
Lesbian, gay, bisexual, and transgender (LGBT) people in the Democratic Republic of the Congo (DRC) face discrimination and legal challenges not experienced by non-LGBT residents. Same-sex sexual activity is legal for both males and females in the Democratic Republic of the Congo, although LGBT individuals may still be targeted for prosecution under public indecency provisions on occasion.

Lesbian, gay, bisexual, and transgender (LGBT) people in the Islamic Emirate of Afghanistan face severe challenges not experienced by non-LGBT residents. Afghan members of the LGBT community are forced to keep their gender identity and sexual orientation secret, in fear of violence and the death penalty. The religious nature of the country has limited any opportunity for public discussion, with any mention of homosexuality and related terms deemed taboo.

Lesbian, gay, bisexual, and transgender (LGBT) people in Kenya face significant challenges not experienced by non-LGBT residents. Sodomy is a felony per Section 162 of the Kenyan Penal Code, punishable by 21 years' imprisonment, and any sexual practices are a felony under section 165 of the same statute, punishable by 5 years' imprisonment. On 24 May 2019, the High Court of Kenya refused an order to declare sections 162 and 165 unconstitutional. The state does not recognise any relationships between persons of the same sex; same-sex marriage is banned under the Kenyan Constitution since 2010. There are no explicit protections against discrimination on the basis of sexual orientation and gender identity. Adoption is restricted to heterosexual couples only.

Lesbian, gay, bisexual, and transgender (LGBT) rights in Cyprus have evolved in recent years, but LGBT people still face legal challenges not experienced by non-LGBT residents. Both male and female expressions of same-sex sexual activity were decriminalised in 1998, and civil unions which grant several of the rights and benefits of marriage have been legal since December 2015. Conversion therapy was banned in Cyprus in May 2023. However, adoption rights in Cyprus are reserved for heterosexual couples only.
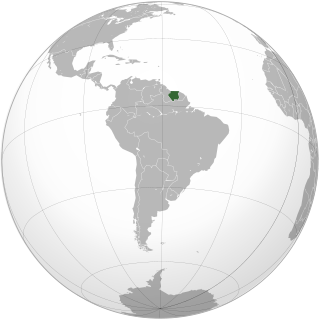
Lesbian, gay, bisexual, and transgender (LGBT) people in Suriname may face legal challenges not experienced by non-LGBT residents. Both male and female expressions of same-sex sexual activity are legal in Suriname. Since 2015, hate speech and discrimination in employment and the provision of goods and services on the basis of sexual orientation has been banned in the country. Same-sex marriage and civil unions are not recognised by law. Nevertheless, Suriname is legally bound to the January 2018 Inter-American Court of Human Rights ruling, which held that same-sex marriage is a human right protected by the American Convention on Human Rights.

Lesbian, gay, bisexual, and transgender (LGBT) people in Armenia face legal and social challenges not experienced by non-LGBT residents, due in part to the lack of laws prohibiting discrimination on the grounds of sexual orientation and gender identity and in part to prevailing negative attitudes about LGBT persons throughout society.

Lesbian, gay, bisexual, and transgender (LGBT) people in Azerbaijan face significant challenges not experienced by non-LGBT residents. Same-sex sexual activity has been legal in Azerbaijan since 1 September 2000. Nonetheless, discrimination on the basis of sexual orientation and gender identity are not banned in the country and same-sex marriage is not recognized.

Lesbian, gay, bisexual, and transgender (LGBT) people in Moldova face legal and social challenges and discrimination not experienced by non-LGBT residents. Households headed by same-sex couples are not eligible for the same rights and benefits as households headed by opposite-sex couples. Same-sex unions are not recognized in the country, so consequently same-sex couples have little to no legal protection. Nevertheless, Moldova bans discrimination based on sexual orientation in the workplace, and same-sex sexual activity has been legal since 1995.

Lesbian, gay, bisexual, and transgender (LGBT) people in Botswana face legal issues not experienced by non-LGBT citizens. Both female and male same-sex sexual acts have been legal in Botswana since 11 June 2019 after a unanimous ruling by the High Court of Botswana. Despite an appeal by the government, the ruling was upheld by the Botswana Court of Appeal on 29 November 2021.
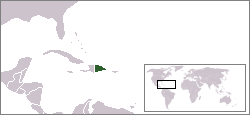
Lesbian, gay, bisexual, and transgender (LGBT) people in the Dominican Republic do not possess the same legal protections as non-LGBT residents, and face social challenges that are not experienced by other people. While the Dominican Criminal Code does not expressly prohibit same-sex sexual relations or cross-dressing, it also does not address discrimination or harassment on the account of sexual orientation or gender identity, nor does it recognize same-sex unions in any form, whether it be marriage or partnerships. Households headed by same-sex couples are also not eligible for any of the same rights given to opposite-sex married couples, as same-sex marriage is constitutionally banned in the country.
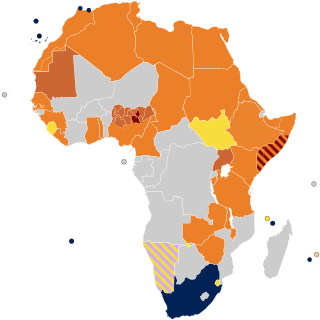
Lesbian, gay, bisexual, and transgender (LGBT) rights in Africa are in most countries very poor in comparison to the Americas, Western Europe and Oceania.

Lesbian, gay, bisexual, and transgender (LGBT) people in Guinea-Bissau face legal challenges not experienced by non-LGBT residents. Same-sex sexual activity is legal in Guinea-Bissau, but same-sex couples and households headed by same-sex couples are not eligible for the same legal protections available to opposite-sex couples.

Lesbian, gay, bisexual, and transgender (LGBT) rights in Mauritius have expanded in the 21st century, although LGBT Mauritians may still face legal difficulties not experienced by non-LGBT residents. Prior to 2023, sodomy was criminalized by Section 250 of the Criminal Code. However, Mauritius fully decriminalized homosexuality in October 2023. Although same-sex marriage is not recognized in Mauritius, LGBT people are broadly protected from discrimination in areas such as employment and the provision of goods and services, making it one of the few African countries to have such protections for LGBT people. The Constitution of Mauritius guarantees the right of individuals to a private life.

Lesbian, gay, bisexual, and transgender (LGBT) people in Seychelles face legal challenges not experienced by non-LGBT residents. Same-sex sexual activity has been legal since 2016, and employment discrimination on the basis of sexual orientation is banned in Seychelles, making it one of the few African countries to have such protections for LGBT people. However, LGBT people may nonetheless face stigmatization among the broader population.
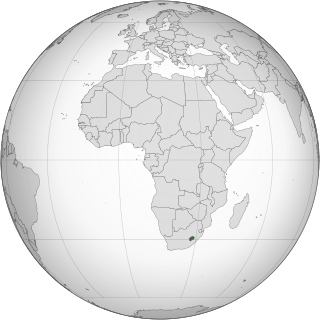
Lesbian, gay, bisexual, and transgender (LGBT) people in Lesotho face legal challenges not experienced by non-LGBT residents. Lesotho does not recognise same-sex marriages or civil unions, nor does it ban discrimination on the basis of sexual orientation or gender identity.
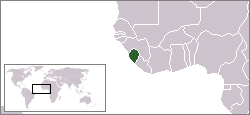
Lesbian, gay, bisexual, and transgender (LGBT) people in Sierra Leone face legal challenges not experienced by non-LGBT residents. Male same-sex sexual activity is illegal in Sierra Leone and carries a possible penalty of life imprisonment, although this law is seldom enforced.

Lesbian, gay, bisexual, and transgender (LGBT) persons in Macau, a special administrative region of China, face legal challenges not experienced by non-LGBT residents. While same-sex sexual activity was decriminalized in 1996, same-sex couples and households headed by same-sex couples remain ineligible for some legal rights available to opposite-sex couples.

Lesbian, gay, bisexual, and transgender (LGBT) people in Samoa face legal challenges not faced by non-LGBT residents. Sexual contact between men is illegal; punishable by up to seven years imprisonment, but the law is not enforced.

Lesbian, gay, bisexual, and transgender (LGBT) people in North Macedonia face discrimination and some legal and social challenges not experienced by non-LGBT residents. Both male and female same-sex sexual activity have been legal in North Macedonia since 1996, but same-sex couples and households headed by same-sex couples are not eligible for the same legal protections available to opposite-sex married couples.
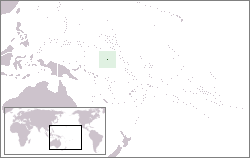
Lesbian, gay, bisexual, and transgender (LGBT) people living in Nauru may face legal and social challenges not experienced by non-LGBT residents. Same-sex sexual activity has been legal since May 2016, but there are no legal recognition of same-sex unions, or protections against discrimination in the workplace or the provision of goods and services.




















