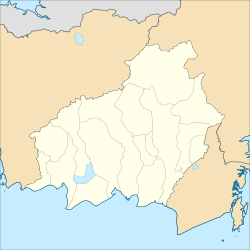
South Kalimantan is a province of Indonesia. It is the smallest province in Kalimantan, the Indonesian territory of Borneo. The provincial capital was Banjarmasin until 15 February 2022 when it was legally moved to Banjarbaru. The population of South Kalimantan was recorded at just over 3.625 million people at the 2010 Census, and at 4.07 million at the 2020 Census. The official estimate as at mid 2021 was 4,112,576. One of the five Indonesian provinces in Kalimantan, it is bordered by the Makassar Strait in the east, Central Kalimantan in the west and north, the Java Sea in the south, and East Kalimantan in the north. The province also includes the island of Laut, located off the eastern coast of Kalimantan. The province is divided into 11 regencies and 2 cities. South Kalimantan is the traditional homeland of the Banjar people, although some parts of East Kalimantan and Central Kalimantan are also included in this criteria. Nevertheless, South Kalimantan, especially the former capital city Banjarmasin has always been the cultural capital of Banjarese culture. Many Banjarese have migrated to other parts of Indonesia, as well as neighbouring countries such as Singapore and Malaysia. In addition, other ethnic groups also inhabit the province, such as several groups of the Dayaks, who mostly live in the interior part of the province, as well as the Javanese, who mostly migrated from Java due to the Transmigration program which dated from the Dutch colonial era.
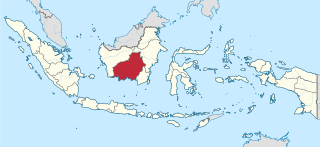
Central Kalimantan is a province of Indonesia. It is one of five provinces in Kalimantan, the Indonesian part of Borneo. Its provincial capital is Palangka Raya and in 2010 its population was over 2.2 million, while the 2015 Intermediate Census showed a rise to 2.49 million and the 2020 Census showed a total of 2.67 million; the official estimate as at mid 2021 was 2,702,200.

Palangka Raya is the capital and largest city of the Indonesian province of Central Kalimantan. The city is situated between the Kahayan and the Sabangau rivers on the island of Borneo. As of the 2020 census, the city has a population of 293,500. Palangka Raya is the largest city by land area in Indonesia. Most of the area is forested. It also has the highest Human Development Index rating of any city in Kalimantan.

Ma'anyan, Dayak Maanyan or Eastern Barito Dayak people are a sub-ethnic group of the Dayak people indigenous to Borneo. They are also considered as part of the east Barito Dusun group with the name Dusun Ma'anyan. According to J. Mallinckrodt (1927), the Dusun people group is part of the Ot Danum people cluster, although later that theory was disproved by A. B. Hudson (1967), who argues that the Ma'anyan people are a branch of the Barito family. The Ma'anyan people who are often referred to as Dayak people are also referred to as Dayak Ma'anyan. The Dayak Ma'anyan people inhabit the east side of Central Kalimantan, especially in the East Barito Regency and parts of South Barito Regency which are grouped as Ma'anyan I. The Dayak Ma'anyan people also inhabit the northern parts of South Kalimantan, especially in Tabalong Regency which refers to the Dayak Warukin people. The Dayak Balangan people or Dusun Balangan people which are found in the Balangan Regency and the Dayak Samihim people that are found in the Kotabaru Regency are grouped together with the Dayak Ma'anyan people group. The Dayak Ma'anyan people in South Kalimantan are grouped as Ma'anyan II.
Lawangan or Luangan people are a sub-ethnic of the Dayak Dusun people group, sometimes also referred to as Dusun Lawangan or Dayak Lawangan. The Lawangan people inhabit the eastern side of Central Kalimantan and West Kutai Regency, East Kalimantan, Indonesia. In Tabalong Regency, South Kalimantan, the Lawangan people can be found only in Binjai village. They speak Lawangan language.

Bakumpai or Baraki are indigenous people of Borneo and are considered as a sub-ethnic group of the Dayak Ngaju people group with Islamic background. The Bakumpai people first occupy along the Barito riverbanks in South Kalimantan and Central Kalimantan, from Marabahan to Puruk Cahu, Murung Raya Regency. The Bakumpai people first appeared as a newly recognized people group in census 2000 and were made up of 7.51% of Central Kalimantan population, which before this the Bakumpai people were considered as part of the Dayak people in a 1930 census.
The Negara River is a river of Borneo, Indonesia. It flows in the southeast region of the island, within the Negara District, province of South Kalimantan. It is the second longest river in the province after the Barito River, which the Negara River flows into.

South Barito Regency is a regency in Central Kalimantan province of Indonesia. The regency seat is located in town of Buntok, located in South Dusun district. The population of South Barito Regency was 124,128 at the 2010 Census and 131,100 at the 2020 Census.

North Barito Regency is one of the thirteen regencies which divide the Central Kalimantan Province on the island of Kalimantan, Indonesia. Muara Teweh is the capital of North Barito Regency, which covers an area of 8,300 km2. The population of North Barito Regency was 121,573 at the 2010 Census, and 154,800 at the 2020 Census.

Gunung Mas Regency is one of the thirteen regencies of Central Kalimantan Province, Indonesia. The regency seat is located at the town of Kuala Kurun in Kurun District. The population of Gunung Mas Regency was 96,900 at the 2010 Census ; and 135,373 at the 2020 Census.

Kapuas Regency is one of the thirteen regencies which divide Central Kalimantan Province, on the island of Kalimantan, Indonesia. It formerly covered a wider area, but in 2002 two further regencies were cut out of it, and the residual area is now 14,999 km.2 Its population was 329,646 at the 2010 Census and 410,400 at the 2020 Census. The capital is the town of Kuala Kapuas.

Seruyan Regency is one of the thirteen regencies which comprise the Central Kalimantan Province on the island of Kalimantan (Borneo), Indonesia. The town of Kuala Pembuang in Seruyan Hilir District is the capital of Seruyan Regency. The population of the Regency was 139,931 at the 2010 Census and 162,906 at the 2020 census.

Tanjung Selor is the capital of both the North Kalimantan province in Indonesia, and of the Bulungan Regency. It is among provincial capitals in Indonesia that as of 2021 does not yet have city status, together with Mamuju in West Sulawesi, Sofifi in North Maluku, Nabire in Central Papua, Wamena in Highland Papua, Merauke in South Papua, and Manokwari in West Papua. The district has an area of 677.77 km2 and had a population of 39,439 at the 2010 Census and 56,569 at the 2020 Census.

Tamiang Layang, a sub-district in the district of Dusun Timur, is the regency seat of East Barito Regency and also one of the towns in Central Kalimantan. This town is at a distance of 287 km east of Palangka Raya city, the capital of Central Kalimantan Province. The population of this town is roughly 10,780 people as of 2021.

Kuala Kurun, a sub-district in the district of Kurun, is the regency seat of Gunung Mas Regency and also one of the towns in Central Kalimantan. This town is located 163 km north of Palangka Raya city, the capital of Central Kalimantan Province. The population of this town is roughly 12,870 people as of 2021.

Buntok, a sub-district in the district of Dusun Selatan, is the regency seat of South Barito Regency and also one of the towns in Central Kalimantan province, Indonesia. This town is also called Buntok Kota by the people from Central Kalimantan. This town is at a distance of 197 km east of Palangka Raya city, the capital of Central Kalimantan Province. The population of this town is roughly 16,864 people as of 2020.

Puruk Cahu, a sub-district in the district of Murung, is the regency seat of Murung Raya Regency and also one of the towns in Central Kalimantan. This town is at a distance of 322 km northeast of Palangka Raya city, the capital of Central Kalimantan Province. The population of this town is approximately 2,659 people as of 2021.