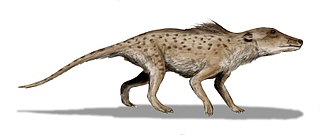
Pakicetidae is an extinct family of Archaeoceti that lived during the Early Eocene in Pakistan.

The evolution of cetaceans is thought to have begun in the Indian subcontinent from even-toed ungulates (Artiodactyla) 50 million years ago (mya) and to have proceeded over a period of at least 15 million years. Cetaceans are fully aquatic marine mammals belonging to the order Artiodactyla and branched off from other artiodactyls around 50 mya. Cetaceans are thought to have evolved during the Eocene, the second epoch of the present-extending Cenozoic Era. Molecular and morphological analyses suggest Cetacea share a relatively recent closest common ancestor with hippopotami and that they are sister groups. Being mammals, they surface to breathe air; they have 5 finger bones (even-toed) in their fins; they nurse their young; and, despite their fully aquatic life style, they retain many skeletal features from their terrestrial ancestors. Research conducted in the late 1970s in Pakistan revealed several stages in the transition of cetaceans from land to sea.

Ambulocetidae is a family of early cetaceans from Pakistan. The genus Ambulocetus, after which the family is named, is by far the most complete and well-known ambulocetid genus due to the excavation of an 80% complete specimen of Ambulocetus natans. The other two genera in the family, Gandakasia and Himalayacetus, are known only from teeth and mandibular fragments. Retaining large hindlimbs, it was once thought that they could walk on land—indeed, their name means "walking whales"—, but recent research suggests they may have been fully aquatic like modern cetaceans. Though the research has some limits that cast doubt on this conclusion.

Basilosauridae is a family of extinct cetaceans. They lived during the middle to the early late Eocene and are known from all continents, including Antarctica. They were probably the first fully aquatic cetaceans. The group is noted to be a paraphyletic assemblage of stem group whales from which the monophyletic Neoceti are derived.

Pakicetus is an extinct genus of amphibious cetacean of the family Pakicetidae, which was endemic to Pakistan during the Ypresian period, about 50 million years ago. It was a wolf-like animal, about 1 metre to 2 metres long, and lived in and around water where it ate fish and other small animals. The vast majority of paleontologists regard it as the most basal whale, representing a transitional stage between land mammals and whales. It belongs to the even-toed ungulates with the closest living non-cetacean relative being the hippopotamus.

Archaeoceti, or Zeuglodontes in older literature, is a paraphyletic group of primitive cetaceans that lived from the Early Eocene to the late Oligocene. Representing the earliest cetacean radiation, they include the initial amphibious stages in cetacean evolution, thus are the ancestors of both modern cetacean suborders, Mysticeti and Odontoceti. This initial diversification occurred in the shallow waters that separated India and Asia 53 to 45 mya, resulting in some 30 species adapted to a fully oceanic life. Echolocation and filter-feeding evolved during a second radiation 36 to 35 mya.
Himalayacetus is an extinct genus of carnivorous aquatic mammal of the family Ambulocetidae. The holotype was found in Himachal Pradesh, India, in what was the remnants of the ancient Tethys Ocean during the Early Eocene. This makes Himalayacetus the oldest archaeocete known, extending the fossil record of whales some 3.5 million years.

Ichthyolestes is an extinct genus of archaic cetacean that was endemic to Indo-Pakistan during the Lutetian stage. To date, this monotypic genus is only represented by Ichthyolestes pinfoldi.

Kutchicetus is an extinct genus of early whale of the family Remingtonocetidae that lived during Early-Middle Eocene in what is now the coastal border of Pakistan and India. It is closely related to Andrewsiphius with which it was synonymized by Gingerich et al. 2001. Thewissen & Bajpai 2009 proposed a new clade, Andrewsiphiinae, for the two species. Later authors, however, still accept both as separate genera.

Remingtonocetus is an extinct genus of early cetacean freshwater aquatic mammals of the family Remingtonocetidae endemic to the coastline of the ancient Tethys Ocean during the Eocene. It was named after naturalist Remington Kellogg.

Cynthiacetus is an extinct genus of basilosaurid early whale that lived during the Late Eocene Specimens have been found in the southeastern United States and Peru.
Dalanistes is an extinct genus of remingtonocetid early whale known from the late early Eocene of Kutch, India and Punjab and Balochistan, Pakistan. Dalanistes is closely related to Remingtonocetus, but also shares several features with Ambulocetus, and, with its combination of terrestrial and amphibious adaptations, Dalanistes apparently is an intermediate form between these two groups. Isotopic evidence suggest that Dalanistes had a marine diet.
Gaviacetus is an extinct archaeocete whale that lived approximately 45 million years ago. Gaviacetus was named for its characteristic narrow rostrum and the fast pursuit predation suggested by its unfused sacral vertebrae.

Saghacetus is an extinct genus of basilosaurid early whale, fossils of which have been found in the Upper Eocene Qasr el Sagha Formation, Egypt.

Andrewsiphius is an extinct remingtonocetid early whale known from the Eocene of Gujarat and Kutch, India and Balochistan, Pakistan.

Indocetus is a protocetid early whale known from the late early Eocene Harudi Formation in Kutch, India.
Eocetus is an extinct protocetid early whale known from the early late Eocene Giushi Formation in Gebel Mokattam, outside Cairo, Egypt. The specimen was first named by Fraas as Mesocetus schweinfurthi. However, the name Mesocetus was previously used causing a change to the species name to Eocetus schweinfurthi. Since the genus was first described in the early 20th century, several other specimens, mostly isolated vertebrae, have been attributed to Eocetus, but the taxonomic status of these widely distributed specimens remain disputed.
Rayanistes is a genus of remingtonocetid whale from the Middle Eocene deposits in Egypt.

The Andrewsiphiinae is an extinct subfamily of early whales of the family Remingtonocetidae. Thiewessen & Bajpai (2009) proposed the clade when Andrewsiphius and Kuchicetus were accepted as separate genera. Kuchicetus was originally synonymized with Andrewsiphius in 2001 by Gingerich et al., but later authors, however, still accept both as separate genera.















