| Mission type | Mars orbiter |
|---|---|
| Mission duration | Failed to orbit |
| Spacecraft properties | |
| Spacecraft type | 2M |
| Manufacturer | NPO Lavochkin |
| Launch mass | 4,850 kg (10,690 lb) |
| Start of mission | |
| Launch date | March 27, 1969, 10:40:45 UTC |
| Rocket | Proton-K/D s/n 240-01 |
| Launch site | Baikonur 81/23 |
Mars 2M No.521, [1] also known as Mars M-69 No.521 and sometimes identified by NASA as Mars 1969A, was a Soviet spacecraft which was lost in a launch failure in 1969. [2] It consisted of an orbiter. The spacecraft was intended to image the surface of Mars using three cameras, with images being encoded for transmission back to Earth as television signals. It also carried a radiometer, a series of spectrometers, and an instrument to detect water vapour in the atmosphere of Mars. It was one of two Mars 2M spacecraft, along with Mars 2M No.522, which was launched in 1969 as part of the Mars programme. Neither launch was successful. [3]
The Mars 2M probes were originally intended to consist of both an orbiter and a lander. Time constraints did not permit the development of a soft lander, so engineers decided to simply use a hard lander that would crash into the Martian surface but gather data during its descent. At first, a modified Luna E-8 bus was to be used for the spacecraft, however it had a number of limitations that made it unsuitable for the long journey to Mars. Halfway through the project, Lavochkin Bureau design chief Georgi Babakin decided to simply discard the Luna E-8 derived probe and design a completely new one from scratch.
However, the 2M probes ended significantly heavier than intended and engineers also ran out of time to conduct drop tests of the lander, so that part was abandoned which left only the orbiter. If successful, this would still be a major propaganda success for the Soviets as NASA was nearly three years away from attempting a Mars orbiter.
As 1968 drew to a close, the project was lagging behind schedule and the US was also making significant headway in the space race with Mariner 6 and 7 scheduled to launch to Mars early in the next year and Apollo 8 taking astronauts into lunar orbit. The Kremlin wanted the Mars probes readied as soon as possible and the second of the two probes was completed in the middle of January. Despite doubts that the probes were ready to fly, they were delivered to Baikonour.
Mars 2M No.521 was launched at 10:40:45 UTC on March 27, 1969, atop a Proton-K 8K78K carrier rocket with a Blok D upper stage, flying from Baikonur Cosmodrome Site 81/23. [1] [4] First and second stage burn went normally, followed by payload shroud jettison. However, third stage ignition did not occur on time and reports filtered back to the launch center that the booster had exploded. Investigation found that an imbalanced rotor in the third stage oxidizer turbopump had started a fire, which led to loss of thrust and vehicle breakup. The remains of the third stage and probe impacted in the Altai Mountains. [2] Even more difficult for Soviet engineers was the news that Mariner 7 had been successfully launched from Cape Canaveral a few days earlier, and their next Mars launch also failed a few days later.
The scientific instruments were: [5]

The Mariner program was conducted by the American space agency NASA to explore other planets. Between 1962 and late 1973, NASA's Jet Propulsion Laboratory (JPL) designed and built 10 robotic interplanetary probes named Mariner to explore the inner Solar System - visiting the planets Venus, Mars and Mercury for the first time, and returning to Venus and Mars for additional close observations.

Mariner 9 was a robotic spacecraft that contributed greatly to the exploration of Mars and was part of the NASA Mariner program. Mariner 9 was launched toward Mars on May 30, 1971, from LC-36B at Cape Canaveral Air Force Station, Florida, and reached the planet on November 14 of the same year, becoming the first spacecraft to orbit another planet – only narrowly beating the Soviet probes Mars 2 and Mars 3, which both arrived at Mars only weeks later.

Mariner 2, an American space probe to Venus, was the first robotic space probe to report successfully from a planetary encounter. The first successful spacecraft in the NASA Mariner program, it was a simplified version of the Block I spacecraft of the Ranger program and an exact copy of Mariner 1. The missions of the Mariner 1 and 2 spacecraft are sometimes known as the Mariner R missions. Original plans called for the probes to be launched on the Atlas-Centaur, but serious developmental problems with that vehicle forced a switch to the much smaller Agena B second stage. As such, the design of the Mariner R vehicles was greatly simplified. Far less instrumentation was carried than on the Soviet Venera probes of this period—for example, forgoing a TV camera—as the Atlas-Agena B had only half as much lift capacity as the Soviet 8K78 booster. The Mariner 2 spacecraft was launched from Cape Canaveral on August 27, 1962, and passed as close as 34,773 kilometers (21,607 mi) to Venus on December 14, 1962.

Mariner 6 and Mariner 7 were two uncrewed NASA robotic spacecraft that completed the first dual mission to Mars in 1969 as part of NASA's wider Mariner program. Mariner 6 was launched from Launch Complex 36B at Cape Canaveral Air Force Station and Mariner 7 from Launch Complex 36A. The two craft flew over the equator and south polar regions, analyzing the atmosphere and the surface with remote sensors, and recording and relaying hundreds of pictures. The mission's goals were to study the surface and atmosphere of Mars during close flybys, in order to establish the basis for future investigations, particularly those relevant to the search for extraterrestrial life, and to demonstrate and develop technologies required for future Mars missions. Mariner 6 also had the objective of providing experience and data which would be useful in programming the Mariner 7 encounter five days later.
The Mars program was a series of uncrewed spacecraft launched by the Soviet Union between 1960 and 1973. The spacecraft were intended to explore Mars, and included flyby probes, landers and orbiters.
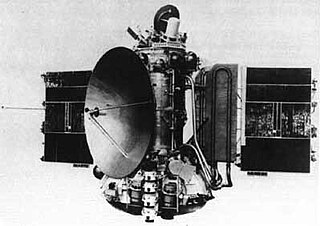
Mars 4, also known as 3MS No.52S was a Soviet spacecraft intended to explore Mars. A 3MS spacecraft launched as part of the Mars programme, it was intended to enter orbit around Mars in 1974. However, computer problems prevented orbital insertion from occurring.

Mars 5, also known as 3MS No.53S was a Soviet spacecraft launched to explore Mars. A 3MS spacecraft launched as part of the Mars programme, it successfully entered orbit around Mars in 1974. However, it failed a few weeks later.

Mars 6, also known as 3MP No.50P was a Soviet spacecraft launched to explore Mars. A 3MP bus spacecraft launched as part of the Mars program, it consisted of a lander, and a coast stage with instruments to study Mars as it flew past.

Mars 7, also known as 3MP No.51P was a Soviet spacecraft launched in 1973 to explore Mars. A 3MP bus spacecraft which comprised the final mission of the Mars programme, it consisted of a lander and a coast stage with instruments to study Mars as it flew past. Due to a malfunction, the lander failed to perform a maneuver necessary to enter the Martian atmosphere, missing the planet and remaining in heliocentric orbit along with the coast stage.

The Mars 2 was an uncrewed space probe of the Mars program, a series of uncrewed Mars landers and orbiters launched by the Soviet Union beginning 19 May 1971. The Mars 2 and Mars 3 missions consisted of identical spacecraft, each with an orbiter and an attached lander. The orbiter is identical to the Venera 9 bus. The type of bus/orbiter is the 4MV. They were launched by a Proton-K heavy launch vehicle with a Blok D upper stage. The lander of Mars 2 became the first human-made object to reach the surface of Mars, although the landing system failed and the lander was lost.

A lander is a spacecraft that descends towards, then comes to rest on the surface of an astronomical body other than Earth. In contrast to an impact probe, which makes a hard landing that damages or destroys the probe upon reaching the surface, a lander makes a soft landing after which the probe remains functional.

The Phobos program was an uncrewed space mission consisting of two probes launched by the Soviet Union to study Mars and its moons Phobos and Deimos. Phobos 1 was launched on 7 July 1988, and Phobos 2 on 12 July 1988, each aboard a Proton-K rocket.

Phobos 2 was the last space probe designed by the Soviet Union. It was designed to explore the moons of Mars, Phobos and Deimos. It was launched on 12 July 1988, and entered orbit on 29 January 1989.

The planet Mars has been explored remotely by spacecraft. Probes sent from Earth, beginning in the late 20th century, have yielded a large increase in knowledge about the Martian system, focused primarily on understanding its geology and habitability potential. Engineering interplanetary journeys is complicated and the exploration of Mars has experienced a high failure rate, especially the early attempts. Roughly sixty percent of all spacecraft destined for Mars failed before completing their missions, with some failing before their observations could even begin. Some missions have been met with unexpected success, such as the twin Mars Exploration Rovers, Spirit and Opportunity, which operated for years beyond their specification.

Kosmos 419, also known as 3MS No.170 was a failed Soviet spacecraft intended to visit Mars. The spacecraft was launched on 10 May 1971, however due to an upper stage malfunction it failed to depart low Earth orbit.

A Moon landing or lunar landing is the arrival of a spacecraft on the surface of the Moon, including both crewed and robotic missions. The first human-made object to touch the Moon was Luna 2 in 1959.
Mars 2M No.522, also known as Mars M-69 No.522 and sometimes identified by NASA as Mars 1969B, was a Soviet spacecraft which was lost in a launch failure in 1969. It consisted of an orbiter. The spacecraft was intended to image the surface of Mars using three cameras, with images being encoded for transmission back to Earth as television signals. It also carried a radiometer, a series of spectrometers, and an instrument to detect water vapour in the atmosphere of Mars. It was one of two Mars 2M spacecraft, along with Mars 2M No.521, which was launched in 1969 as part of the Mars program. Neither launch was successful.

A Mars flyby is a movement of spacecraft passing in the vicinity of the planet Mars, but not entering orbit or landing on it. Uncrewed space probes have used this method to collect data on Mars, as opposed to orbiting or landing. A spacecraft designed for a flyby is also known as a "flyby bus" or "flyby spacecraft".

A flyby is a spaceflight operation in which a spacecraft passes in proximity to another body, usually a target of its space exploration mission and/or a source of a gravity assist to impel it towards another target. Spacecraft which are specifically designed for this purpose are known as flyby spacecraft, although the term has also been used in regard to asteroid flybys of Earth for example. Important parameters are the time and distance of closest approach.

The Mars-69/M-69 or 2M was the designation given to 2 Soviet Mars probes that were to be sent in 1969. Based on the Luna E-8 landers used for Luna 15-24, they were the first attempted Mars and Interplanetary Orbiters. The probes, however, were both destroyed in separate launches in early 1969.