Related Research Articles

The enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay (ELISA) is a commonly used analytical biochemistry assay, first described by Eva Engvall and Peter Perlmann in 1971. The assay is a solid-phase type of enzyme immunoassay (EIA) to detect the presence of a ligand in a liquid sample using antibodies directed against the ligand to be measured. ELISA has been used as a diagnostic tool in medicine, plant pathology, and biotechnology, as well as a quality control check in various industries.
A biosensor is an analytical device, used for the detection of a chemical substance, that combines a biological component with a physicochemical detector. The sensitive biological element, e.g. tissue, microorganisms, organelles, cell receptors, enzymes, antibodies, nucleic acids, etc., is a biologically derived material or biomimetic component that interacts with, binds with, or recognizes the analyte under study. The biologically sensitive elements can also be created by biological engineering. The transducer or the detector element, which transforms one signal into another one, works in a physicochemical way: optical, piezoelectric, electrochemical, electrochemiluminescence etc., resulting from the interaction of the analyte with the biological element, to easily measure and quantify. The biosensor reader device connects with the associated electronics or signal processors that are primarily responsible for the display of the results in a user-friendly way. This sometimes accounts for the most expensive part of the sensor device, however it is possible to generate a user friendly display that includes transducer and sensitive element. The readers are usually custom-designed and manufactured to suit the different working principles of biosensors.
An assay is an investigative (analytic) procedure in laboratory medicine, mining, pharmacology, environmental biology and molecular biology for qualitatively assessing or quantitatively measuring the presence, amount, or functional activity of a target entity. The measured entity is often called the analyte, the measurand, or the target of the assay. The analyte can be a drug, biochemical substance, chemical element or compound, or cell in an organism or organic sample. An assay usually aims to measure an analyte's intensive property and express it in the relevant measurement unit.
Plate readers, also known as microplate readers or microplate photometers, are instruments which are used to detect biological, chemical or physical events of samples in microtiter plates. They are widely used in research, drug discovery, bioassay validation, quality control and manufacturing processes in the pharmaceutical and biotechnological industry and academic organizations. Sample reactions can be assayed in 1-1536 well format microtiter plates. The most common microplate format used in academic research laboratories or clinical diagnostic laboratories is 96-well with a typical reaction volume between 100 and 200 µL per well. Higher density microplates are typically used for screening applications, when throughput and assay cost per sample become critical parameters, with a typical assay volume between 5 and 50 µL per well. Common detection modes for microplate assays are absorbance, fluorescence intensity, luminescence, time-resolved fluorescence, and fluorescence polarization.

A radioimmunoassay (RIA) is an immunoassay that uses radiolabeled molecules in a stepwise formation of immune complexes. A RIA is a very sensitive in vitro assay technique used to measure concentrations of substances, usually measuring antigen concentrations by use of antibodies.
An immunoassay (IA) is a biochemical test that measures the presence or concentration of a macromolecule or a small molecule in a solution through the use of an antibody (usually) or an antigen (sometimes). The molecule detected by the immunoassay is often referred to as an "analyte" and is in many cases a protein, although it may be other kinds of molecules, of different sizes and types, as long as the proper antibodies that have the required properties for the assay are developed. Analytes in biological liquids such as serum or urine are frequently measured using immunoassays for medical and research purposes.

A lateral flow test (LFT), is an assay also known as a lateral flow device (LFD), lateral flow immunochromatographic assay, or rapid test. It is a simple device intended to detect the presence of a target substance in a liquid sample without the need for specialized and costly equipment. LFTs are widely used in medical diagnostics in the home, at the point of care, and in the laboratory. For instance, the home pregnancy test is an LFT that detects a specific hormone. These tests are simple and economical and generally show results in around five to thirty minutes. Many lab-based applications increase the sensitivity of simple LFTs by employing additional dedicated equipment. Because the target substance is often a biological antigen, many lateral flow tests are rapid antigen tests.

Anti-double stranded DNA (Anti-dsDNA) antibodies are a group of anti-nuclear antibodies (ANA) the target antigen of which is double stranded DNA. Blood tests such as enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay (ELISA) and immunofluorescence are routinely performed to detect anti-dsDNA antibodies in diagnostic laboratories. They are highly diagnostic of systemic lupus erythematosus (SLE) and are implicated in the pathogenesis of lupus nephritis.
Magnetic immunoassay (MIA) is a type of diagnostic immunoassay using magnetic beads as labels in lieu of conventional enzymes (ELISA), radioisotopes (RIA) or fluorescent moieties to detect a specified analyte. MIA involves the specific binding of an antibody to its antigen, where a magnetic label is conjugated to one element of the pair. The presence of magnetic beads is then detected by a magnetic reader (magnetometer) which measures the magnetic field change induced by the beads. The signal measured by the magnetometer is proportional to the analyte concentration in the initial sample.
A reverse phase protein lysate microarray (RPMA) is a protein microarray designed as a dot-blot platform that allows measurement of protein expression levels in a large number of biological samples simultaneously in a quantitative manner when high-quality antibodies are available.
Suspension array technology is a high throughput, large-scale, and multiplexed screening platform used in molecular biology. SAT has been widely applied to genomic and proteomic research, such as single nucleotide polymorphism (SNP) genotyping, genetic disease screening, gene expression profiling, screening drug discovery and clinical diagnosis. SAT uses microsphere beads to prepare arrays. SAT allows for the simultaneous testing of multiple gene variants through the use of these microsphere beads as each type of microsphere bead has a unique identification based on variations in optical properties, most common is fluorescent colour. As each colour and intensity of colour has a unique wavelength, beads can easily be differentiated based on their wavelength intensity. Microspheres are readily suspendable in solution and exhibit favorable kinetics during an assay. Similar to flat microarrays, an appropriate receptor molecule, such as DNA oligonucleotide probes, antibodies, or other proteins, attach themselves to the differently labeled microspheres. This produces thousands of microsphere array elements. Probe-target hybridization is usually detected by optically labeled targets, which determines the relative abundance of each target in the sample.
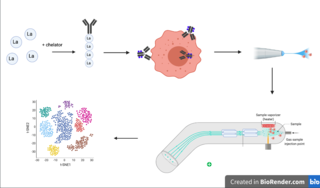
Cytometry by time of flight, or CyTOF, is an application of mass cytometry used to quantify labeled targets on the surface and interior of single cells. CyTOF allows the quantification of multiple cellular components simultaneously using an ICP-MS detector.
Mass spectrometric immunoassay (MSIA) is a rapid method is used to detect and/ or quantify antigens and or antibody analytes. This method uses an analyte affinity isolation to extract targeted molecules and internal standards from biological fluid in preparation for matrix assisted laser desorption ionization-time of flight mass spectrometry (MALDI-TOF-MS). This method allows for "top down" and "bottom up" analysis. This sensitive method allows for a new and improved process for detecting multiple antigens and antibodies in a single assay. This assay is also capable of distinguishing mass shifted forms of the same molecule via a panantibody, as well as distinguish point mutations in proteins. Each specific form is detected uniquely based on their characteristic molecular mass. MSIA has dual specificity because of the antibody-antigen reaction coupled with the power of a mass spectrometer.
A ligand binding assay (LBA) is an assay, or an analytic procedure, which relies on the binding of ligand molecules to receptors, antibodies or other macromolecules. A detection method is used to determine the presence and extent of the ligand-receptor complexes formed, and this is usually determined electrochemically or through a fluorescence detection method. This type of analytic test can be used to test for the presence of target molecules in a sample that are known to bind to the receptor.
Ayoxxa Biosystems is a biotechnology company founded in 2010 in Singapore, and headquartered in Germany.
A hybridization assay comprises any form of quantifiable hybridization i.e. the quantitative annealing of two complementary strands of nucleic acids, known as nucleic acid hybridization.
Stable isotope standards and capture by anti-peptide antibodies (SISCAPA) is a mass spectrometry method for measuring the amount of a protein in a biological sample.

Fluorescence polarization immunoassay (FPIA) is a class of in vitro biochemical test used for rapid detection of antibody or antigen in sample. FPIA is a competitive homogenous assay, that consists of a simple prepare and read method, without the requirement of separation or washing steps.

Multiplexed point-of-care testing (xPOCT) is a more complex form of point-of-care testing (POCT), or bedside testing. Point-of-care testing is designed to provide diagnostic tests at or near the time and place that the patient is admitted. POCT uses the concentrations of analytes to provide the user with information on the physiological state of the patient. An analyte is a substance, chemical or biological, that is being analyzed using a certain instrument. While point-of-care testing is the quantification of one analyte from one in vitro sample, multiplexed point-of-care testing is the simultaneous on-site quantification of various analytes from a single sample.
The proximity extension assay (PEA) is a method for detecting and quantifying the amount of many specific proteins present in a biological sample such a serum or plasma. The method is used in the research field of proteomics, specifically affinity proteomics, where in one searches for differences in the abundance of many specific proteins in blood for use as a biomarker. Biomarkers and biomarker signature combinations, are useful for determining disease states and drug efficacy. Most methods for detecting proteins involve the use of a solid phase for first capturing and immobilizing the protein analyte, where in one or a few proteins are quantified, such as ELISA. In contrast, PEA is performed without a solid phase in a homogeneous one tube reaction solution where in sets of antibodies coupled to unique DNA sequence tags, so called proximity probes, work in pairs specific for each target protein. PEA is often performed using antibodies and is a type of immunoassay. Target binding by the proximity probes increases their local relative effective concentration of the DNA-tags enabling hybridization of weak complementarity to each other which then enables a DNA polymerase mediated extension forming a united DNA sequence specific for each target protein detected. The use of 3'exonuclease proficient polymerases lowers background noise and hyper thermostable polymerases mediate a simple assay with a natural hot-start reaction. This created pool of extension products of DNA sequence forms amplicons amplified by PCR where each amplicon sequence corresponds to a target proteins identity and the amount reflects its quantity. Subsequently, these amplicons are detected and quantified by either real-time PCR or next generation DNA sequencing by DNA-tag counting. PEA enables the detection of many proteins simultaneously due to the readout requiring the combination of two correctly bound antibodies per protein to generate a detectable DNA sequence from the extension reaction. Only cognate pairs of sequence are detected as true signal, enabling multiplexing beyond solid phase capture methods limited at around 30 proteins at a time. The DNA amplification power also enable minute sample volumes even below one microliter. PEA has been used in over 1000 research publications.
References
- ↑ Elshal, Mohamed F.; McCoy, J. Philip (2005-11-01). "Multiplex bead array assays: Performance evaluation and comparison of sensitivity to ELISA". Methods. 38 (4): 317–323. doi:10.1016/j.ymeth.2005.11.010. PMC 1534009 . PMID 16481199.
- ↑ Tighe, Patrick J.; Ryder, Richard R.; Todd, Ian; Fairclough, Lucy C. (April 2015). "ELISA in the multiplex era: Potentials and pitfalls". Proteomics – Clinical Applications. 9 (3–4): 406–422. doi:10.1002/prca.201400130. PMC 6680274 . PMID 25644123.
- ↑ Leng, SX; McElhaney, JE; Walston, JD; Xie, D; Fedarko, NS; Kuchel, GA (August 2008). "ELISA and multiplex technologies for cytokine measurement in inflammation and aging research". The Journals of Gerontology. Series A, Biological Sciences and Medical Sciences. 63 (8): 879–84. doi:10.1093/gerona/63.8.879. PMC 2562869 . PMID 18772478.