
Central Asia is a subregion of Asia that stretches from the Caspian Sea in the southwest and Eastern Europe in the northwest to Western China and Mongolia in the east, and from Afghanistan and Iran in the south to Russia in the north. It includes Kazakhstan, Kyrgyzstan, Tajikistan, Turkmenistan, and Uzbekistan. The countries as a group are also colloquially referred to as the "-stans" as all have names ending with the Persian suffix "-stan" in both respective native languages and most other languages.

Kazakhstan, officially the Republic of Kazakhstan, is a landlocked country mostly in Central Asia, with a part in Eastern Europe. It borders Russia to the north and west, China to the east, Kyrgyzstan to the southeast, Uzbekistan to the south, and Turkmenistan to the southwest, with a coastline along the Caspian Sea. Its capital is Astana, while the largest city and leading cultural and commercial hub is Almaty. Kazakhstan is the world's ninth-largest country by land area and the largest landlocked country. It has a population of 20 million and one of the lowest population densities in the world, at fewer than 6 people per square kilometre. Ethnic Kazakhs constitute a majority, while ethnic Russians form a significant minority. Officially secular, Kazakhstan is a Muslim-majority country, although ethnic Russians in the country form a sizeable Christian community.
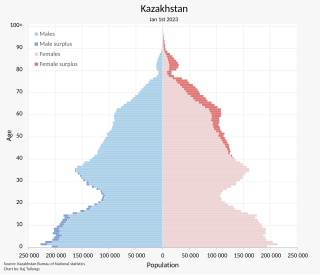
The demographics of Kazakhstan enumerate the demographic features of the population of Kazakhstan, including population growth, population density, ethnicity, education level, health, economic status, religious affiliations, and other aspects of the population. Some use the word Kazakh to refer to the Kazakh ethnic group and language and Kazakhstani to refer to Kazakhstan and its citizens regardless of ethnicity, but it is common to use Kazakh in both senses. It is expected that by 2050, the population will range from 23.5 to 27.7 million people.

Russian is an East Slavic language, spoken primarily in Russia. It is the native language of the Russians and belongs to the Indo-European language family. It is one of four living East Slavic languages, and is also a part of the larger Balto-Slavic languages. It was the de facto and de jure official language of the former Soviet Union. Russian has remained an official language in independent Russia, Belarus, Kazakhstan, Kyrgyzstan, and Tajikistan, and is still commonly used as a lingua franca in Ukraine, Moldova, the Caucasus, Central Asia, and to a lesser extent in the Baltic states and Israel.

Astana, previously known as Akmolinsk, Tselinograd, Akmola, and most recently Nur-Sultan, is the capital city of Kazakhstan.

Kazakh or Qazaq is a Turkic language of the Kipchak branch spoken in Central Asia by Kazakhs. It is closely related to Nogai, Kyrgyz and Karakalpak. It is the official language of Kazakhstan and a significant minority language in the Ili Kazakh Autonomous Prefecture in Xinjiang, north-western China, and in the Bayan-Ölgii Province of western Mongolia. The language is also spoken by many ethnic Kazakhs throughout the former Soviet Union, Germany, and Turkey.

Uzbek, formerly known as Turki, is a Karluk Turkic language spoken by Uzbeks. It is the official and national language of Uzbekistan and formally succeeded Chagatai, an earlier Karluk language also known as "Turki", as the literary language of Uzbekistan in the 1920s.

Almaty, formerly known as Alma-Ata, is the largest city in Kazakhstan, with a population of over two million. It was the capital of Kazakhstan from 1929 to 1936, while the country was an autonomous republic of the Soviet Union, then from 1936 to 1991, a union republic and finally from 1991, an independent state. In 1997, the government relocated the capital to Akmola.

The Kazakh Soviet Socialist Republic, also known as Soviet Kazakhstan, the Kazakh SSR, or simply Kazakhstan, was one of the transcontinental constituent republics of the Soviet Union (USSR) from 1936 to 1991. Located in northern Central Asia, it was created on 5 December 1936 from the Kazakh ASSR, an autonomous republic of the Russian SFSR.

The Kazakhs are a Turkic ethnic group native to Central Asia and Eastern Europe, mainly Kazakhstan, but also parts of northern Uzbekistan and the border regions of Russia, as well as northwestern China and western Mongolia. The Kazakhs arose from the merging of the medieval tribes of Turkic and Mongolic origin in the 15th century.

The tenge is the currency of Kazakhstan. It is divided into 100 tiyn.

Kokshetau, formerly known as Kokchetav is a lakeside city in northern Kazakhstan and the capital of Akmola Region (oblys), which stretches along the southern shore of Lake Kopa, lying in the north of Kokshetau Hills, a northern subsystem of the Kokshetau Uplands (Saryarka) and the southern edge of the Ishim Plain. It is named after the Mount Kokshe.

Kassym-Jomart Kemeluly Tokayev is a Kazakh politician and diplomat who has served as the President of Kazakhstan since 2019. Between 20 March and 12 June 2019, he served as acting president after the resignation of Nursultan Nazarbayev, who had been president for nearly three decades.

Soviet Central Asia was the part of Central Asia administered by the Soviet Union between 1918 and 1991, when the Central Asian republics declared independence. It is nearly synonymous with Russian Turkestan in the Russian Empire. Soviet Central Asia went through many territorial divisions before the current borders were created in the 1920s and 1930s.

Christianity in Kazakhstan is the second most practiced religion after Islam and one of the major religions of Kazakhstan.

Karatal District is a district of Jetisu Region in Kazakhstan. The administrative center of the district is the town of Ushtobe. Population: 47,760 ; 47,824 ; 46,744.

Kazakhstan–Russia relations are the bilateral foreign relations between Kazakhstan and the Russian Federation. Kazakhstan has an embassy in Moscow, a consulate-general in Saint Petersburg, Astrakhan, and Omsk. Russia has an embassy in Astana and consulates in Almaty and Oral.

Kazakhstan is a multiethnic country where the indigenous ethnic group, the Kazakhs, comprise the majority of the population. As of 2023, ethnic Kazakhs are about 71% of the population and ethnic Russians in Kazakhstan are about 15%. These are the two dominant ethnic groups in the country with a wide array of other groups represented, including Ukrainians, Uzbeks, Germans, Tatars, Chechens, Ingush, Uyghurs, Koreans, and Meskhetian Turks.

The Kazakh famine of 1930–1933, also known as the Asharshylyk, was a famine during which approximately 1.5 million people died in the Kazakh Autonomous Socialist Soviet Republic, then part of the Russian Socialist Federative Soviet Republic in the Soviet Union, of whom 1.3 million were ethnic Kazakhs. An estimated 38 to 42 percent of all Kazakhs died, the highest percentage of any ethnic group killed by the Soviet famine of 1930–1933. Other research estimates that as many as 2.3 million died. A committee created by the Kazakhstan parliament chaired by Historian Manash Kozybayev concluded that the famine was "a manifestation of the politics of genocide", with 1.75 million victims.
Derussification is a process or public policy in different states of the former Russian Empire and the Soviet Union or certain parts of them, aimed at restoring national identity of indigenous peoples: their language, culture and historical memory, lost due to Russification. The term may also refer to the marginalization of the Russian language, culture and other attributes of the Russian-speaking society through the promotion of other, usually autochthonous, languages and cultures.




















