
A copyright is a type of intellectual property that gives the creator of an original work, or another right holder, the exclusive and legally secured right to copy, distribute, adapt, display, and perform a creative work, usually for a limited time. The creative work may be in a literary, artistic, educational, or musical form. Copyright is intended to protect the original expression of an idea in the form of a creative work, but not the idea itself. A copyright is subject to limitations based on public interest considerations, such as the fair use doctrine in the United States.
Project Gutenberg (PG) is a volunteer effort to digitize and archive cultural works, as well as to "encourage the creation and distribution of eBooks." It was founded in 1971 by American writer Michael S. Hart and is the oldest digital library. Most of the items in its collection are the full texts of books or individual stories in the public domain. All files can be accessed for free under an open format layout, available on almost any computer. As of 13 February 2024, Project Gutenberg had reached 70,000 items in its collection of free eBooks.

Michael Stern Hart was an American author, best known as the inventor of the e-book and the founder of Project Gutenberg (PG), the first project to make e-books freely available via the Internet. He published e-books via ARPANET years before the Internet existed, and later on BBS networks and Gopher servers.
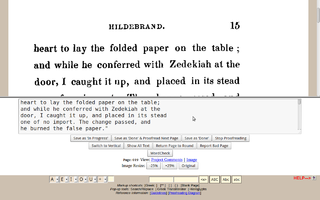
Distributed Proofreaders is a web-based project that supports the development of e-texts for Project Gutenberg by allowing many people to work together in proofreading drafts of e-texts for errors. As of March 2021, the site had digitized 41,000 titles.
Electronic publishing includes the digital publication of e-books, digital magazines, and the development of digital libraries and catalogues. It also includes the editing of books, journals, and magazines to be posted on a screen.

The copyright law of Canada governs the legally enforceable rights to creative and artistic works under the laws of Canada. Canada passed its first colonial copyright statute in 1832 but was subject to imperial copyright law established by Britain until 1921. Current copyright law was established by the Copyright Act of Canada which was first passed in 1921 and substantially amended in 1988, 1997, and 2012. All powers to legislate copyright law are in the jurisdiction of the Parliament of Canada by virtue of section 91(23) of the Constitution Act, 1867.
The Copyright Act is the federal statute governing copyright law in Canada. It is jointly administered by the Department of Industry Canada and the Department of Canadian Heritage. The Copyright Act was first passed in 1921 and substantially amended in 1988 and 1997. Several attempts were made between 2005 and 2011 to amend the Act, but each of the bills failed to pass due to political opposition. In 2011, with a majority in the House of Commons, the Conservative Party introduced Bill C-11, titled the Copyright Modernization Act. Bill C-11 was passed and received Royal Assent on June 29, 2012.
Project Gutenberg Australia, abbreviated as PGA, is an Internet site which was founded in 2001 by Colin Choat. It is a sister site of Project Gutenberg, though there is no formal relationship between the two organizations. The site hosts free ebooks or e-texts which are in the public domain in Australia. Volunteers have prepared and submitted the ebooks.

Google Books is a service from Google that searches the full text of books and magazines that Google has scanned, converted to text using optical character recognition (OCR), and stored in its digital database. Books are provided either by publishers and authors through the Google Books Partner Program, or by Google's library partners through the Library Project. Additionally, Google has partnered with a number of magazine publishers to digitize their archives.
LibriVox is a group of worldwide volunteers who read and record public domain texts, creating free public domain audiobooks for download from their website and other digital library hosting sites on the internet. It was founded in 2005 by Hugh McGuire to provide "Acoustical liberation of books in the public domain" and the LibriVox objective is "To make all books in the public domain available, for free, in audio format on the internet".

Public Domain Day (PDD) is an observance of when copyrights expire and works enter into the public domain. This legal transition of copyright works into the public domain usually happens every year on January 1 based on the individual copyright laws of each country.

The International Music Score Library Project (IMSLP), also known as the Petrucci Music Library after publisher Ottaviano Petrucci, is a subscription-based digital library of public-domain music scores. The project uses MediaWiki software, and as of 24 November 2023 has uploaded more than 736,000 scores and 80,700 recordings by 1,900 performers of more than 226,000 works by 27,400 composers. IMSLP has both an iOS app and an Android app.
Distributed Proofreaders Canada is a volunteer organization that transfers books into electronic format and releases them as public domain books in formats readable by electronic devices. It was launched in December 2007 and as of 2023 has published about 8,000 books. Books that are released are stored on a book archive called Faded Page. While its focus is on Canadian publications and preserving Canadiana, it also includes books from other countries as well. It is modelled after Distributed Proofreaders, and performs the same function as similar projects in other parts of the world such as Project Gutenberg in the United States and Project Gutenberg Australia.
Crown copyright is a type of copyright protection. It subsists in works of the governments of some Commonwealth realms and provides special copyright rules for the Crown, i.e. government departments and (generally) state entities. Each Commonwealth realm has its own Crown copyright regulations. There are therefore no common regulations that apply to all or a number of those countries. There are some considerations being made in Canada, UK, Australia and New Zealand regarding the "reuse of Crown-copyrighted material, through new licences".

The public domain (PD) consists of all the creative work to which no exclusive intellectual property rights apply. Those rights may have expired, been forfeited, expressly waived, or may be inapplicable. Because no one holds the exclusive rights, anyone can legally use or reference those works without permission.
When a work's copyright expires, it enters the public domain. The following is a list of creators whose works enter the public domain in 2020. Since laws vary globally, the copyright status of some works is not uniform.
When a work's copyright expires, it enters the public domain. The following is a list of creators whose works enter the public domain in 2021. Since laws vary globally, the copyright status of some works are not uniform.
When a work's copyright expires, it enters the public domain. The following is a list of creators whose works enter the public domain in 2023. Since laws vary globally, the copyright status of some works are not uniform.
When a work's copyright expires, it enters the public domain. The following is a list of creators whose works enter the public domain in 2024. Since laws vary globally, the copyright status of some works are not uniform.
When a work's copyright expires, it enters the public domain. The following is a list of creators whose works enter the public domain in 2025. Since laws vary globally, the copyright status of some works are not uniform.









