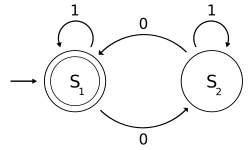
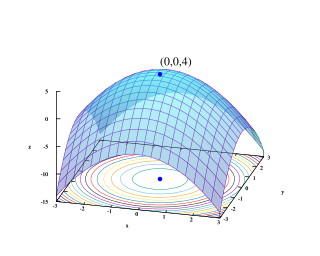
Construction
In business and engineering, mathematical models may be used to maximize a certain output. The system under consideration will require certain inputs. The system relating inputs to outputs depends on other variables too: decision variables, state variables, exogenous variables, and random variables. Decision variables are sometimes known as independent variables. Exogenous variables are sometimes known as parameters or constants. The variables are not independent of each other as the state variables are dependent on the decision, input, random, and exogenous variables. Furthermore, the output variables are dependent on the state of the system (represented by the state variables).
Objectives and constraints of the system and its users can be represented as functions of the output variables or state variables. The objective functions will depend on the perspective of the model's user. Depending on the context, an objective function is also known as an index of performance, as it is some measure of interest to the user. Although there is no limit to the number of objective functions and constraints a model can have, using or optimizing the model becomes more involved (computationally) as the number increases. For example, economists often apply linear algebra when using input–output models. Complicated mathematical models that have many variables may be consolidated by use of vectors where one symbol represents several variables.
A priori information

Mathematical modeling problems are often classified into black box or white box models, according to how much a priori information on the system is available. A black-box model is a system of which there is no a priori information available. A white-box model (also called glass box or clear box) is a system where all necessary information is available. Practically all systems are somewhere between the black-box and white-box models, so this concept is useful only as an intuitive guide for deciding which approach to take.
Usually, it is preferable to use as much a priori information as possible to make the model more accurate. Therefore, the white-box models are usually considered easier, because if you have used the information correctly, then the model will behave correctly. Often the a priori information comes in forms of knowing the type of functions relating different variables. For example, if we make a model of how a medicine works in a human system, we know that usually the amount of medicine in the blood is an exponentially decaying function, but we are still left with several unknown parameters; how rapidly does the medicine amount decay, and what is the initial amount of medicine in blood? This example is therefore not a completely white-box model. These parameters have to be estimated through some means before one can use the model.
In black-box models, one tries to estimate both the functional form of relations between variables and the numerical parameters in those functions. Using a priori information we could end up, for example, with a set of functions that probably could describe the system adequately. If there is no a priori information we would try to use functions as general as possible to cover all different models. An often used approach for black-box models are neural networks which usually do not make assumptions about incoming data. Alternatively, the NARMAX (Nonlinear AutoRegressive Moving Average model with eXogenous inputs) algorithms which were developed as part of nonlinear system identification [8] can be used to select the model terms, determine the model structure, and estimate the unknown parameters in the presence of correlated and nonlinear noise. The advantage of NARMAX models compared to neural networks is that NARMAX produces models that can be written down and related to the underlying process, whereas neural networks produce an approximation that is opaque.
Subjective information
Sometimes it is useful to incorporate subjective information into a mathematical model. This can be done based on intuition, experience, or expert opinion, or based on convenience of mathematical form. Bayesian statistics provides a theoretical framework for incorporating such subjectivity into a rigorous analysis: we specify a prior probability distribution (which can be subjective), and then update this distribution based on empirical data.
An example of when such approach would be necessary is a situation in which an experimenter bends a coin slightly and tosses it once, recording whether it comes up heads, and is then given the task of predicting the probability that the next flip comes up heads. After bending the coin, the true probability that the coin will come up heads is unknown; so the experimenter would need to make a decision (perhaps by looking at the shape of the coin) about what prior distribution to use. Incorporation of such subjective information might be important to get an accurate estimate of the probability.
Complexity
In general, model complexity involves a trade-off between simplicity and accuracy of the model. Occam's razor is a principle particularly relevant to modeling, its essential idea being that among models with roughly equal predictive power, the simplest one is the most desirable. While added complexity usually improves the realism of a model, it can make the model difficult to understand and analyze, and can also pose computational problems, including numerical instability. Thomas Kuhn argues that as science progresses, explanations tend to become more complex before a paradigm shift offers radical simplification. [9]
For example, when modeling the flight of an aircraft, we could embed each mechanical part of the aircraft into our model and would thus acquire an almost white-box model of the system. However, the computational cost of adding such a huge amount of detail would effectively inhibit the usage of such a model. Additionally, the uncertainty would increase due to an overly complex system, because each separate part induces some amount of variance into the model. It is therefore usually appropriate to make some approximations to reduce the model to a sensible size. Engineers often can accept some approximations in order to get a more robust and simple model. For example, Newton's classical mechanics is an approximated model of the real world. Still, Newton's model is quite sufficient for most ordinary-life situations, that is, as long as particle speeds are well below the speed of light, and we study macro-particles only. Note that better accuracy does not necessarily mean a better model. Statistical models are prone to overfitting which means that a model is fitted to data too much and it has lost its ability to generalize to new events that were not observed before.
Training, tuning, and fitting
Any model which is not pure white-box contains some parameters that can be used to fit the model to the system it is intended to describe. If the modeling is done by an artificial neural network or other machine learning, the optimization of parameters is called training, while the optimization of model hyperparameters is called tuning and often uses cross-validation. [10] In more conventional modeling through explicitly given mathematical functions, parameters are often determined by curve fitting.[ citation needed ]
Evaluation and assessment
A crucial part of the modeling process is the evaluation of whether or not a given mathematical model describes a system accurately. This question can be difficult to answer as it involves several different types of evaluation.
Prediction of empirical data
Usually, the easiest part of model evaluation is checking whether a model predicts experimental measurements or other empirical data not used in the model development. In models with parameters, a common approach is to split the data into two disjoint subsets: training data and verification data. The training data are used to estimate the model parameters. An accurate model will closely match the verification data even though these data were not used to set the model's parameters. This practice is referred to as cross-validation in statistics.
Defining a metric to measure distances between observed and predicted data is a useful tool for assessing model fit. In statistics, decision theory, and some economic models, a loss function plays a similar role. While it is rather straightforward to test the appropriateness of parameters, it can be more difficult to test the validity of the general mathematical form of a model. In general, more mathematical tools have been developed to test the fit of statistical models than models involving differential equations. Tools from nonparametric statistics can sometimes be used to evaluate how well the data fit a known distribution or to come up with a general model that makes only minimal assumptions about the model's mathematical form.
Scope of the model
Assessing the scope of a model, that is, determining what situations the model is applicable to, can be less straightforward. If the model was constructed based on a set of data, one must determine for which systems or situations the known data is a "typical" set of data. The question of whether the model describes well the properties of the system between data points is called interpolation, and the same question for events or data points outside the observed data is called extrapolation.
As an example of the typical limitations of the scope of a model, in evaluating Newtonian classical mechanics, we can note that Newton made his measurements without advanced equipment, so he could not measure properties of particles traveling at speeds close to the speed of light. Likewise, he did not measure the movements of molecules and other small particles, but macro particles only. It is then not surprising that his model does not extrapolate well into these domains, even though his model is quite sufficient for ordinary life physics.
Philosophical considerations
Many types of modeling implicitly involve claims about causality. This is usually (but not always) true of models involving differential equations. As the purpose of modeling is to increase our understanding of the world, the validity of a model rests not only on its fit to empirical observations, but also on its ability to extrapolate to situations or data beyond those originally described in the model. One can think of this as the differentiation between qualitative and quantitative predictions. One can also argue that a model is worthless unless it provides some insight which goes beyond what is already known from direct investigation of the phenomenon being studied.
An example of such criticism is the argument that the mathematical models of optimal foraging theory do not offer insight that goes beyond the common-sense conclusions of evolution and other basic principles of ecology. [11] It should also be noted that while mathematical modeling uses mathematical concepts and language, it is not itself a branch of mathematics and does not necessarily conform to any mathematical logic, but is typically a branch of some science or other technical subject, with corresponding concepts and standards of argumentation. [2]