Octane is a hydrocarbon and an alkane with the chemical formula C8H18, and the condensed structural formula CH3(CH2)6CH3. Octane has many structural isomers that differ by the amount and location of branching in the carbon chain. One of these isomers, 2,2,4-trimethylpentane (commonly called iso-octane) is used as one of the standard values in the octane rating scale.
Ethane is an organic chemical compound with chemical formula C
2H
6. At standard temperature and pressure, ethane is a colorless, odorless gas. Like many hydrocarbons, ethane is isolated on an industrial scale from natural gas and as a petrochemical by-product of petroleum refining. Its chief use is as feedstock for ethylene production.

Terpenes are a class of natural products consisting of compounds with the formula (C5H8)n. Comprising more than 30,000 compounds, these unsaturated hydrocarbons are produced predominantly by plants, particularly conifers. Terpenes are further classified by the number of carbons: monoterpenes (C10), sesquiterpenes (C15), diterpenes (C20), etc. A well known monoterpene is alpha-pinene, a major component of turpentine.
Decane is an alkane hydrocarbon with the chemical formula C10H22. Although 75 structural isomers are possible for decane, the term usually refers to the normal-decane ("n-decane"), with the formula CH3(CH2)8CH3. All isomers, however, exhibit similar properties and little attention is paid to the composition. These isomers are flammable liquids. Decane is a component of gasoline (petrol) and kerosene. Like other alkanes, it is a nonpolar solvent, does not dissolve in water, and is readily combustible. Although it is a component of fuels, it is of little importance as a chemical feedstock, unlike a handful of other alkanes.
Dodecane (also known as dihexyl, bihexyl, adakane 12, or duodecane) is a liquid alkane hydrocarbon with the chemical formula CH3(CH2)10CH3 (or C12H26), an oily liquid of the paraffin series. It has 355 isomers.
Tridecane or n-tridecane is an alkane with the chemical formula CH3(CH2)11CH3 Tridecane is a combustible colourless liquid. In industry, they have no specific value aside from being components of various fuels and solvents. In the research laboratory, tridecane is also used as a distillation chaser.
Tetradecane is an alkane hydrocarbon with the chemical formula CH3(CH2)12CH3.
Heptadecane is an organic compound, an alkane hydrocarbon with the chemical formula C17H36. The name may refer to any of 24894 theoretically possible structural isomers, or to a mixture thereof.
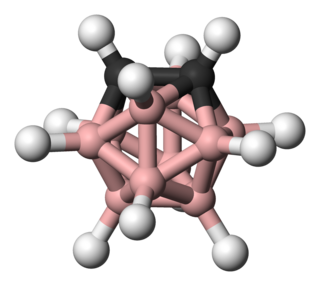
Carboranes are electron-delocalized clusters composed of boron, carbon and hydrogen atoms that may also contain other metallic and nonmetallic elements in the cluster framework. Like many of the related boron hydrides, these clusters are polyhedra or fragments of polyhedra, and are similarly classified as closo-, nido-, arachno-, hypho-, etc., based on whether they represent a complete (closo-) polyhedron or a polyhedron that is missing one (nido-), two (arachno-), three (hypho-), or more vertices. Carboranes are a notable example of heteroboranes.

2,2,4-Trimethylpentane, also known as isooctane or iso-octane, is an organic compound with the formula (CH3)3CCH2CH(CH3)2. It is one of several isomers of octane (C8H18). This particular isomer is the standard 100 point on the octane rating scale (the zero point is n-heptane). It is an important component of gasoline, frequently used in relatively large proportions to increase the knock resistance of the fuel.
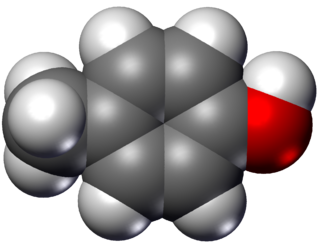
para-Cresol, also 4-methylphenol, is an organic compound with the formula CH3C6H4(OH). It is a colourless solid that is widely used intermediate in the production of other chemicals. It is a derivative of phenol and is an isomer of o-cresol and m-cresol.
Carbon–hydrogen bond functionalization is a type of reaction in which a carbon–hydrogen bond is cleaved and replaced with a carbon–X bond. The term usually implies that a transition metal is involved in the C-H cleavage process. Reactions classified by the term typically involve the hydrocarbon first to react with a metal catalyst to create an organometallic complex in which the hydrocarbon is coordinated to the inner-sphere of a metal, either via an intermediate "alkane or arene complex" or as a transition state leading to a "M−C" intermediate. The intermediate of this first step can then undergo subsequent reactions to produce the functionalized product. Important to this definition is the requirement that during the C–H cleavage event, the hydrocarbyl species remains associated in the inner-sphere and under the influence of "M".

Triterpenes are a class of chemical compounds composed of three terpene units with the molecular formula C30H48; they may also be thought of as consisting of six isoprene units. Animals, plants and fungi all produce triterpenes, including squalene, the precursor to all steroids.

Tetrathiafulvalene is an organosulfur compound with the formula (H2C2S2C)2. Studies on this heterocyclic compound contributed to the development of molecular electronics. TTF is related to the hydrocarbon fulvalene, (C5H4)2, by replacement of four CH groups with sulfur atoms. Over 10,000 scientific publications discuss TTF and its derivatives.
Tributyltin hydride is an organotin compound with the formula (C4H9)3SnH. It is a colorless liquid that is soluble in organic solvents. The compound is used as a source of hydrogen atoms in organic synthesis.
Organosodium chemistry is the chemistry of organometallic compounds containing a carbon to sodium chemical bond. The application of organosodium compounds in chemistry is limited in part due to competition from organolithium compounds, which are commercially available and exhibit more convenient reactivity.
Tetramethylbutane, sometimes called hexamethylethane, is a hydrocarbon with formula C8H18 or (H3C-)3C-C(-CH3)3. It is the most heavily branched and most compact of the many octane isomers, the only one with a butane (C4) backbone. Because of its highly symmetrical structure, it has a very high melting point and a short liquid range; in fact, it is the smallest saturated acyclic hydrocarbon that appears as a solid at a room temperature of 25 °C. (Among cyclic hydrocarbons, cubane, C8H8 is even smaller and is also solid at room temperature.)
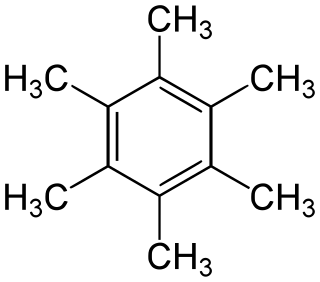
Hexamethylbenzene, also known as mellitene, is a hydrocarbon with the molecular formula C12H18 and the condensed structural formula C6(CH3)6. It is an aromatic compound and a derivative of benzene, where benzene's six hydrogen atoms have each been replaced by a methyl group. In 1929 Kathleen Lonsdale reported the crystal structure of hexamethylbenzene, demonstrating that the central ring is hexagonal and flat and thereby ending an ongoing debate about the physical parameters of the benzene system. This was a historically significant result, both for the field of X-ray crystallography and for understanding aromaticity.
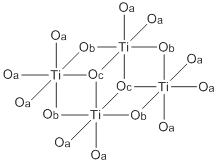
Titanium ethoxide is a chemical compound with the formula Ti4(OCH2CH3)16. It is a colorless liquid that is soluble in organic solvents but hydrolyzes readily. It is sold commercially as a colorless solution. Alkoxides of titanium(IV) and zirconium(IV) are used in organic synthesis and materials science. They adopt more complex structures than suggested by their empirical formulas.

Ortho-carborane is the organoboron compound with the formula C2B10H12. The prefix ortho is derived from ortho. It is the most prominent carborane. This derivative has been considered for a wide range of applications from heat-resistant polymers to medical applications. It is a colorless solid that melts, without decomposition, at 320 °C.









