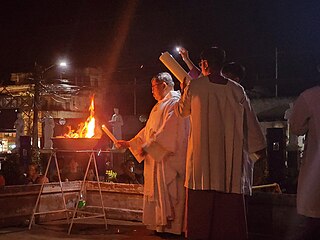Maundy Thursday or Holy Thursday, among other names, is the day during Holy Week that commemorates the Washing of the Feet (Maundy) and Last Supper of Jesus Christ with the Apostles, as described in the canonical gospels.

Holy Week is the most sacred week in the liturgical year in Christianity. For all Christian traditions, it is a moveable observance. In Eastern Christianity, which also calls it Great Week, it is the week following Great Lent and Lazarus Saturday, starting on the evening of Palm Sunday and concluding on the evening of Great Saturday. In Western Christianity, Holy Week is the sixth and last week of Lent, beginning with Palm Sunday and concluding on Holy Saturday.

Holy Saturday, also known as Great and Holy Saturday, Low Saturday, the Great Sabbath, Hallelujah Saturday, Saturday of the Glory, Sábado de Gloria, and Black Saturday or Easter Eve, and called "Joyous Saturday", "the Saturday of Light", and "Mega Sabbatun" among Coptic Christians, is the final day of Holy Week, between Good Friday and Easter Sunday, when Christians prepare for the latter.

The Paschal Triduum or Easter Triduum, Holy Triduum, or the Three Days, is the period of three days that begins with the liturgy on the evening of Maundy Thursday, reaches its high point in the Easter Vigil, and closes with evening prayer on Easter Sunday. It is a moveable observance recalling the Passion, Crucifixion, Death, burial, and Resurrection of Jesus, as portrayed in the canonical Gospels.

A votive candle or prayer candle is a small candle, typically white or beeswax yellow, intended to be burnt as a votive offering in an act of Christian prayer, especially within the Anglican, Lutheran, and Roman Catholic Christian denominations, among others. In Christianity, votive candles are commonplace in many churches, as well as home altars, and symbolize the "prayers the worshipper is offering for him or herself, or for other people." The size of a votive candle is often two inches tall by one and a half inches diameter, although other votive candles can be significantly taller and wider. In other religions, such as Hinduism and Buddhism, similar offerings exist, which include diyas and butter lamps.

Eastertide or Paschaltide is a festal season in the liturgical year of Christianity that focuses on celebrating the Resurrection of Jesus Christ. Preceded by Lent, it begins on Easter Sunday, which initiates Easter Week in Western Christianity, and Bright Week in Eastern Christianity.

Tenebrae is a religious service of Western Christianity held during the three days preceding Easter Day, and characterized by gradual extinguishing of candles, and by a "strepitus" or "loud noise" taking place in total darkness near the end of the service.
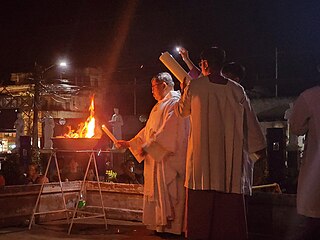
The Easter Vigil, also called the Paschal Vigil, the Great Vigil of Easter, or Holy Saturday in the Easter Vigil on the Holy Night of Easter is a liturgy held in traditional Christian churches as the first official celebration of the Resurrection of Jesus. Historically, it is during this liturgy that people are baptized and that adult catechumens are received into full communion with the Church. It is held in the hours of darkness between sunset on Holy Saturday and sunrise on Easter Day – most commonly in the evening of Holy Saturday or midnight – and is the first celebration of Easter, days traditionally being considered to begin at sunset.

The Exsultet, also known as the Easter Proclamation, is a lengthy sung proclamation delivered before the paschal candle, ideally by a deacon, during the Easter Vigil in the Roman Rite of Mass. In the absence of a deacon, it may be sung by a priest or by a cantor. It is sung after a procession with the paschal candle before the beginning of the Liturgy of the Word. It is also used in Anglican and various Lutheran churches, as well as other Western Christian denominations.

The Chrism Mass is a religious service held in certain Christian denominations, such as Roman Catholicism, Lutheranism, and Anglicanism. It is usually celebrated each year on Maundy Thursday or on another day of Holy Week. During the ceremony, the holy oils used for sacraments and rituals are blessed or consecrated.

In the Roman Rite of the Catholic Church, Lutheranism, Methodism and Anglicanism, an altar bell is typically a small hand-held bell or set of bells. The primary reason for the use of such bells is to create a “joyful noise to the Lord” as a way to give thanks for the miracle taking place atop the altar.

Easter Saturday, on the Christian calendar, is the seventh day of Eastertide, being the Saturday of Easter or Bright Week. In the kalendar of Western Christianity it is the last day of Easter Week, sometimes referred to as the Saturday of Easter Week or Saturday in Easter Week. It is the seventh day in the Octave of Easter too. In the liturgy of Eastern Christianity it is the last day of Bright Week, and called Bright Saturday, The Bright and Holy Septave Saturday of Easter Eve, or The Bright and Holy Septave Paschal Artos and Octoechoes Saturday of Iscariot's Byzantine Easter Eve. Easter Saturday is the day preceding the Second Sunday of Easter.

The ceremonial use of lights occurs in liturgies of various Christian Churches, as well as in Jewish, Zoroastrian, and Hindu rites and customs.

During the Liturgy of the Eucharist, the second part of the Mass, the elements of bread and wine are considered to have been changed into the veritable Body and Blood of Jesus Christ. The manner in which this occurs is referred to by the term transubstantiation, a theory of St. Thomas Aquinas, in the Roman Catholic Church. Members of the Orthodox, Anglican, and Lutheran communions also believe that Jesus Christ is really and truly present in the bread and wine, but they believe that the way in which this occurs must forever remain a sacred mystery. In many Christian churches, some portion of the consecrated elements is set aside and reserved after the reception of Communion and referred to as the reserved sacrament. The reserved sacrament is usually stored in a tabernacle, a locked cabinet made of precious materials and usually located on, above, or near the high altar. In Western Christianity usually only the Host, from Latin: hostia, meaning "victim", is reserved, except where wine might be kept for the sick who cannot consume a host.

The altar of repose is a temporary altar where the Communion hosts consecrated on Maundy Thursday during the Mass of the Lord's Supper are placed, or "reserved", for use on the following day, Good Friday.

The Mass of the Lord's Supper, also known as A Service of Worship for Maundy Thursday, is a Holy Week service celebrated on the evening of Maundy Thursday. It inaugurates the Easter Triduum, and commemorates the Last Supper of Jesus with his disciples, more explicitly than other celebrations of the Mass.

The Paschal trikirion is a liturgical triple-candlestick used at Easter time in the Eastern Orthodox and Byzantine Catholic traditions.

Lumen Christi is a versicle sung in Catholic, Lutheran and some Anglican churches as part of the Easter Vigil. In Lutheran and Anglican services, it is sung in the local language. It is chanted by the deacon on Holy Saturday as he lights the candle. In the English Sarum Rite, one candle is lit.

Easter fires, also called Paschal fires, are typically bonfires lit at Easter as part of liturgical and cultural celebrations.

Easter Water is the name given to water used in rituals during the Easter Vigil in the Catholic Church, Lutheran Churches, and Anglican Communion. A part of this water is set aside for use as a sacramental in the church and at home, the remainder being ceremonially mixed with consecrated oils and used for baptisms in the church.