
The California Institute of Technology (branded as Caltech or CIT) is a private research university in Pasadena, California. The university is responsible for many modern scientific advancements and is among a small group of institutes of technology in the United States which are strongly devoted to the instruction of pure and applied sciences. Due to its history of technological innovation, Caltech is widely considered to be one of the world's most prestigious universities.

The Massachusetts Institute of Technology (MIT) is a private land-grant research university in Cambridge, Massachusetts. Established in 1861, MIT has played a significant role in the development of many areas of modern technology and science. MIT is widely considered to be one of the most prestigious universities in the world.

The Technion – Israel Institute of Technology is a public research university located in Haifa, Israel. Established in 1912 under the dominion of the Ottoman Empire, the Technion is the oldest university in the country. The Technion is ranked as one of the top universities in both Israel and the Middle East, and in the world's top 100 universities in the 2022 Academic Ranking of World Universities.

The Harbin Institute of Technology is a public research university in China. It is a member of China's elite C9 League and University Alliance of the Silk Road. HIT is a Chinese Ministry of Education Class A Double First Class University. It has three campuses, spanning the country from north to south: the Harbin campus in Heilongjiang Province, the Weihai campus in Shandong Province and the Shenzhen campus in Guangdong Province. HIT is known as the 'MIT of China' due to its dominant reputation in science & engineering research within China.
The Stanford Graduate School of Business is the graduate business school of Stanford University, a private research university in Stanford, California. For several years it has been the most selective business school in the United States, admitting only about 6% of applicants.
Computer science and engineering (CSE) is an academic program at many universities which comprises scientific and engineering aspects of computing. CSE is also a term often used in Europe to translate the name of engineering informatics academic programs. It is offered in both undergraduate as well postgraduate with specializations.

Southeast University is a public research university located in Nanjing, Jiangsu, China. Established in 1921, the university is a member of the Double First Class University Plan, Project 985, and Project 211.

The Federal University of Technology Akure is a federal government-owned university located in Akure, Ondo State, Nigeria. It was founded in 1981 driven by the federal government of Nigeria to create universities that specialised in producing graduates with practical as well as theoretical knowledge of technologies.
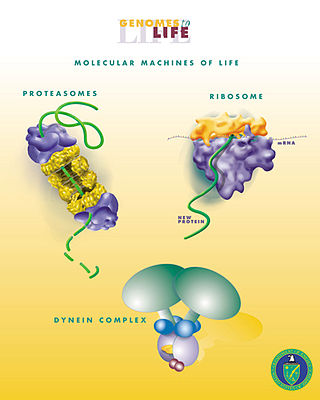
Biological engineering or bioengineering is the application of principles of biology and the tools of engineering to create usable, tangible, economically viable products. Biological engineering employs knowledge and expertise from a number of pure and applied sciences, such as mass and heat transfer, kinetics, biocatalysts, biomechanics, bioinformatics, separation and purification processes, bioreactor design, surface science, fluid mechanics, thermodynamics, and polymer science. It is used in the design of medical devices, diagnostic equipment, biocompatible materials, renewable energy, ecological engineering, agricultural engineering, process engineering and catalysis, and other areas that improve the living standards of societies.

The Harvard John A. Paulson School of Engineering and Applied Sciences (SEAS) is the engineering school within Harvard University's Faculty of Arts and Sciences, offering degrees in engineering and applied sciences to graduate students admitted directly to SEAS, and to undergraduates admitted first to Harvard College. Previously the Lawrence Scientific School and then the Division of Engineering and Applied Sciences, the Paulson School assumed its current structure in 2007. Francis J. Doyle III has been its dean since 2015.

Leo Rafael Reif is a Venezuelan American electrical engineer and academic administrator. He previously served as the 17th president of the Massachusetts Institute of Technology from 2012 to 2022, provost of the institute from 2005 to 2012, and dean of the institute's EECS department from 2004 to 2005.

Edward S. Boyden is an American neuroscientist at MIT. He is the Y. Eva Tan Professor in Neurotechnology, a faculty member in the MIT Media Lab and an associate member of the McGovern Institute for Brain Research. In 2018 he was named a Howard Hughes Medical Institute Investigator. He is recognized for his work on optogenetics. In this technology, a light-sensitive ion channel such as channelrhodopsin-2 is genetically expressed in neurons, allowing neuronal activity to be controlled by light. There were early efforts to achieve targeted optical control dating back to 2002 that did not involve a directly light-activated ion channel, but it was the method based on directly light-activated channels from microbes, such as channelrhodopsin, emerging in 2005 that turned out to be broadly useful. Optogenetics in this way has been widely adopted by neuroscientists as a research tool, and it is also thought to have potential therapeutic applications. Boyden joined the MIT faculty in 2007, and continues to develop new optogenetic tools as well as other technologies for the manipulation of brain activity. Previously, Boyden received degrees in electrical engineering, computer science, and physics from MIT. During high school, Boyden attended the Texas Academy of Mathematics and Science.
Karim R. Lakhani is the Dorothy & Michael Hintze Professor of Business Administration at Harvard Business School. He is the principal investigator of the Crowd Innovation Lab at the Harvard Institute for Quantitative Social Science. His research and teaching focuses on open innovation and user innovation. Lakhani is the founder and one of the principal investigators of the Laboratory for Innovation Science at Harvard (LISH).

The MIT Center for International Studies (CIS) is an academic research center at the Massachusetts Institute of Technology. It sponsors work focusing on international relations, security studies, international migration, human rights and justice, political economy and technology policy. The center was founded in 1951.
Robert J. Wood is a roboticist and a professor of electrical engineering at the Harvard School of Engineering and Applied Sciences and the Wyss Institute for Biologically Inspired Engineering at Harvard University, and is the director of the Harvard Microrobotics Laboratory. At Harvard, he directs the NSF-funded RoboBees project, a 5-year project to build a swarm of robotic bees.

Birla Institute of Technology & Science, Pilani is a deemed university in Pilani, Rajasthan, India. It focuses primarily on higher education and research in engineering and sciences. BITS Pilani is one of the first six institutes in India to be granted Institute of Eminence status. According to 2012 data, BITS Pilani has an acceptance rate of 1.47%, making it one of the most exclusive and prestigious technical universities in the world.
Kenneth Akito Oye is an American political scientist and Professor of Political Science and Data Systems and Society at the Massachusetts Institute of Technology. He is Director of the MIT Program on Emerging Technologies and former Director of the MIT Center for International Studies.

The Information Technology University (ITU) is a public university in Lahore, Punjab, Pakistan. Founded in 2012, the university was founded and headed by Umar Saif and is modeled after the MIT.

The Louvain School of Engineering or École polytechnique de Louvain (EPL) is a faculty of the University of Louvain, Belgium, founded in 1864. Known as the Faculty of Applied Sciences prior to 2008, it currently operates on the campuses of Louvain-la-Neuve and UCLouvain Charleroi.

Takayuki Ito is a Japanese computer scientist who specialized in the fields of artificial intelligence and multi-agent systems. He worked as assistant professor in the computer science department of Japan Advanced Institute of Science and Technology from 2001 until 2003, served as associate professor in the computer science department of Nagoya Institute of Technology (2006–2014), worked as full professor in the computer science department of Nagoya Institute of Technology (2014–2020). He also served as chair of the department (2016–2018)and also director the NITech Artificial Intelligence Research Center at Nagoya Institute of Technology.














