Full-spectrum dominance also known as full-spectrum superiority, is a military entity's achievement of control over all dimensions of the battlespace, effectively possessing an overwhelming diversity of resources in such areas as terrestrial, aerial, maritime, subterranean, extraterrestrial, psychological, and bio- or cyber-technological warfare.
A revolution in military affairs (RMA) is a hypothesis in military theory about the future of warfare, often connected to technological and organizational recommendations for military reform.

Power projection in international relations is the capacity of a state to deploy and sustain forces outside its territory. The ability of a state to project its power into an area may serve as an effective diplomatic lever, influencing the decision-making processes and acting as a potential deterrent on other states' behavior.

The Field Artillery Branch is a combat arms branch of the United States Army that is responsible for field artillery.

The AN/APG-63 and AN/APG-70 are a family of all-weather multimode radar systems designed by Hughes Aircraft for the F-15 Eagle air superiority fighter. These X band pulse-Doppler radar systems are designed for both air-air and air-ground missions; they are able to look up at high-flying targets and down at low-flying targets without being confused by ground clutter. The systems can detect and track aircraft and small high-speed targets at distances beyond visual range down to close range, and at altitudes down to treetop level. The radar feeds target information into the aircraft's central computer for effective weapons delivery. For close-in dogfights, the radar automatically acquires enemy aircraft and projects this information onto the cockpit head-up display. The name is assigned from the Army Navy Joint Electronics Type Designation System.

Hypersonic flight is flight through the atmosphere below altitudes of about 90 km at speeds greater than Mach 5, a speed where dissociation of air begins to become significant and high heat loads exist. Speeds over Mach 25 have been achieved below the thermosphere as of 2020.

A conflict continuum is a model or concept various social science researchers use when modeling conflict on a continuum from low to high-intensity, such as from aggression to irritation to explosiveness.
A sixth-generation fighter is a conceptualized class of jet fighter aircraft design more advanced than the fifth-generation jet fighters that are currently in service and development. Several countries have announced the development of a national sixth-generation aircraft program, including the United States, Russia and China, while Japan, Italy, the United Kingdom, France, Germany, Spain, and Sweden have joined together in collaborative multinational programs in an effort to spread development costs. The first sixth-generation fighters are expected to enter service in the 2030s.

The U.S. Army Joint Modernization Command, or JMC, based in Fort Bliss, Texas, gains insights from "Fight Tonight" units about future ways of fighting, future technology, and force structure during realistic live, constructive, and/or simulated training exercises. Joint Modernization Command is subordinate to the Army Futures & Concepts Center in Joint Base Langley-Eustis, Virginia; both report to the U.S. Army's newest Four-Star Command, the Army Futures Command (AFC) based in Austin, Texas.

The Human Dimension is a framework for United States Army to Optimize Human Performance as part of Force 2025 and Beyond. The Human Dimension White Paper expands on the topic covered in this page.
The transformation of the United States Army is part of a strategy using Multi-Domain Operations (MDO). In 2019, the planning was for Large Scale ground Combat Operations at echelons above the brigade combat team. Multi-Domain Task Forces operate in a combatant commander's theater.
In air and missile defense (AMD), the Integrated Air-and-Missile Defense system (IAMD) is an SMDC research program to augment the aging surface-to-air missile defense systems and to provide the United States Army with a low-cost, but effective complement to kinetic energy solutions to take out air threats. Brigade level higher energy lasers are used in truck mounted systems called HELMTT. At lower levels, the Army needs to develop interceptors that don't cost more than small, unmanned aircraft systems. In early research they have successfully used 5-kilowatt lasers on a Stryker combat vehicle. The Mobile Expeditionary High-Energy Laser (MEHEL) was used at MFIX at Fort Sill, Oklahoma, in the first half of April, 2017.

The United States Army Futures Command (AFC) is a United States Army command that runs modernization projects. It is headquartered in Austin, Texas.

The United States Army Acquisition Corps (AAC) is the officer / NCO corps of the United States Army Acquisition Workforce (AAW), a branch which includes civilians, officers, and NCOs. The Acquisition Corps is composed of army officers who serve in acquisition, a specialized form of product development, fielding, and support and Noncommissioned Officers who specialize in Contracting, Level I Program Management and Purchasing. These officers begin their careers in the other branches of the army for eight years, after which they may elect the Acquisition branch as their career as assistant program managers (APMs), program managers (PMs), and program executive officers (PEOs). The Noncommissioned Officers (NCOs) are reclassified in the Army Acquisition NCO Corps after serving 7-10 years in their respective enlisted career management fields, and serve primarily in the Army Acquisition Career Management Field - 51 and (MOS) 51C. 4% percentage of the Army Acquisition Officers serve among the 40,000 members of the army acquisition workforce, 6% in MOS 51C - Acquisition, Logistics and Technology Contracting Noncommissioned Officer, and the remainder 90% percentage consist largely of Department of the Army civilians.

Cedric Terry Wins is a retired U.S. Army general officer. Major General Wins was the last commander of RDECOM, in the U.S. Army Materiel Command, and the first commanding general (CG) of Combat Capabilities Development Command (DEVCOM), in the combat development element of U.S. Army Futures Command. In all, some 13,000 people work in some Science and Technology (S&T), or capacity for DEVCOM.

The Joint Artificial Intelligence Center (JAIC) (pronounced "jake") was an American organization on exploring the usage of Artificial Intelligence (AI) (particularly Edge computing), Network of Networks and AI-enhanced communication for use in actual combat. In February 2022, JAIC was integrated into the Chief Digital and Artificial Intelligence Office (CDAO).
Joint All-Domain Command and Control or JADC2 is the concept that the Department of Defense has developed to connect sensors from all branches of the armed forces into a § unified network powered by artificial intelligence. These branches include the Air Force, Army, Marine Corps, and Navy, as well as Space Force.
The US Army's Integrated Tactical Network (ITN) "is not a new or separate network but rather a concept"—PEO C3T. Avoid overspecifying the requirements for Integrated Tactical Network Information Systems Initial Capabilities Document. Instead, meet operational needs, such as interoperability with other networks, and release ITN capabilities incrementally.

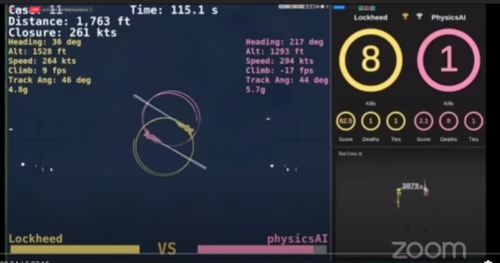
Collaborative combat aircraft (CCA) is a US program for unmanned combat air vehicles (UCAVs) that is considered broadly equivalent to a loyal wingman. CCAs are intended to operate in collaborative teams with the next generation of manned combat aircraft, including sixth-generation fighters and bombers such as the Northrop Grumman B-21 Raider. Unlike the conventional UCAVs, the CCA incorporates artificial intelligence (AI), denoted an "autonomy package", increasing its survivability on the battlefield. It is still expected to cost much less than a manned aircraft with similar capabilities. The US Air Force plans to spend more than $6 billion on its CCA programs from 2023 to 2028. The success of the CCA program may lessen the need for additional manned squadrons.
A loyal wingman is a proposed type of unmanned combat air vehicle (UCAV) which incorporates artificial intelligence (AI) and is capable of collaborating with the next generation of manned combat aircraft, including sixth-generation fighters and bombers such as the Northrop Grumman B-21 Raider. Also unlike the conventional UCAV, the loyal wingman is expected to be capable of surviving on the battlefield but to be significantly lower-cost than a manned aircraft with similar capabilities. In the US, the concept is known as the collaborative combat aircraft (CCA).