
The Reading Company was a Philadelphia-headquartered railroad that provided passenger and commercial rail transport in eastern Pennsylvania and neighboring states that operated from 1924 until its acquisition by Conrail in 1976.

The SEPTA Regional Rail system is a commuter rail network owned by SEPTA and serving the Philadelphia metropolitan area. The system has 13 branches and more than 150 active stations in Philadelphia, Pennsylvania, its suburbs and satellite towns and cities. It is the fifth-busiest commuter railroad in the United States, and the busiest outside of the New York and Chicago metropolitan areas. In 2016, the Regional Rail system had an average of 132,000 daily riders and 118,800 daily riders.
Schuylkill River Passenger Rail is a proposed passenger train service along the Schuylkill River between Philadelphia and Reading, Pennsylvania, with intermediate stops in Norristown, King of Prussia, Phoenixville, and Pottstown.

The SEPTA Main Line is the section of the SEPTA Regional Rail system from the Zoo Interlocking in West Philadelphia to Lansdale Station in Lansdale, Pennsylvania. The line is 26.25 miles (42.25 km) long, and serves all 13 SEPTA Regional Rail lines.

Lansdale station, also known as the Lansdale Transportation Center, is a SEPTA Regional Rail station in Lansdale, Pennsylvania. Located at Main Street and Green Street, it serves the Lansdale/Doylestown Line. It was originally built in 1902 by the Reading Company, opening on February 7, 1903; a freight house was added in 1909. Historically, the station hosted the Interstate Express and the Scranton Flyer. Additionally, the station served commuter trains on the Reading's branch to Bethlehem until service was ended in 1981. The historic station building was listed on the National Register of Historic Places in 2021.

The Trenton Subdivision is a railroad line owned by CSX Transportation in the U.S. states of Pennsylvania and New Jersey. The line runs from CP PARK in Philadelphia, Pennsylvania, northeast to Port Reading Junction in Manville, New Jersey, along a former Reading Company line.
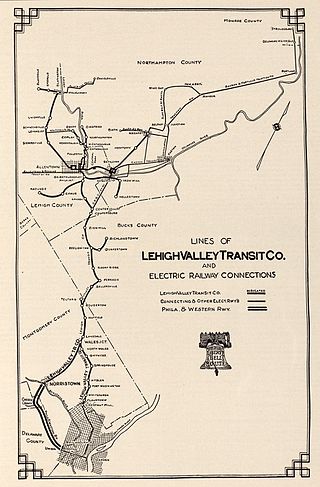
The Lehigh Valley Transit Company (LVT) was a regional transport company that was headquartered in Allentown, Pennsylvania. The company began operations in 1901, as an urban trolley and interurban rail transport company. It operated successfully into the 1930s, but struggled financially during the Great Depression, and was saved from abandonment by a dramatic ridership increase during and following World War II.

The Perkasie Tunnel is a train tunnel located behind the Post Office in Perkasie, Pennsylvania on 7th Street, on a line owned by SEPTA and operated by the East Penn Railroad. The tunnel itself is located near 8th Street and Ridge Road. Northbound passenger trains going through the tunnel traveled to Union Station in Bethlehem and points beyond. Many southbound passenger trains were destined for Reading Terminal in Philadelphia. The Perkasie station on 8th Street was formerly equipped with a water tower, of which not a trace remains.

The Warminster Line is a route of the SEPTA Regional Rail commuter rail system. It serves stations between its namesake town, Warminster, and Center City, Philadelphia. Half of the route is shared by other lines, including the Lansdale/Doylestown Line, West Trenton Line, Fox Chase Line, Chestnut Hill East Line, and Manayunk/Norristown Line. The great majority of trains continue as part of the Airport Line.

The Lansdale/Doylestown Line is a SEPTA Regional Rail line connecting Center City Philadelphia to Doylestown in Bucks County, Pennsylvania. Until 1981, diesel-powered trains continued on the Bethlehem Branch from Lansdale to Quakertown, Bethlehem, and Allentown. Restored service has been proposed, but is not planned by SEPTA. The line is currently used by the East Penn Railroad, serving Quakertown's industrial complexes and distribution centers. With around 17,000 daily riders every weekday in 2019, it is the second busiest line in SEPTA's Regional Rail network.

The Pennsylvania Northeastern Railroad is a short-line railroad operating on trackage mostly in Bucks and Montgomery counties to the north of Philadelphia, Pennsylvania. It was created in 2011, taking over former operations from CSX Transportation. The Pennsylvania Northeastern Railroad interchanges with CSX in Lansdale, the East Penn Railroad in Telford, and the New Hope Railroad in Warminster.

Bethlehem Union Station is a former train station located in the South Side neighborhood of Bethlehem, Pennsylvania. It was built in 1924 by the Lehigh Valley Railroad and the Reading Company, replacing an earlier station built in 1867. Passenger service to Philadelphia on the SEPTA Regional Rail Bethlehem Line lasted until 1981. The station was renovated in 2002 and used for medical clinics beginning in 2003. It is owned by St. Luke's Hospital.
The Bethlehem Line was a SEPTA Regional Rail service on the former Reading Company Bethlehem Branch between Lansdale and Bethlehem, Pennsylvania. Some trains continued over the electrified Lansdale/Doylestown Line to the Reading Terminal in Philadelphia.

The New York Branch or the Bound Brook Route was a railway line in Pennsylvania and New Jersey. It was operated by the Reading Company and owned by two of its subsidiaries, the North Pennsylvania Railroad and the Delaware and Bound Brook Railroad. It formed part of the Reading's route from Philadelphia to New York City, used by the famed Crusader. The line was transferred to Conrail in 1976 and was split into the Neshaminy Line and Trenton Line. SEPTA continues to operate commuter trains to West Trenton as part of its West Trenton Line.

The Ninth Street Branch was an elevated railway line in Philadelphia, Pennsylvania. It was operated by the Reading Company; ownership was split between the Reading and its subsidiary the Philadelphia, Germantown and Norristown Railroad. It was a four-tracked main line beginning at the Reading Terminal, the Reading's terminus in Philadelphia, and extending north into the city to a junction with the Bethlehem Branch. After the final bankruptcy of the Reading the line passed to Conrail and later SEPTA. The portion south of the Temple University station was abandoned in 1984 with the opening of the Center City Commuter Connection and is now known as the Reading Viaduct; the portion north is now part of the SEPTA Main Line.
The Stony Creek Branch is a railway line in Montgomery County, Pennsylvania. It runs 9.9 miles (15.9 km) from Lansdale, Pennsylvania, to Norristown, Pennsylvania, connecting the Bethlehem and Doylestown Branches with the Norristown Branch. Although SEPTA owns the line, it is freight-only. CSX Transportation, Norfolk Southern Railway, and the Pennsylvania Northeastern Railroad have trackage rights on the branch.

Perkasie is a defunct train station formerly operated by SEPTA Regional Rail in Perkasie, Pennsylvania, USA. It closed on July 29, 1981, after SEPTA cancelled its diesel train routes.

The Neshaminy Line is a railway line in the states of Pennsylvania and New Jersey. It runs 21.7 miles (34.9 km) from a junction with the SEPTA Main Line just north of Jenkintown–Wyncote to West Trenton, just across the Delaware River. It was originally built in 1876 as part of the much longer New York Branch, which continued north to Bound Brook, New Jersey. The electrified section between Jenkin and West Trenton was designated the Neshaminy Line and is now owned by SEPTA. It hosts the West Trenton Line commuter rail service. The freight-only Trenton Subdivision runs parallel between Neshaminy Falls and West Trenton.

The Pottsville line was a commuter rail service in the Delaware Valley, connecting Pottsville, Reading, and Pottstown with Philadelphia. It was the last vestige of passenger service on the former Reading main line. The service lasted into the SEPTA era and was discontinued in 1981. SEPTA continues to operate Manayunk/Norristown Line commuter trains between Philadelphia and Norristown.

















