United States of America by declaring full independence in July 1776.
A satellite state is a country that is formally independent in the world, but under heavy political, economic and military influence or control from another country. The term was coined by analogy to planetary objects orbiting a larger object, such as smaller moons revolving around larger planets, and is used mainly to refer to Central and Eastern European countries of the Warsaw Pact during the Cold War or to Mongolia or Tannu Tuva between 1924 and 1990, for example. As used for Central and Eastern European countries it implies that the countries in question were "satellites" under the hegemony of the Soviet Union. In some contexts it also refers to other countries in the Soviet sphere of influence during the Cold War—such as North Korea and Cuba, and to some countries in the American sphere of influence—such as South Vietnam. In Western usage, the term has seldom been applied to states other than those in the Soviet orbit. In Soviet usage, the term applied to the states in the orbit of Nazi Germany, Fascist Italy, and Imperial Japan.
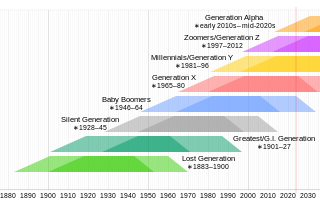
Baby boomers are the demographic cohort following the Silent Generation and preceding Generation X. The generation is often defined as people born from 1946 to 1964, during the post–World War II baby boom. The term is also used outside the United States, but the dates, the demographic context, and the cultural identifiers may vary. The baby boom has been described variously as a "shockwave" and as "the pig in the python". Most baby boomers are children of either the Greatest Generation or the Silent Generation, and are often parents of late Gen Xers and Millennials. Late baby boomers can also be the parents of generation z.
Anti-clericalism is opposition to religious authority, typically in social or political matters. Historical anti-clericalism has mainly been opposed to the influence of Roman Catholicism. Anti-clericalism is related to secularism, which seeks to separate the church from public and political life.

State atheism is the incorporation of positive atheism or non-theism into political regimes. It may also refer to large-scale secularization attempts by governments. It is a form of religion-state relationship that is usually ideologically linked to irreligion and the promotion of irreligion to some extent. State atheism may refer to a government's promotion of anti-clericalism, which opposes religious institutional power and influence in all aspects of public and political life, including the involvement of religion in the everyday life of the citizen. In some instances, religious symbols and public practices that were once held by religion were replaced with secularized versions. State atheism can also exist in a politically neutral fashion, in which case it is considered as non-secular.
Revolutionary songs are political songs that advocate or praise revolutions. They are used to boost morale, as well as for political propaganda or agitation. Amongst the most well-known revolutionary songs are "La Marseillaise" and "The Internationale". Many protest songs can be considered revolutionary - or later become canonized as revolutionary songs following a successful revolution. On the other hand, once a revolution is established, some of the aspects of protest song may be considered counter-revolutionary.
The history of communism encompasses a wide variety of ideologies and political movements sharing the core theoretical values of common ownership of wealth, economic enterprise and property. Most modern forms of communism are grounded at least nominally in Marxism, a theory and method conceived by Karl Marx during the 19th century. Marxism subsequently gained a widespread following across much of Europe and throughout the late 1800s its militant supporters were instrumental in a number of failed revolutions on that continent. During the same era, there was also a proliferation of communist parties which rejected armed revolution, but embraced the Marxist ideal of collective property and a classless society.

Marxism is a method of socioeconomic analysis that uses a materialist interpretation of historical development, better known as historical materialism, to understand class relations and social conflict as well as a dialectical perspective to view social transformation. It originates from the works of 19th-century German philosophers Karl Marx and Friedrich Engels. As Marxism has developed over time into various branches and schools of thought, currently no single, definitive Marxist theory exists.
Evarts Boutell Greene (1870–1947) was an American historian, born in Kobe, Japan, where his parents were missionaries. He graduated Harvard University, and began teaching American history (1894) at the University of Illinois, where he was also (1906–1913) dean of the college of arts and literature.

The Revolutions of 1989 formed part of a revolutionary wave in the late 1980s and early 1990s that resulted in the end of communist rule in Central and Eastern Europe and beyond. The period is often also called the Fall of Communism, and sometimes the Fall of Nations or the Autumn of Nations, a play on the term Spring of Nations that is sometimes used to describe the Revolutions of 1848.

Cuba, officially the Republic of Cuba, is a country comprising the island of Cuba, as well as Isla de la Juventud and several minor archipelagos. Cuba is located where the northern Caribbean Sea, Gulf of Mexico, and Atlantic Ocean meet. Cuba is located at the east of the Yucatán Peninsula (Mexico), south of both the American state of Florida and the Bahamas, west of Hispaniola, and north of both Jamaica and the Cayman Islands. Havana is the largest city and capital; other major cities include Santiago de Cuba and Camagüey. The official area of the Republic of Cuba is 109,884 km2 (42,426 sq mi). The main island of Cuba is the largest island in Cuba and in the Caribbean, with an area of 104,556 km2 (40,369 sq mi). Cuba is the second-most populous country in the Caribbean after Haiti, with over 11 million inhabitants.

The rise of nationalism in Europe initiated with the Spring of Nations in 1848. American political science professor Leon Baradat has argued that “nationalism calls on people to identify with the interests of their national group and to support the creation of a state – a nation-state – to support those interests.” Nationalism was the ideological impetus that, in a few decades, transformed Europe. Rule by monarchies and foreign control of territory was replaced by self-determination and newly formed national governments. Some countries, such as Germany and Italy were formed by uniting various regional states with a common "national identity". Others, such as Greece, Serbia, Poland and Bulgaria, were formed by uprisings against the Ottoman Empire and the Russian Empire. Romania is a special case, formed by the unification of the principalities of Moldavia and Wallachia on 1859 and later gaining independence from the Ottoman Empire in 1878.

A revolutionary wave or revolutionary decade is one series of revolutions occurring in various locations within a similar time-span. In many cases, past revolutions and revolutionary waves have inspired current ones, or an initial revolution has inspired other concurrent "affiliate revolutions" with similar aims. The causes of revolutionary waves have become the subjects of study by historians and political philosophers, including Robert Roswell Palmer, Crane Brinton, Hannah Arendt, Eric Hoffer, and Jacques Godechot.

Oliver Morton Dickerson was an American historian, author, and educator. Like his fellow historians Charles McLean Andrews and Lawrence Henry Gipson, Dickerson was a proponent of the "Imperial school" of historians who believed that the American colonies could not be studied or understood except as part of the British Empire. Among his publications were works on the British Board of Trade, the Navigation Acts, and Boston under military rule.
References
- ↑ William T. Smelser (1963), Personality and social systems, pp. 360–362, ISBN 9780471799238
- ↑ Samuel Farber (2006), The origins of the Cuban Revolution reconsidered, p. 46, ISBN 978-0-8078-3001-7
- ↑ Evarts Boutell Greene (1945), The revolutionary generation, 1763-1790
- ↑ Tun-jen Cheng; Jacques Delisle; Deborah Brown (2006), China under Hu Jintao, p. 34, ISBN 978-981-256-347-7
- ↑ Jan E. Goldstein (2005), The post-revolutionary self, Harvard University Press, pp. 149–150, ISBN 978-0-674-01680-4
- ↑ Frank B. Tipton (2003), "ch. 3 A Revolutionary Generation", A history of modern Germany since 1815, ISBN 978-0-8264-4910-8