
A drum is a cylindrical shipping container used for shipping bulk cargo. Drums can be made of steel, dense paperboard, or plastic, and are generally used for the transportation and storage of liquids and powders. Drums are often stackable, and have dimensions designed for efficient warehouse and logistics use. This type of packaging is frequently certified for transporting dangerous goods. Proper shipment requires the drum to comply with all applicable regulations.

Plastic shopping bags, carrier bags, or plastic grocery bags are a type of plastic bag used as shopping bags and made from various kinds of plastic. In use by consumers worldwide since the 1960s, these bags are sometimes called single-use bags, referring to carrying items from a store to a home. However, it is rare for bags to be worn out after single use and in the past some retailers incentivised customers to reuse 'single use' bags by offering loyalty points to those doing so. Even after they are no longer used for shopping, reuse for storage or trash is common, and modern plastic shopping bags are increasingly recyclable or compostable. In recent decades, numerous countries have introduced legislation restricting the provision of plastic bags, in a bid to reduce littering and plastic pollution.

A plastic bag, poly bag, or pouch is a type of container made of thin, flexible, plastic film, nonwoven fabric, or plastic textile. Plastic bags are used for containing and transporting goods such as foods, produce, powders, ice, magazines, chemicals, and waste. It is a common form of packaging.

A bin bag, rubbish bag, garbage bag, bin liner, trash bag or refuse sack is a disposable bag used to contain solid waste. Such bags are useful to line the insides of waste containers to prevent the insides of the receptacle from becoming coated in waste material. Most bags today are made out of plastic, and are typically black, white, or green in color.

Marine debris, also known as marine litter, is human-created waste that has deliberately or accidentally been released in a sea or ocean. Floating oceanic debris tends to accumulate at the center of gyres and on coastlines, frequently washing aground, when it is known as beach litter or tidewrack. Deliberate disposal of wastes at sea is called ocean dumping. Naturally occurring debris, such as driftwood and drift seeds, are also present. With the increasing use of plastic, human influence has become an issue as many types of (petrochemical) plastics do not biodegrade quickly, as would natural or organic materials. The largest single type of plastic pollution (~10%) and majority of large plastic in the oceans is discarded and lost nets from the fishing industry. Waterborne plastic poses a serious threat to fish, seabirds, marine reptiles, and marine mammals, as well as to boats and coasts.

A water bottle is a container that is used to hold liquids, mainly water, for the purpose of transporting a drink while travelling or while otherwise away from a supply of potable water.

The throw-away society is a generalised description of human social concept strongly influenced by consumerism, whereby the society tends to use items once only, from disposable packaging, and consumer products are not designed for reuse or lifetime use. The term describes a critical view of overconsumption and excessive production of short-lived or disposable items over durable goods that can be repaired, but at its origins, it was viewed as a positive attribute.

A disposable is a product designed for a single use after which it is recycled or is disposed as solid waste. The term is also sometimes used for products that may last several months to distinguish from similar products that last indefinitely. The word "disposables" is not to be confused with the word "consumables", which is widely used in the mechanical world. For example, welders consider welding rods, tips, nozzles, gas, etc. to be "consumables", as they last only a certain amount of time before needing to be replaced. Consumables are needed for a process to take place, such as inks for printing and welding rods for welding, while disposable products are items that can be discarded after they become damaged or are no longer useful.
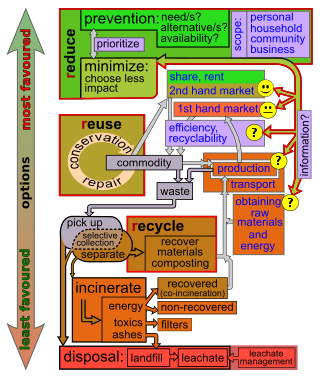
Waste minimisation is a set of processes and practices intended to reduce the amount of waste produced. By reducing or eliminating the generation of harmful and persistent wastes, waste minimisation supports efforts to promote a more sustainable society. Waste minimisation involves redesigning products and processes and/or changing societal patterns of consumption and production.

A bulk box, also known as a bulk bin, skid box, pallet box, bin box, gaylord, or octabin, is a pallet-size box used for storage and shipping of bulk quantities.

A flexible intermediate bulk container (FIBC), jumbo, bulk bag, super sack, big bag, or tonne bag is an industrial container made of flexible fabric that is designed for storing and transporting dry, flowable products, such as sand, fertilizer, and granules of plastic.

Commodity plastics or commodity polymers are plastics produced in high volumes for applications where exceptional material properties are not needed. In contrast to engineering plastics, commodity plastics tend to be inexpensive to produce and exhibit relatively weak mechanical properties. Some examples of commodity plastics are polyethylene, polypropylene, polystyrene, polyvinyl chloride, and poly(methyl methacrylate) .Globally, the most widely used thermoplastics include both polypropylene and polyethylene. Products made from commodity plastics include disposable plates, disposable cups, photographic and magnetic tape, clothing, reusable bags, medical trays, and seeding trays.
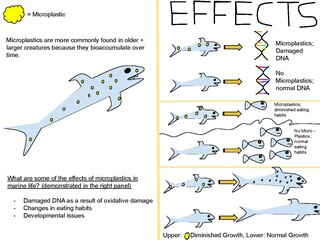
Marine plastic pollution is a type of marine pollution by plastics, ranging in size from large original material such as bottles and bags, down to microplastics formed from the fragmentation of plastic material. Marine debris is mainly discarded human rubbish which floats on, or is suspended in the ocean. Eighty percent of marine debris is plastic. Microplastics and nanoplastics result from the breakdown or photodegradation of plastic waste in surface waters, rivers or oceans. Recently, scientists have uncovered nanoplastics in heavy snow, more specifically about 3,000 tons that cover Switzerland yearly.

Food storage containers are widespread in use throughout the world and have probably been in use since the first human civilizations.

Disposable food packaging comprises disposable products often found in fast-food restaurants, take-out restaurants and catering establishments. Typical products are foam food containers, plates, bowls, cups, utensils, doilies and tray papers. These products can be made from a number of materials including plastics, paper, bioresins, wood and bamboo.

Plastics are a wide range of synthetic or semi-synthetic materials that use polymers as a main ingredient. Their plasticity makes it possible for plastics to be moulded, extruded or pressed into solid objects of various shapes. This adaptability, plus a wide range of other properties, such as being lightweight, durable, flexible, and inexpensive to produce, has led to its widespread use. Plastics typically are made through human industrial systems. Most modern plastics are derived from fossil fuel-based chemicals like natural gas or petroleum; however, recent industrial methods use variants made from renewable materials, such as corn or cotton derivatives.

Plastic pollution is the accumulation of plastic objects and particles in the Earth's environment that adversely affects humans, wildlife and their habitat. Plastics that act as pollutants are categorized by size into micro-, meso-, or macro debris. Plastics are inexpensive and durable, making them very adaptable for different uses; as a result, manufacturers choose to use plastic over other materials. However, the chemical structure of most plastics renders them resistant to many natural processes of degradation and as a result they are slow to degrade. Together, these two factors allow large volumes of plastic to enter the environment as mismanaged waste which persists in the ecosystem and travels throughout food webs.
Plastic-coated paper is a coated or laminated composite material made of paper or paperboard with a plastic layer or treatment on a surface. This type of coated paper is most used in the food and drink packaging industry.

Packaging waste, the part of the waste that consists of packaging and packaging material, is a major part of the total global waste, and the major part of the packaging waste consists of single-use plastic food packaging, a hallmark of throwaway culture. Notable examples for which the need for regulation was recognized early, are "containers of liquids for human consumption", i.e. plastic bottles and the like. In Europe, the Germans top the list of packaging waste producers with more than 220 kilos of packaging per capita.
China's waste import ban, instated at the end of 2017, prevented foreign inflows of waste products. Starting in early 2018, the government of China, under Operation National Sword, banned the import of several types of waste, including plastics with a contamination level of above 0.05 percent. The ban has greatly affected recycling industries worldwide, as China had been the world's largest importer of waste plastics and processed hard-to-recycle plastics for other countries, especially in the West.




















