In telecommunications, RS-232, Recommended Standard 232 is a standard originally introduced in 1960 for serial communication transmission of data. It formally defines signals connecting between a DTE such as a computer terminal, and a DCE, such as a modem. The standard defines the electrical characteristics and timing of signals, the meaning of signals, and the physical size and pinout of connectors. The current version of the standard is TIA-232-F Interface Between Data Terminal Equipment and Data Circuit-Terminating Equipment Employing Serial Binary Data Interchange, issued in 1997. The RS-232 standard had been commonly used in computer serial ports and is still widely used in industrial communication devices.

A data circuit-terminating equipment (DCE) is a device that sits between the data terminal equipment (DTE) and a data transmission circuit. It is also called data communication(s) equipment and data carrier equipment. Usually, the DTE device is the terminal, and the DCE is a modem.

Data terminal equipment (DTE) is an end instrument that converts user information into signals or reconverts received signals. These can also be called tail circuits. A DTE device communicates with the data circuit-terminating equipment (DCE). The DTE/DCE classification was introduced by IBM.

In computing, a serial port is a serial communication interface through which information transfers in or out sequentially one bit at a time. This is in contrast to a parallel port, which communicates multiple bits simultaneously in parallel. Throughout most of the history of personal computers, data has been transferred through serial ports to devices such as modems, terminals, various peripherals, and directly between computers.
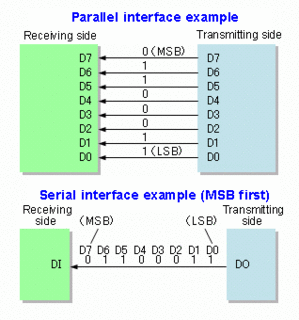
In telecommunication and data transmission, serial communication is the process of sending data one bit at a time, sequentially, over a communication channel or computer bus. This is in contrast to parallel communication, where several bits are sent as a whole, on a link with several parallel channels.
GeoPort is a serial data system used on some models of the Apple Macintosh that could be externally clocked to run at a 2 Mbit/s data rate. GeoPort slightly modified the existing Mac serial port pins to allow the computer's internal DSP hardware or software to send data that, when passed to a digital-to-analog converter, emulated various devices such as modems and fax machines. GeoPort could be found on late-model 68K-based machines as well as many pre-USB Power Macintosh models. Some later Macintosh models also included an internal GeoPort via an internal connector on the Communications Slot. Apple GeoPort technology is now obsolete, and modem support is typically offered through USB.

DMX512 is a standard for digital communication networks that are commonly used to control stage lighting and effects. It was originally intended as a standardized method for controlling light dimmers, which, prior to DMX512, had employed various incompatible proprietary protocols. It soon became the primary method for linking controllers to dimmers and special effects devices such as fog machines and intelligent lights. DMX has also expanded to uses in non-theatrical interior and architectural lighting, at scales ranging from strings of Christmas lights to electronic billboards and stadium or arena concerts. DMX can now be used to control almost anything, reflecting its popularity in theaters and venues.
RS-422, also known as TIA/EIA-422, is a technical standard originated by the Electronic Industries Alliance that specifies electrical characteristics of a digital signaling circuit. It was intended to replace the older RS-232C standard with a standard that offered much higher speed, better immunity from noise, and longer cable lengths. RS-422 systems can transmit data at rates as high as 10 Mbit/s, or may be sent on cables as long as 1,500 meters at lower rates. It is closely related to RS-423, which used the same signaling systems but on a different wiring arrangement.

The D-subminiature or D-sub is a common type of electrical connector. They are named for their characteristic D-shaped metal shield. When they were introduced, D-subs were among the smallest connectors used on computer systems.

Null modem is a communication method to directly connect two DTEs using an RS-232 serial cable. The name stems from the historical use of RS-232 cables to connect two teleprinter devices or two modems in order to communicate with one another; null modem communication refers to using a crossed-over RS-232 cable to connect the teleprinters directly to one another without the modems. It is also used to serially connect a computer to a printer, since both are DTE, and is known as a Printer Cable.
A crossover cable connects two devices of the same type, for example DTE-DTE or DCE-DCE, usually connected asymmetrically (DTE-DCE), by a modified cable called a crosslink. Such a distinction between devices was introduced by IBM.
RS-485, also known as TIA-485(-A) or EIA-485, is a standard defining the electrical characteristics of drivers and receivers for use in serial communications systems. Electrical signaling is balanced, and multipoint systems are supported. The standard is jointly published by the Telecommunications Industry Association and Electronic Industries Alliance (TIA/EIA). Digital communications networks implementing the standard can be used effectively over long distances and in electrically noisy environments. Multiple receivers may be connected to such a network in a linear, multidrop bus. These characteristics make RS-485 useful in industrial control systems and similar applications.
The RS-449 specification, also known as EIA-449 or TIA-449, defines the functional and mechanical characteristics of the interface between data terminal equipment, typically a computer, and data communications equipment, typically a modem or terminal server. The full title of the standard is EIA-449 General Purpose 37-Position and 9-Position Interface for Data Terminal Equipment and Data Circuit-Terminating Equipment Employing Serial Binary Data Interchange.

The mini-DIN connectors are a family of multi-pin electrical connectors used in a variety of applications. Mini-DIN is similar to the larger, older DIN connector. Both are standards of the Deutsches Institut für Normung, the German standards body.

Rollover cable is a type of null-modem cable that is often used to connect a computer terminal to a router's console port. This cable is typically flat to help distinguish it from other types of network cabling. It gets the name rollover because the pinouts on one end are reversed from the other, as if the wire had been rolled over and you were viewing it from the other side.
Assembly Line Diagnostic Link or ALDL is a proprietary on-board diagnostics system developed by General Motors before the standardization of OBD-2. It was previously called Assembly Line Communications Link or ALCL. The two terms are used interchangeably.
Data Carrier Detect, abbreviated as DCD, or alternately Carrier Detect abbreviated as CD, is a control signal present inside an RS-232 serial communications cable that goes between a computer and another device, such as a modem. This signal is a simple "high/low" status bit that is sent "from DCE to DTE", or in a typical scenario, from the peripheral to the computer. It is present on virtually all PC serial ports - pin 1 of a nine-pin (DE9) serial port, or pin 8 over a 25-pin (DB25) port. Its purpose varies depending on the device connected, but the most typical meaning is to indicate when a modem is connected to another remote modem via telephone lines.

A modem – a portmanteau of "modulator-demodulator" – is a hardware device that converts data from a digital format, intended for communication directly between devices with specialized wiring, into one suitable for a transmission medium such as telephone lines or radio. A modem modulates one or more carrier wave signals to encode digital information for transmission, and demodulates signals to decode the transmitted information. The goal is to produce a signal that can be transmitted easily and decoded reliably to reproduce the original digital data.
Data Terminal Ready (DTR) is a control signal in RS-232 serial communications, transmitted from data terminal equipment (DTE), such as a computer, to data communications equipment (DCE), for example a modem, to indicate that the terminal is ready for communications and the modem may initiate a communications channel.










