
Arithmetic is an elementary part of mathematics that consists of the study of the properties of the traditional operations on numbers—addition, subtraction, multiplication, division, exponentiation, and extraction of roots. In the 19th century, Italian mathematician Giuseppe Peano formalized arithmetic with his Peano axioms, which are highly important to the field of mathematical logic today.

The decimal numeral system is the standard system for denoting integer and non-integer numbers. It is the extension to non-integer numbers of the Hindu–Arabic numeral system. The way of denoting numbers in the decimal system is often referred to as decimal notation.
In logic, mathematics, computer science, and linguistics, a formal language consists of words whose letters are taken from an alphabet and are well-formed according to a specific set of rules.

An ideogram or ideograph is a graphic symbol that represents an idea or concept, independent of any particular language, and specific words or phrases. Some ideograms are comprehensible only by familiarity with prior convention; others convey their meaning through pictorial resemblance to a physical object, and thus may also be referred to as pictograms.
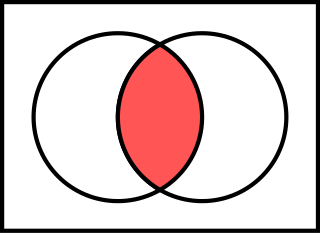
In logic, mathematics and linguistics, and is the truth-functional operator of conjunction or logical conjunction. The logical connective of this operator is typically represented as or or (prefix) or or in which is the most modern and widely used.

A numeral system is a writing system for expressing numbers; that is, a mathematical notation for representing numbers of a given set, using digits or other symbols in a consistent manner.
The unary numeral system is the simplest numeral system to represent natural numbers: to represent a number N, a symbol representing 1 is repeated N times.
0 (zero) is a number representing an empty quantity. As a number, 0 fulfills a central role in mathematics as the additive identity of the integers, real numbers, and other algebraic structures.
In computer science, Backus–Naur form or Backus normal form (BNF) is a metasyntax notation for context-free grammars, often used to describe the syntax of languages used in computing, such as computer programming languages, document formats, instruction sets and communication protocols. It is applied wherever exact descriptions of languages are needed: for instance, in official language specifications, in manuals, and in textbooks on programming language theory.

Assyro-Chaldean Babylonian cuneiform numerals were written in cuneiform, using a wedge-tipped reed stylus to make a mark on a soft clay tablet which would be exposed in the sun to harden to create a permanent record.
A binary number is a number expressed in the base-2 numeral system or binary numeral system, a method of mathematical expression which uses only two symbols: typically "0" (zero) and "1" (one).
Mathematical notation consists of using symbols for representing operations, unspecified numbers, relations, and any other mathematical objects and assembling them into expressions and formulas. Mathematical notation is widely used in mathematics, science, and engineering for representing complex concepts and properties in a concise, unambiguous, and accurate way.
A numerical digit is a single symbol used alone or in combinations, to represent numbers in a positional numeral system. The name "digit" comes from the fact that the ten digits of the hands correspond to the ten symbols of the common base 10 numeral system, i.e. the decimal digits.

Positional notation usually denotes the extension to any base of the Hindu–Arabic numeral system. More generally, a positional system is a numeral system in which the contribution of a digit to the value of a number is the value of the digit multiplied by a factor determined by the position of the digit. In early numeral systems, such as Roman numerals, a digit has only one value: I means one, X means ten and C a hundred. In modern positional systems, such as the decimal system, the position of the digit means that its value must be multiplied by some value: in 555, the three identical symbols represent five hundreds, five tens, and five units, respectively, due to their different positions in the digit string.
Bijective numeration is any numeral system in which every non-negative integer can be represented in exactly one way using a finite string of digits. The name refers to the bijection that exists in this case between the set of non-negative integers and the set of finite strings using a finite set of symbols.

The Hindu–Arabic numeral system or Indo-Arabic numeral system is a positional decimal numeral system, and is the most common system for the symbolic representation of numbers in the world.
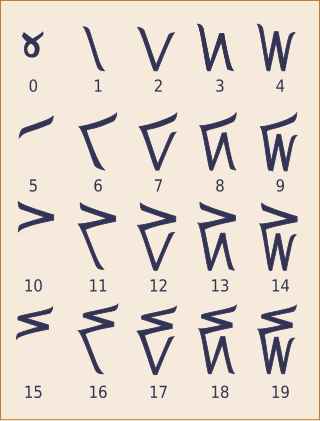
The Kaktovik numerals or Kaktovik Iñupiaq numerals are a base-20 system of numerical digits created by Alaskan Iñupiat. They are visually iconic, with shapes that indicate the number being represented.
Mathematics is a field of study that investigates topics such as number, space, structure, and change.









