
Sedimentary rocks are types of rock that are formed by the accumulation or deposition of mineral or organic particles at Earth's surface, followed by cementation. Sedimentation is the collective name for processes that cause these particles to settle in place. The particles that form a sedimentary rock are called sediment, and may be composed of geological detritus (minerals) or biological detritus. The geological detritus originated from weathering and erosion of existing rocks, or from the solidification of molten lava blobs erupted by volcanoes. The geological detritus is transported to the place of deposition by water, wind, ice or mass movement, which are called agents of denudation. Biological detritus was formed by bodies and parts of dead aquatic organisms, as well as their fecal mass, suspended in water and slowly piling up on the floor of water bodies. Sedimentation may also occur as dissolved minerals precipitate from water solution.
Sedimentology encompasses the study of modern sediments such as sand, silt, and clay, and the processes that result in their formation, transport, deposition and diagenesis. Sedimentologists apply their understanding of modern processes to interpret geologic history through observations of sedimentary rocks and sedimentary structures.

Stratigraphy is a branch of geology concerned with the study of rock layers (strata) and layering (stratification). It is primarily used in the study of sedimentary and layered volcanic rocks. Stratigraphy has three related subfields: lithostratigraphy, biostratigraphy, and chronostratigraphy.

A geological formation, or simply formation, is a body of rock having a consistent set of physical characteristics (lithology) that distinguishes it from adjacent bodies of rock, and which occupies a particular position in the layers of rock exposed in a geographical region. It is the fundamental unit of lithostratigraphy, the study of strata or rock layers.
A stratigraphic unit is a volume of rock of identifiable origin and relative age range that is defined by the distinctive and dominant, easily mapped and recognizable petrographic, lithologic or paleontologic features (facies) that characterize it.

Lithostratigraphy is a sub-discipline of stratigraphy, the geological science associated with the study of strata or rock layers. Major focuses include geochronology, comparative geology, and petrology.

In geology, cross-bedding, also known as cross-stratification, is layering within a stratum and at an angle to the main bedding plane. The sedimentary structures which result are roughly horizontal units composed of inclined layers. The original depositional layering is tilted, such tilting not being the result of post-depositional deformation. Cross-beds or "sets" are the groups of inclined layers, which are known as cross-strata.

In geology, a graded bed is a bed characterized by a systematic change in grain or clast size from bottom to top of the bed. Most commonly this takes the form of normal grading, with coarser sediments at the base, which grade upward into progressively finer ones. Such a bed is also described as fining upward. Normally graded beds generally represent depositional environments which decrease in transport energy as time passes, but these beds can also form during rapid depositional events. They are perhaps best represented in turbidite strata, where they indicate a sudden strong current that deposits heavy, coarse sediments first, with finer ones following as the current weakens. They can also form in terrestrial stream deposits.

In geology, a bed is a layer of sediment, sedimentary rock, or volcanic rock "bounded above and below by more or less well-defined bedding surfaces". Specifically in sedimentology, a bed can be defined in one of two major ways. First, Campbell and Reineck and Singh use the term bed to refer to a thickness-independent layer comprising a coherent layer of sedimentary rock, sediment, or pyroclastic material bounded above and below by surfaces known as bedding planes. By this definition of bed, laminae are small beds that constitute the smallest (visible) layers of a hierarchical succession and often, but not always, internally comprise a bed.
A stratigraphic column is a representation used in geology and its subfield of stratigraphy to describe the vertical location of rock units in a particular area. A typical stratigraphic column shows a sequence of sedimentary rocks, with the oldest rocks on the bottom and the youngest on top.
Colorado is a geologic name applied to certain rocks of Cretaceous age in the North America, particularly in the western Great Plains. This name was originally applied to classify a group of specific marine formations of shale and chalk known for their importance in Eastern Colorado. The surface outcrop of this group produces distinctive landforms bordering the Great Plains and it is a significant feature of the subsurface of the Denver Basin and the Western Canadian Sedimentary Basin. These formations record important sequences of the Western Interior Seaway. As the geology of this seaway was studied, this name came to be used in states beyond Colorado but later was replaced in several of these states with more localized names.

Marker horizons are stratigraphic units of the same age and of such distinctive composition and appearance, that, despite their presence in separate geographic locations, there is no doubt about their being of equivalent age (isochronous) and of common origin. Such clear markers facilitate the correlation of strata, and used in conjunction with fossil floral and faunal assemblages and paleomagnetism, permit the mapping of land masses and bodies of water throughout the history of the earth. They usually consist of a relatively thin layer of sedimentary rock that is readily recognized on the basis of either its distinct physical characteristics or fossil content and can be mapped over a very large geographic area. As a result, a key bed is useful for correlating sequences of sedimentary rocks over a large area. Typically, key beds were created as the result of either instantaneous events or very short episodes of the widespread deposition of a specific types of sediment. As the result, key beds often can be used for both mapping and correlating sedimentary rocks and dating them. Volcanic ash beds and impact spherule beds, and specific megaturbidites are types of key beds created by instantaneous events. The widespread accumulation of distinctive sediments over a geologically short period of time have created key beds in the form of peat beds, coal beds, shell beds, marine bands, black shales in cyclothems, and oil shales. A well-known example of a key bed is the global layer of iridium-rich impact ejecta that marks the Cretaceous–Paleogene boundary.

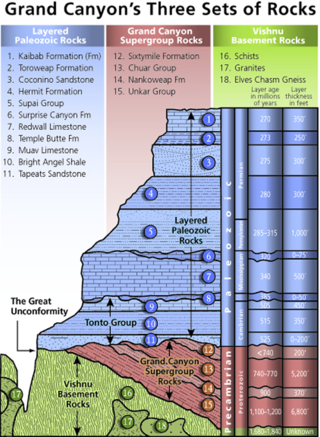
Except where underlain by the Sixtymile Formation, the Tapeats Sandstone is the Cambrian geologic formation that is the basal geologic unit of the Tonto Group. Typically, it is also the basal geologic formation of the Phanerozoic strata exposed in the Grand Canyon, Arizona, and parts of northern Arizona, central Arizona, southeast California, southern Nevada, and southeast Utah. The Tapeats Sandstone is about 230 feet (70 m) thick, at its maximum. The lower and middle sandstone beds of the Tapeats Sandstone are well-cemented, resistant to erosion, and form brownish, vertical cliffs that rise above the underlying Precambrian strata outcropping within Granite Gorge. They form the edge of the Tonto Platform. The upper beds of the Tapeats Sandstone form the surface of the Tonto Platform. The overlying soft shales and siltstones of the Bright Angel Shale underlie drab-greenish slopes that rise from the Tonto Platform to cliffs formed by limestones of the Muav Limestone and dolomites of the Frenchman Mountain Dolostone.
In geology, a horizon is either a bedding surface where there is marked change in the lithology within a sequence of sedimentary or volcanic rocks, or a distinctive layer or thin bed with a characteristic lithology or fossil content within a sequence. Examples of the former can include things such as volcanic eruptions as well as things such as meteorite impacts and tsunamis. Examples of the latter include things such as ice ages and other large climate events, as well as large but temporary geological features and changes such as inland oceans. In the interpretation of seismic reflection data, horizons are the reflectors picked on individual profiles. These reflectors represent a change in rock properties across a boundary between two layers of rock, particularly seismic velocity and density. It can also represent changes in the density of the material and the composition of it and the pressure under which it was produced. Thus, not only do the properties change but so too do the conditions of formation and other differences in the rock. The horizons can sometimes be very prominent, such as visible changes in cliff sides, to extremely subtle chemical differences.

The Bright Angel Shale is one of five geological formations that comprise the Cambrian Tonto Group. It and the other formations of the Tonto Group outcrop in the Grand Canyon, Arizona, and parts of northern Arizona, central Arizona, southeast California, southern Nevada, and southeast Utah. The Bright Angel Shale consists of locally fossiliferous, green and red-brown, micaceous, fissile shale (mudstone) and siltstone with local, thicker beds of brown to tan sandstone and limestone. It ranges in thickness from 57 to 450 feet. Typically, its thin-bedded shales and sandstones are interbedded in cm-scale cycles. They also exhibit abundant sedimentary structures that include current, oscillation, and interference ripples. The Bright Angel Shale also gradually grades downward into the underlying Tapeats Sandstone. It also complexly interfingers with the overlying Muav Limestone. These characters make the upper and lower contacts of the Bright Angel Shale often difficult to define. Typically, its thin-bedded shales and sandstones erode into green and red-brown slopes that rise from the Tonto Platform up to cliffs formed by limestones of the overlying Muav Limestone and dolomites of the Frenchman Mountain Dolostone.

The Jordan Formation is a siliciclastic sedimentary rock unit identified in Illinois, Michigan, Wisconsin, Minnesota, and Iowa. Named for distinctive outcrops in the Minnesota River Valley near the town of Jordan, it extends throughout the Iowa Shelf and eastward over the Wisconsin Arch and Lincoln anticline into the Michigan Basin.
A geological contact is a boundary which separates one rock body from another. A contact can be formed during deposition, by the intrusion of magma, or through faulting or other deformation of rock beds that brings distinct rock bodies into contact.

A pinch-out or wedge-out is a point where a stratum or other lithologically distinct body of rock thins to a feather edge and disappears, so that the underlying and overlying strata separated by the pinching out stratum come into direct contact. The term also is used in petroleum geology to describe a stratigraphic trap created by a pinch-out. Petroleum migrating through a porous stratum is trapped where the stratum pinches out between impermeable underlying and overlying strata.

The Gai-As Formation is an Early to Middle Permian geologic formation correlated with the Ecca Group and designated "Ecca" Group, because it does not belong to the Karoo, in the southwestern Kunene Region and northern Erongo Region of northwestern Namibia. The Gai-As Formation represents the second-oldest sedimentary unit of the Huab Basin, overlying the Huab Formation. The formation was deposited in a fluvial to lacustrine setting.
The Officer Basin is an intracratonic sedimentary basin that covers roughly 320,000 km2 along the border between southern and western Australia. Exploration for hydrocarbons in this basin has been sparse, but the geology has been examined for its potential as a hydrocarbon reservoir. This basin's extensive depositional history, with sedimentary thicknesses exceeding 6 km and spanning roughly 350 Ma during the Neoproterozoic, make it an ideal candidate for hydrocarbon production.






















