
The People's Liberation Army Navy, also known as the People's Navy, PLA Navy or simply Chinese Navy, is the naval warfare branch of the People's Liberation Army, the standing armed force of the People's Republic of China. As of 2024, it is the second-largest navy in the world in terms of total displacement, and the largest navy per number of ships in active service.

The People's Liberation Army (PLA) is the armed wing of the Chinese Communist Party (CCP) and the principal military force of the People's Republic of China. The PLA consists of four services — Ground Force, Navy, Air Force, and Rocket Force — and four arms — Aerospace Force, Cyberspace Force, Information Support Force, and Joint Logistics Support Force. It is led by the Central Military Commission (CMC) with its chairman as commander-in-chief.

The People's Liberation Army Naval Air Force is the naval aviation branch of the People's Liberation Army Navy.

The People's Liberation Army Navy Marine Corps (PLANMC), also known as the People's Liberation Army Marine Corps (PLAMC), is the marine force of the People's Liberation Army (PLA) and one of five major branches of the People's Liberation Army Navy (PLAN) responsible for amphibious warfare, expeditionary operations and rapid responses. It currently consists of seven 6,000-man combined armed brigades and four other supporting brigades including aviation, engineering & chemical defense, artillery and service-support brigades for a total of 40,000. The marine corps also includes a brigade-level special operations unit called "Jiaolong Commando Unit"

The Republic of Vietnam Navy (RVNN; Vietnamese: Hải quân Việt Nam Cộng hòa - HQVNCH; was the naval branch of the South Vietnamese military, the official armed forces of the former Republic of Vietnam from 1955 to 1975. The early fleet consisted of boats from France; after 1955, and the transfer of the armed forces to Vietnamese control, the fleet was supplied from the United States. With American assistance, in 1972 the VNN became the largest Southeast Asian navy and, by some estimates, the fourth largest navy in the world, just behind the Soviet Union, the United States and the People's Republic of China, with 42,000 personnel, 672 amphibious ships and craft, 20 mine warfare vessels, 450 patrol craft, 56 service craft, and 242 junks. Other sources state that VNN was the ninth largest navy in the world. The Republic of Vietnam Navy was responsible for the protection of the country's national waters, islands, and interests of its maritime economy, as well as for the co-ordination of maritime police, customs service and the maritime border defence force.

The Eastern Theater Command Navy (ETCN), or the East Sea Fleet (ESF) before February 2018, is a formation of China's People's Liberation Army Navy (PLAN) and the naval component of the Eastern Theater Command.

The Battle of the Paracel Islands was a military engagement between the naval forces of China and South Vietnam in the Paracel Islands on January 19, 1974. The battle was an attempt by the South Vietnamese navy to expel the Chinese navy from the vicinity. The confrontation took place towards the end of the Vietnam War.

In the People's Republic of China, the special operations forces of the People's Liberation Army are units that conduct direct action and reconnaissance, including in enemy rear areas, to prepare the advance of friendly forces; they also perform counter-terrorism operations, although that mission is formally assigned to People's Armed Police. PLA SOF does not control, but may support, psychological warfare operations.
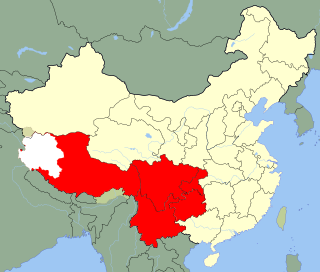
The Chengdu Military Region was one of seven military districts and is located in the southwest of the People's Republic of China, covering Chongqing, Sichuan, Yunnan, Guizhou, and the Xizang/Tibet Autonomous Region. It includes some of the area previously within the Kunming Military Region and has its headquarters in Chengdu. It was probably established in 1955.
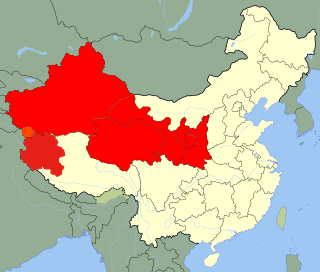
The Lanzhou Military Region was one of seven military regions in the People's Republic of China. It directed all People's Liberation Army and People's Armed Police forces in Xinjiang, Qinghai, Gansu, Ningxia, Shaanxi, and Ngari Prefecture in northwest Tibet. It was headquartered in Lanzhou in Gansu Province. It is bordered to the south by the Chengdu Military Region, and to the north by Mongolia, the Altai Republic, which is a political subdivision of the Russian Federation, and Kazakhstan. This region is now part of the Western Theater Command due to the military reforms of 2015.

A theater command (中国人民解放军战区) is a joint military command of the Central Military Commission that is composed of units from the service branches of the People's Liberation Army in its area of responsibility, and conducts broad and continuing missions. There are 5 theater commands: Eastern, Southern, Western, Northern, and Central theater commands, organized by a geographical basis. They are responsible for developing strategy, plans, tactics, and policy specific to their assigned area of responsibility. They are intended to take operational control of the multi-service units under their jurisdiction, while the branches retain administrative and "constructive" control.
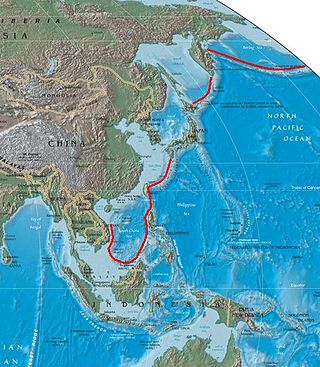
The first island chain refers to the first chain of major Pacific archipelagos out from the East Asian continental mainland coast. It is principally composed of the Kuril Islands, the Japanese archipelago, the Ryukyu Islands, Taiwan (Formosa), the northern Philippines, and Borneo, hence extending all the way from the Kamchatka Peninsula in the northeast to the Malay Peninsula in the southwest. The first island chain forms one of three island chain doctrines within the island chain strategy in the U.S. foreign policy.
Bai Wenqi is a Chinese naval aviator who is a lieutenant general of the People's Liberation Army Air Force (PLAAF) and a former vice admiral of the People's Liberation Army Naval Air Force (PLANAF). He has been the inaugural political commissar of the Northern Theater Command Air Force since its establishment in February 2016. He formerly served as political commissar of the Jinan Military Region Air Force, and political commissar of the North Sea Fleet.

The Southern Theater Command is one of the five theater commands of the People's Liberation Army, founded on 1 February 2016. Its predecessor was the Guangzhou Military Region.

The Central Theater Command is one of the five theater commands of the People's Liberation Army of China, and was founded on 1 February 2016. Its predecessors were the Beijing Military Region and Jinan Military Region.

The Northern Theater Command is one of the five theater commands of the People's Liberation Army, founded on 1 February 2016. Its predecessor is the Shenyang Military Region, Jinan Military Region and Beijing Military Region. Its headquarters is in the Heping District of Shenyang, Liaoning Province. The Northern Theater Command shares borders with North Korea, Russia and Mongolia.

The Eastern Theater Command is one of the five theater commands of the People's Liberation Army (PLA), founded 1 February 2016. It replaced the Nanjing Military Region. The command is headquartered in Nanjing.

Shen Jinlong is a Chinese admiral who served as Commander of the People's Liberation Army Navy (PLAN) from 2017 to 2021.

Zhang Wendan is a retired vice admiral of the Chinese People's Liberation Army Navy. He served as Chief of Staff of the PLA Navy from January 2018 to December 2019, and previously served as Chief of Staff and Deputy Commander of the South Sea Fleet, Deputy Chief of Staff of the Southern Theater Command, and Commander of the North Sea Fleet (2017–2018). He commanded the PLA Navy's fifth Gulf of Aden anti-piracy task force in 2010.

Dong Jun is a Chinese admiral (shangjiang) of the People's Liberation Army Navy (PLA) who has served as the 14th Minister of National Defense since December 2023.

















