
The Middle East is a geopolitical region commonly encompassing Arabia, Asia Minor, East Thrace, Egypt, Iran, the Levant, Mesopotamia, and the Socotra Archipelago. The term came into widespread usage as a replacement of the term Near East beginning in the early 20th century. The term "Middle East" has led to some confusion over its changing definitions, and has been viewed by some to be discriminatory or too Eurocentric. The region includes the vast majority of the territories included in the closely associated definition of Western Asia, but without the South Caucasus, and additionally includes all of Egypt and all of Turkey.
The Arab world, formally the Arab homeland, also known as the Arab nation, the Arabsphere, or the Arab states, refers to a vast group of countries, mainly located in Western Asia and Northern Africa, that linguistically or culturally share an Arab identity. A majority of people in these countries are either ethnically Arab or are Arabized, speaking the Arabic language, which is used as the lingua franca throughout the Arab world.
Yemen is a country on the Arabian Peninsula, and the music of Yemen is primarily known abroad for a series of pan-Arab popular stars and the Yemenite Jews who became musical stars in Israel during the 20th century. In the Arab world, Yemen has long been a cultural capital.
The music of Iran encompasses music that is produced by Iranian artists. In addition to the traditional folk and classical genres, it also includes pop and internationally celebrated styles such as jazz, rock, and hip hop.
Mizrahi Jews, also known as Mizrahim (מִזְרָחִים) or Mizrachi (מִזְרָחִי) and alternatively referred to as Oriental Jews or Edot HaMizrach, are a grouping of Jewish communities comprising those who remained in the Land of Israel and those who existed in diaspora throughout and around the Middle East and North Africa (MENA) from biblical times into the modern era.

Tamer Nafar is an Israeli rapper, actor, screenwriter and social activist who identifies as Palestinian. He is the leader and a founding member of DAM, the first Palestinian hip hop group.
Israeli hip hop refers to hip hop and rap music in Israel.
Tanzanian Hip-hop, which is sometimes called Bongo Flava by many outside of Tanzania's hip hop community, encompasses a large variety of different sounds, but it is particularly known for heavy synth riffs and an incorporation of Tanzanian pop. There is some debate over whether Bongo Flava, which has emerged as a defined pop movement, can really still be qualified under the overarching term "hip hop" and not a movement unto itself, when it is beginning to develop a distinctive sound that differs from hardcore rap or, for example, the Maasai Hip hop of X Plastaz, who use the tradition of the Maasai tribe as the focal point for their sound and style. Tanzanian hip hop influenced the sound of the Bongo Flava genre. While Tanzanian hip hop retains many of the elements found in hip hop globally in terms of sound and lyricism, Bongo flava, derived from the Swahili word "ubongo", incorporates hip hop, Indian filmi, taraab, muzik wa dansi, and dancehall beats. It all began in the 1980s when Tanzanian teenagers were really interested in the American hip hop scene. At first, they took American beats and rapped to them. As the youth rapped, the hip hop in Tanzania began to develop into a mix of traditional and localized hip hop scene. As a result, it began a wave of interest from other people in Eastern Africa.
The various nations of the region include the Arabic-speaking countries of the Middle East, the Iranian traditions of Persia, the Jewish music of Israel and the diaspora, Armenian music, Kurdish music, Azeri Music, the varied traditions of Cypriot music, the music of Turkey, traditional Assyrian music, Coptic ritual music in Egypt as well as other genres of Egyptian music in general, and the Andalusian music very much alive in the greater Middle East, all maintain their own traditions. It is widely regarded that some Middle-Eastern musical styles have influenced Central Asia, as well as Spain, and the Balkans.
Arabic hip-hop is a segment of hip hop music performed in the Arabic-speaking world. Due to variety of dialects and local genres which exist in the localities, Arabic hip-hop music may appear very diverse depending on the country of the song. Like most artists of the genre, the hip-hop artists from the Arabic-speaking world are highly influenced by American hip-hop. Emcees of the worldwide Arabic diaspora, including Europe, North America, and Australia, are also attributed as part of Arabic hip-hop scene.
Iranian hip hop, also known to as Persian hip hop, refers to hip hop music developed in Iran (Persia) and in Persian language. It is rooted in American hip hop culture, but it has sometimes incorporated local elements such as Iranian classical music and literature.

Political hip-hop is a subgenre of hip hop music that was developed in the 1980s as a way of turning hip hop into a call for political and/or social action and a form of social and/or political activism. Inspired by 1970s political artists such as The Last Poets and musician Gil Scott-Heron, Public Enemy was the first predominantly political hip-hop group. The genre has helped to create a new form of social expression for subordinate groups to speak about their exclusions, injustices and lack of power. Political hip-hop is the use of hip hop music to send political messages to inspire action or social change or to convince the listener of a particular worldview. There is no all-encompassing political hip-hop ideology; rather, there are multiple perspectives that range anywhere from anarchism to Marxism to the values of the Five-Percent Nation. Hip hop and politics have long been intertwined, with many hip hop artists using their music as a means to speak out about political issues and express their views on current events. Over the years, there have been a number of hip hop songs that have addressed political issues such as police brutality, racism, and poverty, among others. Some well-known examples of political hip hop songs include "F*ck tha Police" by N.W.A., "Changes" by Tupac Shakur, and "Fight the Power" by Public Enemy.

The composite Turko-Persian, Turco-Persian or Turco-Iranian tradition was a distinctive culture that arose in the 9th and 10th centuries in Khorasan and Transoxiana.

Palestinian hip hop reportedly started in 1998 with Tamer Nafar's group DAM. These Palestinian youth forged the new Palestinian musical subgenre, which blends Arabic melodies and hip hop beats. Lyrics are often sung in Arabic, Hebrew, English, and sometimes French. Since then, the new Palestinian musical subgenre has grown to include artists in Palestine, Israel, Great Britain, the United States and Canada.

Soroush Lashkari, known professionally as Hichkas, is an Iranian rapper, singer, and songwriter. Credited with popularizing Persian hip hop to the Iranian people and other Persian-speaking countries such as Afghanistan and Tajikistan, Hichkas's national success and acclaimed works are widely regarded as having broken the barriers that were in place by the Islamic regime for the acceptance of rappers in popular music. Hichkas is considered one of the pioneers of Iranian hip hop and is nicknamed "Father of Persian Rap" by his fans. He became a representation of the Iranian underclass and reflected the angst of the young Iranians. He has been influential for many artists of various genres and is often cited as one of the greatest rappers of Iranian hip hop.

Shadia Mansour, also known as "the first lady of Arabic hip hop" is a British-Palestinian rapper who performs in Arabic and English. Much of her music revolves around Middle Eastern politics.
Lebanese Hip Hop is a pioneering movement in Arabic hip hop as Lebanese youth were among the first to be affected by hip hop culture. Arabic hip hop has received Western media attention, but most Lebanese rappers think that there is still a lack of local interest in their music. Hip hop in Lebanon is both an art form and a stage for artists to voice their alternative discourse in the public sphere.

Islamic graffiti is a genre of graffiti created by people who usually relate to the Middle East or North Africa, using Arabic or other languages for social or political messages. It is a popular art genre created by "artists, graffiti writers, designers and typographers from the Middle East and around the world who merge Arabic calligraphy with the art of graffiti writing, street art and urban culture."
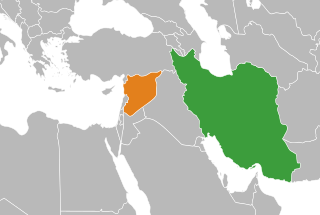
Syria and Iran are strategic allies. Syria is usually called Iran's "closest ally", with ideological conflict between the Arab nationalism ideology of Syria's secular ruling Ba'ath Party and the Islamic Republic of Iran's pan-Islamist policy notwithstanding. Iran and Syria have had a strategic alliance ever since the Iran–Iraq War, when Syria sided with non-Arab Iran against neighbouring Ba'ath-ruled Iraq. The two countries shared a common animosity towards then Iraqi president Saddam Hussein and coordination against the United States and Israel.
Yemeni hip hop is a Yemeni music style and cultural movement related to rap and hip hop culture. It has influences from American hip hop and also from traditional music from the region. It is usually considered to have emerged from mid-2000s and reached its consolidation by 2009 when the first public concert was held in the French Cultural Institute. Although it has a variety of themes, there was an intense production of political songs by the Yemeni Revolution.









