
Catalysis is the increase in rate of a chemical reaction due to an added substance known as a catalyst. Catalysts are not consumed by the reaction and remain unchanged after it. If the reaction is rapid and the catalyst recycles quickly, very small amounts of catalyst often suffice; mixing, surface area, and temperature are important factors in reaction rate. Catalysts generally react with one or more reactants to form intermediates that subsequently give the final reaction product, in the process of regenerating the catalyst.

Cellulose is an organic compound with the formula (C
6H
10O
5)
n, a polysaccharide consisting of a linear chain of several hundred to many thousands of β(1→4) linked D-glucose units. Cellulose is an important structural component of the primary cell wall of green plants, many forms of algae and the oomycetes. Some species of bacteria secrete it to form biofilms. Cellulose is the most abundant organic polymer on Earth. The cellulose content of cotton fiber is 90%, that of wood is 40–50%, and that of dried hemp is approximately 57%.
Furfural is an organic compound with the formula C4H3OCHO. It is a colorless liquid, although commercial samples are often brown. It has an aldehyde group attached to the 2-position of furan. It is a product of the dehydration of sugars, as occurs in a variety of agricultural byproducts, including corncobs, oat, wheat bran, and sawdust. The name furfural comes from the Latin word furfur, meaning bran, referring to its usual source. Furfural is only derived from dryed biomass, In addition to ethanol, acetic acid, and sugar, furfural is one of the oldest organic chemicals available readily purified from natural precursors.

Lignocellulose refers to plant dry matter (biomass), so called lignocellulosic biomass. It is the most abundantly available raw material on the Earth for the production of biofuels. It is composed of two kinds of carbohydrate polymers, cellulose and hemicellulose, and an aromatic-rich polymer called lignin. Any biomass rich in cellulose, hemicelluloses, and lignin are commonly referred to as lignocellulosic biomass. Each component has a distinct chemical behavior. Being a composite of three very different components makes the processing of lignocellulose challenging. The evolved resistance to degradation or even separation is referred to as recalcitrance. Overcoming this recalcitrance to produce useful, high value products requires a combination of heat, chemicals, enzymes, and microorganisms. These carbohydrate-containing polymers contain different sugar monomers and they are covalently bound to lignin.

γ-Valerolactone (GVL) or gamma-valerolactone is an organic compound with the formula C5H8O2. This colourless liquid is one of the more common lactones. GVL is chiral but is usually used as the racemate. It is readily obtained from cellulosic biomass and is a potential fuel and green solvent.
Reactive flash volatilization (RFV) is a chemical process that rapidly converts nonvolatile solids and liquids to volatile compounds by thermal decomposition for integration with catalytic chemistries.

Lanny D. Schmidt was an American chemist, inventor, author, and Regents Professor of Chemical Engineering and Materials Science at the University of Minnesota. He is well known for his extensive work in surface science, detailed chemistry (microkinetics), chemical reaction engineering, catalysis, and renewable energy. He is also well known for mentoring over a hundred graduate students and his work on millisecond reactors and reactive flash volatilization.
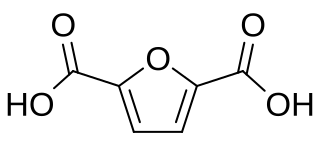
2,5-Furandicarboxylic acid (FDCA) is an organic chemical compound consisting of two carboxylic acid groups attached to a central furan ring. It was first reported as dehydromucic acid by Rudolph Fittig and Heinzelmann in 1876, who produced it via the action of concentrated hydrobromic acid upon mucic acid. It can be produced from certain carbohydrates and as such is a renewable resource, it was identified by the US Department of Energy as one of 12 priority chemicals for establishing the “green” chemistry industry of the future. Furan-2,5-dicarboxylic acid (FDCA) has been suggested as an important renewable building block because it can substitute for terephthalic acid (PTA) in the production of polyesters and other current polymers containing an aromatic moiety.
Bioproducts or bio-based products are materials, chemicals and energy derived from renewable biological material.
Chemical reaction engineering is a specialty in chemical engineering or industrial chemistry dealing with chemical reactors. Frequently the term relates specifically to catalytic reaction systems where either a homogeneous or heterogeneous catalyst is present in the reactor. Sometimes a reactor per se is not present by itself, but rather is integrated into a process, for example in reactive separations vessels, retorts, certain fuel cells, and photocatalytic surfaces. The issue of solvent effects on reaction kinetics is also considered as an integral part.

2-Methyltetrahydrofuran (2-MeTHF) is an organic compound with the molecular formula C5H10O. It is a highly flammable, mobile liquid. It is mainly used as a replacement for Tetrahydrofuran (THF) in specialized applications for its better performance, such as to obtain higher reaction temperatures, or easier separations (as, unlike THF, it is not miscible with water). It is derived from sugars via furfural and is occasionally touted as a biofuel.

2,5-Bis(hydroxymethyl)furan (BHMF) is a heterocyclic organic compound, and is a derivative of a broader class of compounds known as furans. It is produced from cellulose and has received attention as a biofeedstock. It is a white solid, although commercial samples can appear yellowish or tan.
Mahdi Muhammad Abu-Omar is a Palestinian-American chemist, currently the Duncan and Suzanne Mellichamp Professor of Green Chemistry in the Departments of Chemistry & Biochemistry and Chemical Engineering at University of California, Santa Barbara.
Maria Flytzani-Stephanopoulos was a Greek chemical engineer and, at the time of her death, had been the Robert and Marcy Haber Endowed Professor in Energy Sustainability and a distinguished professor at Tufts University. Flytzani-Stephanopoulos had also been the Raytheon Professor of Pollution Prevention at Tufts. She published more than 160 scientific articles with over 14,000 citations as of April 2018. She was a Fellow of AIChE, the American Association for the Advancement of Science and American Institute of Chemical Engineers. She lived in the Greater Boston Area with her husband, Professor Gregory Stephanopoulos of MIT.
Raymond John Gorte is an American chemical engineer, currently the Russel Pearce and Elizabeth Crimian Heuer Endowed Professor of Chemical and Biomolecular Engineering (CBE) and Materials Science & Engineering (MSE) at the University of Pennsylvania. Throughout his career at the University of Pennsylvania and the University of Minnesota, he has advanced the study of fuel cells and catalysts including heterogeneous metals and zeolite materials. He is a member of the U.S. National Academy of Engineering.
Dionisios G. Vlachos is an American chemical engineer, the Allan & Myra Ferguson Endowed Chair Professor of Chemical Engineering at the University of Delaware and director of the Catalysis Center for Energy Innovation, a U.S. Department of Energy - Energy Frontiers Research Center. Throughout his career at University of Delaware and the University of Minnesota, he has advanced the study of catalysts and reaction engineering including catalytic applications in biomass utilization, alkane conversion and zeolites. He is a fellow of the American Association for the Advancement of Science and recipient of the Wilhelm Award of the American Institute of Chemical Engineers (2011).
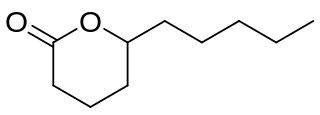
δ-Decalactone (DDL) is a chemical compound, classified as a lactone, that naturally occurs in fruit and milk products in traces. It can be obtained from both chemical and biological sources. Chemically, it is produced from Baeyer–Villiger oxidation of delfone. From biomass, it can be produced via the hydrogenation of 6-amyl-α-pyrone. DDL has applications in food, polymer, and agricultural industries to formulate important products.
In chemistry, catalytic resonance theory was developed to describe the kinetics of reaction acceleration using dynamic catalyst surfaces. Catalytic reactions occurring on surfaces that undergo variation in surface binding energy and/or entropy exhibit overall increase in reaction rate when the surface binding energy frequencies are comparable to the natural frequencies of the surface reaction, adsorption, and desorption.
Alexis Tarassov Bell is an American chemical engineer. He is currently the Dow professor of Sustainable Chemistry in the Department of Chemical and Biomolecular Engineering in UC Berkeley's college of chemistry. He is also the Faculty Senior Scientist at Lawrence Berkeley National Laboratory. He is known for his work with heterogenous catalysts and characterizing the mechanisms of these reactions on a quantum level.
Hilkka Inkeri Kenttämaa is a researcher in organic and bioorganic mass spectrometry, and the Frank Brown Endowed Distinguished Professor of Chemistry at Purdue University. She is a pioneer in distonic radical cation research and laser-induced acoustic desorption.










